Key points about circumference and arc length

The circumferenceThe distance around a circle; its perimeter. of a circle is the perimeterThe total distance around the edge of a shape. of the circle. It can be calculated using one of two formula (formulae)A mathematical rule that links variables, by substituting the values that can be changed with words or letters, eg 𝑎² + 𝑏² = 𝑐². A formula contains an equals (=) sign.:
- C = πd
- C = 2πr
The arc lengthThe length of an arc. is the curved part of a sectorA portion of a circle with a perimeter made up of two radii and an arc. and is a fraction of the circumference. The arc length is calculated using the formula:
- Arc length = θ ÷ 360 × 2πr (where θ is the sector angle)
Make sure you are confident in rounding to a number of decimal placesThe decimal fraction 0·275 is said to have three decimal places. A number may be rounded to a specific number of decimal places, eg 6·83715 to 2 d.p. (two decimal places) is 6·84. (d.p.) or significant figures (s.f.)The digits that give most meaning to a number. A number may be rounded to a given number of significant figures (s.f.). The 1st significant figure in a number is the first non-zero digit. Numbers may be rounded to a given number of significant figures. (s.f.). Questions on finding circumferences and arc lengths may need answers to be given to a specific degree of accuracy.
What are the parts of a circle?
When working with circles it is important to recognise and be able to name different parts of the circle.
Find out more about the parts of a circle below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Which part of a circle is indicated below?
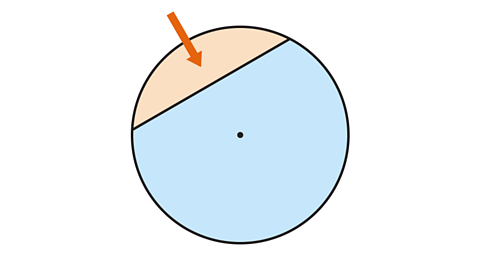
A segment
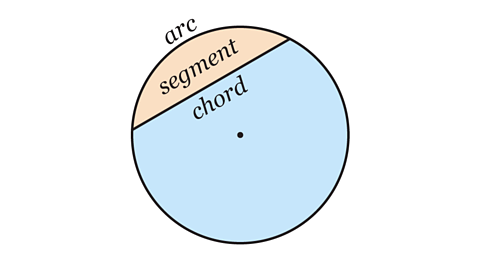
A segment of a circle is an area enclosed by a chord and an arc.
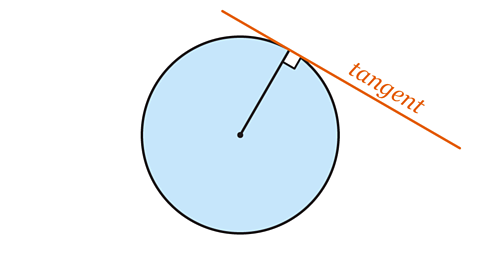
- What is the name given to a straight line which touches the edge of a circle at a single point?
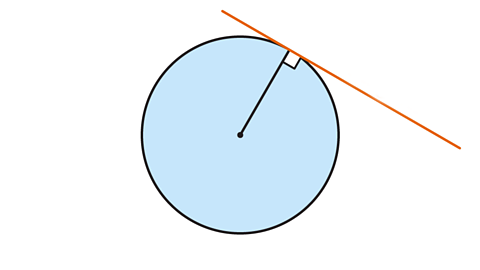
A tangent is a straight line which touches the edge of a circle at a single point.
A tangent makes a 90° angle or is perpendicular to the radius at that point.
How to calculate the circumference of a circle
Find the circumference of a circle by using one of two formulae, depending on the known information:
- When given the diameter, the formula for the circumference is C = πd
The circumference is found by multiplying the diameter by π.
- When given the radius, the formula for the circumference is C = 2πr
The circumference is found by multiplying the radius by 2π.
When finding the circumference of a circle, an approximation for π might be used or the answer could be given in terms of π.
Find out more below, along with worked examples
GCSE exam-style questions
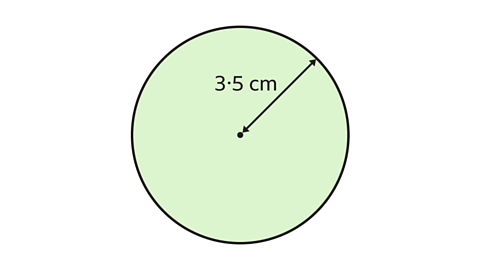
- Work out the circumference of a circle with radius 3·5 cm.
Give your answer in terms of π.
The circumference is 7π cm.
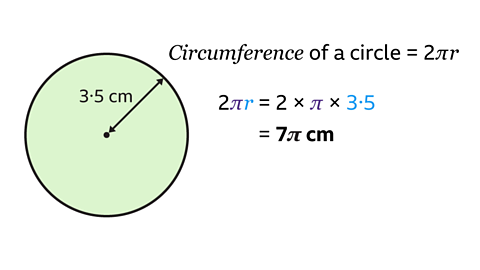
The formula for the circumference using the radius is C = 2πr
Substitute the value of the radius into the formula.
