Key points about area

The area of a 2D shape is the amount of space contained within its sides. Area is measured in square units, such as cm² and m².
Each shape has its own formula, in order to calculate its area:
- Rectangle: \(𝐴 = 𝑙𝑤\)
- Triangle: \(𝐴 = \frac{𝑏ℎ}{2}\) or \(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}𝑏ℎ\)
- Parallelogram: \(𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ\)
- Trapezium: \(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}(𝑎 + 𝑏)ℎ\)
When finding areas, the measurements of lengths used must be in the same units.
Look at this guide on calculating the area of squares, rectangles and compound shapes for extra help.
Video – Areas of triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums
Watch this video to find out how to calculate the areas of triangleA 2D shape with 3 edges and 3 vertices. , parallelogramA quadrilateral with opposite pairs of sides that are both equal in length and parallel. Opposite angles are equal. and trapeziumA quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. using formulae.
Areas of triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums.
To calculate the areas of some shapes, you can use particular formulae.
Let's look at some questions.
Question 1: work out the area of this triangle.
The formula for the area of a triangle is a half multiplied by the base, multiplied by the perpendicular height, or a half 𝑏 ℎ.
‘Perpendicular’ means at a right angle.
So, if you choose the base as any side, the perpendicular height is then the distance to the opposite vertex or corner that meets this base at right angles.
If you don't use perpendicular lengths, the formula doesn't work and you won't find the correct area of the triangle.
The right angle symbol tells you that the 8 cm base is perpendicular to the 4 cm height.
Notice the 6.5 cm side is not relevant here, and you don't need to use it for the calculation.
Substituting the values into the formula for the area of a triangle, a half times base times height, gives a half, or 0.5, multiplied by 8 multiplied by 4, which equals 16 cm squared.
Now question 2: work out the area of this parallelogram.
The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the base multiplied by the perpendicular height, or just 𝑏 ℎ.
Again, you can identify the base as any side, no matter the orientation, but remember the perpendicular height must meet the base at a right angle.
So, from the diagram the base is 12 cm and the perpendicular height is 6 cm.
Be careful to identify the correct sides when answering these types of questions, as extra information that is not needed may be given.
For example, the 7 cm side is not perpendicular to any other given length, so it can be ignored.
This means the area of the parallelogram, the base times height, is 12 multiplied by 6, which equals 72 cm squared.
Finally, question 3: work out the area of this trapezium.
The formula for the area of a trapezium is a half multiplied by the sum of the parallel sides, 𝑎 add 𝑏, multiplied by the perpendicular height, ℎ.
The parallel sides 𝑎 and 𝑏 are marked with arrows in the diagram. So that's 6 cm and 3 cm.
You can choose either side for 𝑎 and 𝑏. Let's say 𝑎 is 6 cm and 𝑏 is 3 cm.
Then, ℎ is the perpendicular height. So, look for the length that meets the parallel sides at a right angle. That's 8 cm as indicated by the right angle symbol.
This length is perpendicular to one of the parallel sides, so it is also perpendicular to the other parallel side.
Now substitute values into the formula: 𝑎 equals 6, 𝑏 equals 3 and ℎ equals 8.
This gives a half multiplied by 6 add 3 multiplied by 8. 6 add 3 is 9. So, this simplifies to a half multiplied by 9 multiplied by 8, which equals 36 cm squared.
Finding the area of triangles and compound shapes
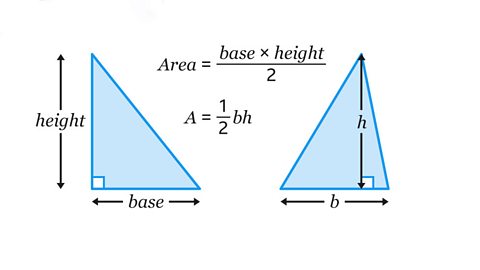
- Calculate the area of a triangle by multiplying the base length by the perpendicularPerpendicular lines are at 90° (right-angles) to each other. height and then halving.
