Geometry and measure
NEW: Angles
Revise the different types of angles and rules for calculating angles. This guide includes interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Angles in parallel lines
Revise alternate, correspondent or co-interior angles within parallel lines. This guide contains a video and a quiz.

NEW: Polygons
Revise triangles, quadrilaterals and other polygons with a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Line and rotational symmetry
Revise reflective and rotational symmetry and the symmetry in different quadrilaterals and polygons. This guide contains interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Constructing triangles
Revise how to construct ASA, SAS and SSS triangles using a ruler, protractor and compass. This guide contains videos, a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Ruler and compass constructions
Revise how to construct perpendiculars to a line and from a point and bisect an angle. This guide contains animations, interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Loci
Revise how to find a locus from a line or two points and loci with bisectors. This guide includes a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Bearings
Revise how to calculate bearings and back bearings and how to calculate them using trigonometry. This guide includes interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Perimeter
Revise how to find the perimeter of 2D shapes and compound shapes. This guide contains a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Area
Revise how to calculate the area of 2D shapes and compound shapes. This guide contains videos, a quiz and interactive videos.

NEW: Volume of a prism
Revise how to find the volume of cylinders, cuboids and prisms, with interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Surface area of a prism
Revise how to calculate the surface area of 3D shapes, nets and cylinders, with video, interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Pyramids, cones and spheres
Revise how to find the volume and surface area of pyramids, cones and spheres. This guide contains a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Nets, plans and elevations
Revise plan and elevation views of 3D shapes and how to draw the nets of 3D shapes. This guide includes a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Circumference and arc length
Revise how to calculate circle circumference, arc lengths and sector perimeters within circles. This guide includes a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Area of circles and sectors
Revise calculating the area of circles, sectors and compound shapes with parts of circles, with a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Higher – Circle Theorems – Calculating angles using circles
Revise angles subtended by arcs or at the circumference by a semi-circle, angles in the same segment, or opposite in a cyclic quadrilateral. With a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Higher – Using the alternate segment theorem, tangents and chords
Revise circle theorems in this guide covering tangent theorems, the alternate segment theorem and the properties of chords. This guide contains a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Reflection
Revise reflection on a coordinates grid, in a diagonal line or on a set of axes. This guide contains interactive activities and a quiz.
NEW: Rotation
Revise rotating an object on a grid or a set of axes. This guide includes an animation, interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Translation
Revise translating shapes on a grid or set of axes, and how to describe a translation, with interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Enlargement
Revise scale factors and enlarging with a positive scale factor, as well as finding the centre of enlargement. This guide contains an animation, interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Higher − Negative enlargements
Revise enlarging with a negative scale factor and centre of enlargement, and describing enlargements using a negative scale factor, with a quiz and interactive activities.

NEW: Higher – Combined transformations and invariant points
Revise plotting and describing combined transformations with this guide containing interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Congruent and similar shapes
Revise congruence conditions, similar shapes and how to calculate missing sides in similar shapes using equations. This guide contains interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Higher – Similarity in 2D and 3D shapes
Revise how to calculate area and volume scale factors and ratios of 2D and 3D shapes in this Higher tier guide. This guide contains a video, interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Pythagoras' theorem
Revise calculating the hypotenuse and a shorter side in a right-angled triangle, and how to prove a triangle is right-angled. This guide contains interactive activities and a quiz.
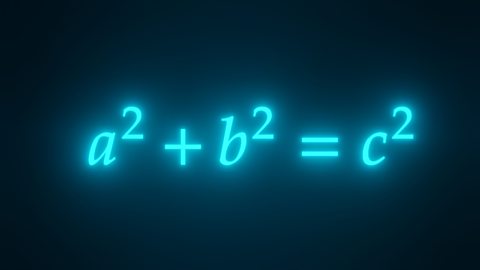
NEW: Solving 2D and 3D problems using Pythagoras' theorem
Revise calculating the length of line segments and using Pythagoras' theorem in 2D, and 3D for Higher tier. This guides includes interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Right-angled trigonometry
Revise finding the length of a side with an unknown numerator or denominator and using trigonometry to calculate an unknown angle, with interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Exact trigonometric values
Revise how to find exact trigonometric values for sinθ, cosθ and tanθ and to solve problems. This guide contains a video, quiz and exam style questions.

NEW: Higher – Sine rule
Revise finding an unknown side or angle using the sine rule, and the ambiguous case when finding unknown angles. This guide for Higher contains interactive activities and a quiz.

NEW: Higher – Cosine rule
Revise the cosine rule with this Higher tier guide. This guide contains exam-style questions and a quiz.

NEW: Higher – 2D and 3D trigonometry problems
Revise the trigonometric formula, sine and cosine rules and find the angle between a line and plane in this Higher tier guide. This guide contains quizzes and exam-style questions.

NEW: Vectors
Revise vectors, calculating with vectors and how to describe a pathway with vectors. This guide contains a video, quiz and exam-style questions.

NEW: Higher – Geometric problems using vectors
Revise proving vectors are parallel and how three points are co-linear with this Higher tier guide. This guide includes a quiz and exam-style questions.

Angles, lines and polygons - Edexcel
Polygons are multi-sided shapes with different properties. Shapes have symmetrical properties and some can tessellate.

Loci and constructions - Edexcel
Loci are a set of points with the same property. Loci can be used to accurately construct lines and shapes. Bearings are three figure angles measured clockwise from North.

Circles, sectors and arcs - Edexcel
The circumference of a circle is its outside edge, and is the same distance from the centre at every point along its length. This distance is called the radius. Learn how to measure and calculate these, along with the area and diameter of a circle.

Circle theorems - Higher - Edexcel
Circles have different angle properties described by different circle theorems. Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs and to calculate angles.

Pythagoras' theorem - Edexcel
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to calculate the length of any side in a right-angled triangle. Pythagoras’ theorem can be applied to solve 3-dimensional problems.

Units of measure - Edexcel
Units of measurement let us describe and compare length, weight, area, volume, density and other values. Units can be imperial or metric and they can be converted using conversion factors.

Trigonometry - Edexcel
The three trigonometric ratios; sine, cosine and tangent are used to calculate angles and lengths in right-angled triangles. The sine and cosine rules calculate lengths and angles in any triangle.

Vectors - Edexcel
A vector quantity has both size and direction. Vectors can be added, subtracted and multiplied by a scalar. Geometrical problems can be solved using vectors.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link