Multiply 2 by π then multiply by the radius: 2 × π × 3·5 = 7π
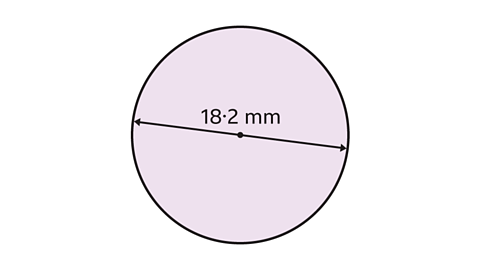
- Work out the circumference of a circle with diameter 18·2 mm.
Use the approximation π = 3·14.
Give the answer to 1 decimal place.
The circumference is 57·1 mm (to 1 decimal place).
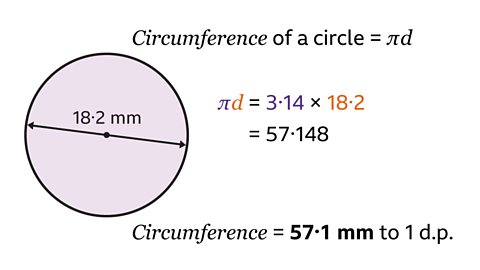
The formula for the circumference using the diameter is C = πd
Substitute the value of the diameter into the formula.
Multiply the approximation π = 3·14 by the diameter of the circle:
3·14 × 18·2 = 57·148
- Round this to 1 decimal place.
- A circle has circumference of 37.68 m. What is its diameter?
Use the approximation π = 3.14
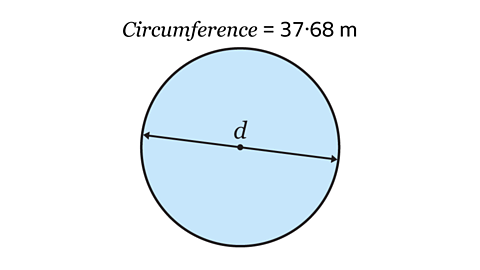
The diameter of the circle is 12 m.
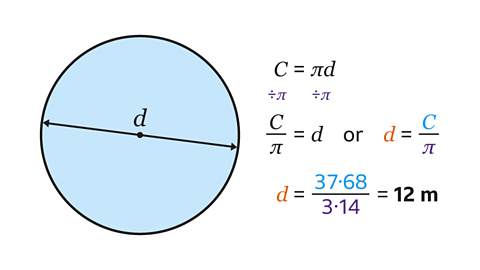
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula C = πd
Multiply the diameter by π to give the circumference. The inverse of multiply by π is divide by π.
The circumference divided by π gives the diameter.
Use the approximation π = 3.14
37.68 ÷ 3.14 = 12
- A circle has circumference 22π cm. What is its radius?
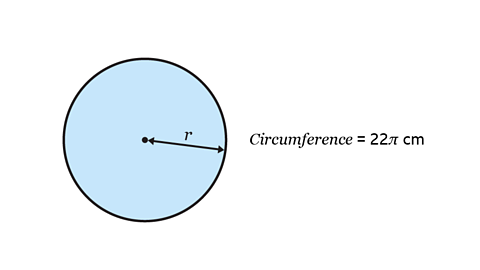
The radius of the circle is 11 cm.
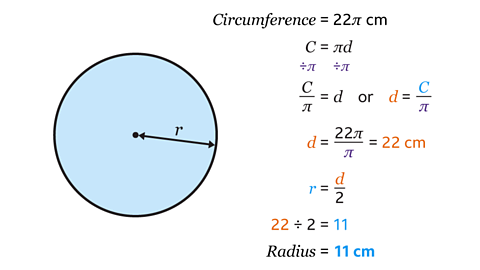
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula C = πd
Multiply the diameter by π to give the circumference.
The inverse of multiply by π is divide by π.
The circumference divided by π gives the diameter:
22π ÷ π = 22 cm
The diameter of the circle is 22 cm.
The radius is half of the diameter: 22 ÷ 2 = 11 cm
How to calculate arc length and the perimeter of sectors
- The arc length is a fraction of the circumference.
For example, the curved length of a semi-circle is found by finding the circumference of a full circle and dividing it by 2.
The arc length is generally calculated using the formula:
Arc length = θ ÷ 360 × 2πr, where θ is the angle of the sectorA portion of a circle with a perimeter made up of two radii and an arc. .
- When finding the perimeter of a fraction of a circle, the straight edges must be added to the arc length.
The arc length or perimeter of the shape could be given in terms of π, or an approximation for π might be used instead.