\(𝐴 = \frac{𝑏ℎ}{2}\)
In this formula:
- 𝐴 is the area of the triangle
- 𝑏 is the length of the base of the triangle
- ℎ is the length of the perpendicular height of the triangle
Alternatively, find it by working out the length of the base, halving it and then multiplying it by the perpendicular height.
\(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}\) × 𝑏 × ℎ
This form is useful when working with larger numbers. Since multiplication is commutativeA calculation which can be done in any order. For example, addition and multiplication are commutative., the multiplication can be calculated in any order.
- Find the area of a compound shape by adding up the areas of the individual shapes.

Find out more below, along with a worked example
Exam-style questions
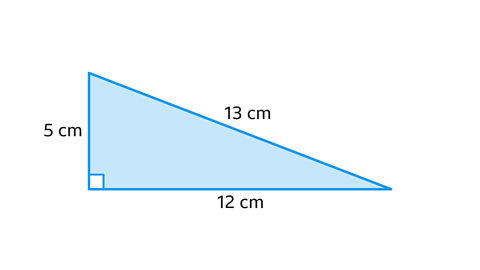
- Calculate the area of the triangle.
The area of the triangle is 30 cm².
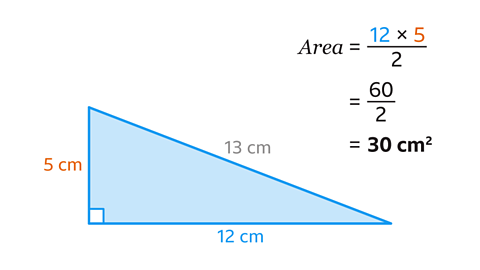
The base and the perpendicular height are at right-angles.
The base of the triangle is 12 cm.
The perpendicular height of the triangle is 5 cm.
The hypotenuse (the third side) which measures 13 cm is not needed in this calculation.
Substitute the base and perpendicular height values into the formula.
(12 × 5 ) ÷ 2 = 30 cm².
- The area of a triangle is 36 cm².
The base of the triangle is 8 cm.
Work out the height of the triangle.
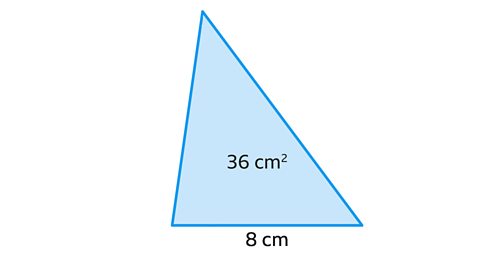
The height of the triangle is 9 cm.
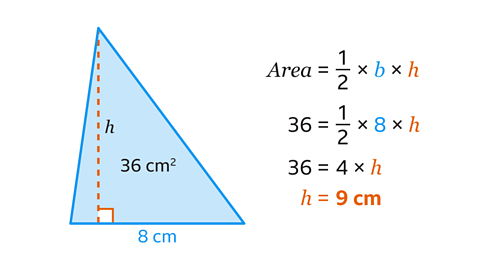
The height of the triangle is perpendicular to the base. The base is 8 cm.
- Find the height of the triangle by substituting the known area and the base length into the formula
\(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}𝑏ℎ\)
This gives 36 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 × ℎ
- The base multiplied by one half is 4, so 36 = 4 × ℎ
Find the height by dividing 36 by 4 giving 9 cm.
- Calculate the area of this compound shape.
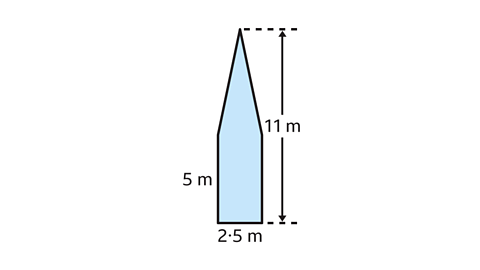
The area of the compound shape is 20 m².