Find out more below, along with worked examples
Arc length and sector area - interactive activity
This interactive activity will help you understand how formulae are used to calculate both arc length and sector area.
GCSE exam-style questions
- Calculate the arc length of the quadrant.
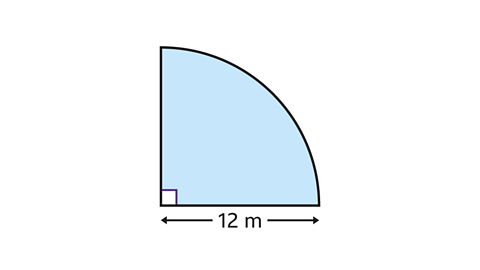
The arc length is 6π m
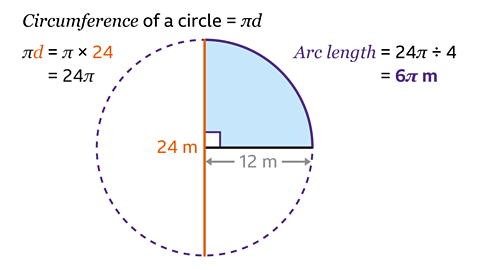
The quadrant is quarter of a circle with diameter 24 m.
Using the diameter, the formula for the circumference of the full circle is C = πd.
- Substitute the value of the diameter into the formula:
π × 24 = 24π
The circumference of the full circle is 24π m.
- Find the arc length of a quadrant by dividing the circumference of the full circle by four.
24π ÷ 4 = 6π
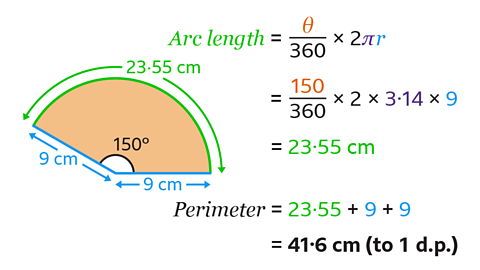
- Calculate the perimeter of the sector. Use the approximation π = 3.14
Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
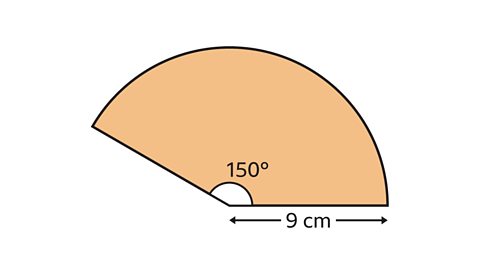
The perimeter of the sector is 41·6 cm (to 1 d.p.)
Arc length = θ ÷ 360 × 2πr.
In the sector, the radius in 9 cm and the angle is 150°.
- Substitute the value of the radius, the approximation of pi and the angle into the formula:
Arc length = 150 ÷ 360 × 2 × 3.14 × 9
The arc length is 23·55 cm.
- To find the perimeter of the sector, add the values of two radii to the arc length.
23·55 + 9 + 9 = 41.6 cm (to 1 d.p.)
- A sector has radius measuring 9 cm.
The arc length of the sector is 3π m.
What is the angle of the sector?
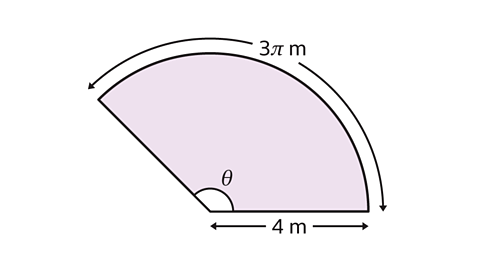
The sector angle θ = 135°
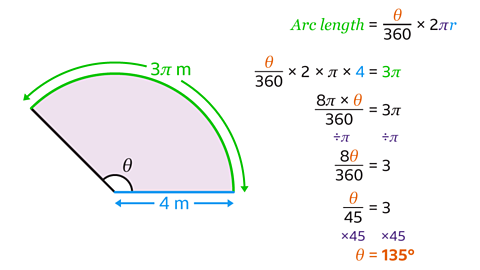
- To find the value of θ, find an expression for the arc length of the sector.
Substitute the value of the radius and θ for the angle into the formula:
θ ÷ 360 × 2 × π × 4
This expression can be simplified to 8π × θ ÷ 360
Form an equation by putting this expression equal to the given arc length of 3π.
8π × θ ÷ 360 = 3π
- Find the value of θ by dividing both sides by π.
8θ ÷ 360 = 3
The fraction 8θ ÷ 360 can cancel to θ ÷ 45 by dividing the numerator and denominator by 8.
- Finally, multiply both sides of the equation by 45 to find the answer.
Quiz – Circumference and arc length
Practise what you've learned about circumference and arc length with this quiz.
Now you've revised circumference and arc length, why not check out surface area of a prism?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count16 of 35

- count19 of 35