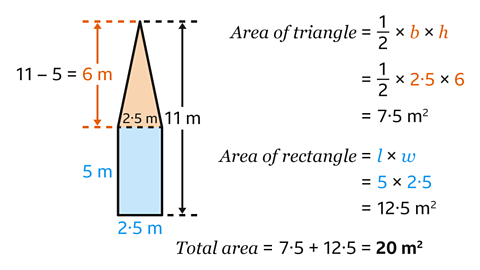
Find the area of the compound shape by splitting the shape into a triangle and a rectangle.
Work out the area of the triangle and rectangle and add these together.
- The height of the triangle is perpendicular to the base. The base is 2·5 m.
Subtract 5 from 11 to find the height of the triangle. The height of the triangle is 6 m.
- Substitute the base and perpendicular height values into the formula:
\(\frac{1}{2} \) × 2·5 × 6 = 7·5 m²
The area of the triangle is 7·5 m².
- Find the area of the rectangle by multiplying the length and width.
The rectangle measures 5 m by 2·5 m.
5 × 2·5 = 12·5
The area of the rectangle is 12·5 m².
- Add the areas of the triangle and rectangle to find the area of the compound shape.
7·5 + 12·5 = 20
The area of the compound shape is 20 m².
- Calculate the area of the compound shape.
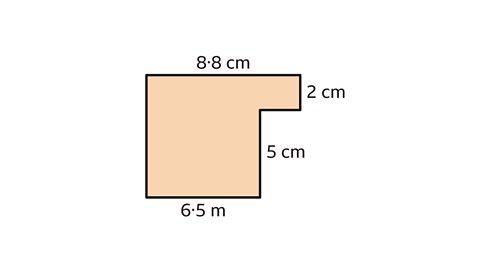
The area of the compound shape is 50·1 cm².
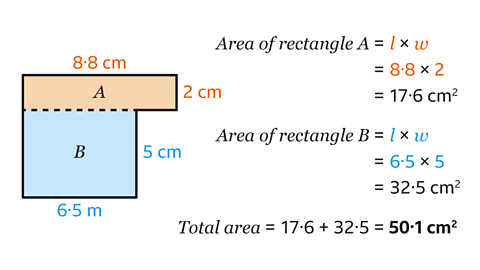
Find the area of the compound shape by splitting the shape into two rectangles.
The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying the length and width.
- Rectangle A measures 8·8 cm by 2 cm.
The area of rectangle A is 17·6 cm².
- Rectangle B measures 6·5 cm by 5 cm.
6·5 × 5 = 32·5
The area of rectangle B is 32·5 cm².
Add the area of the two rectangles to calculate the area of the compound shape.
17·6 + 32·5 = 50·1
The area of the compound shape is 50·1 cm².
How to work out the area of a parallelogram
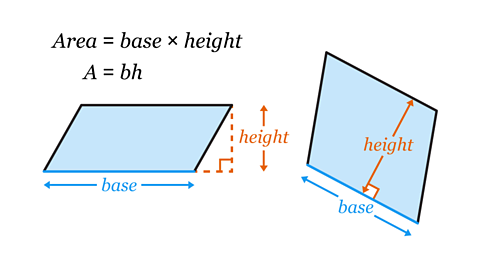
The area of a parallelogram is calculated by multiplying the base length by the perpendicular height.
\( 𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ \)
- 𝐴 is the area of the parallelogram.
- 𝑏 is the length of the base of the parallelogram.
- ℎ is the length of the perpendicular height of the parallelogram.

Find out more below, along with a worked example
Exam-style questions
- Calculate the area of the parallelogram.
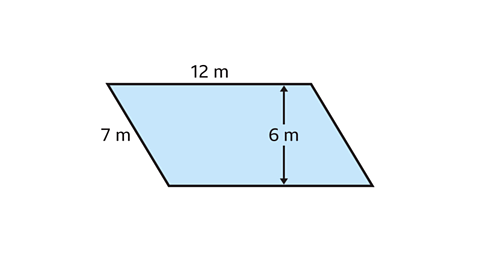
The area of the parallelogram is 72 m².
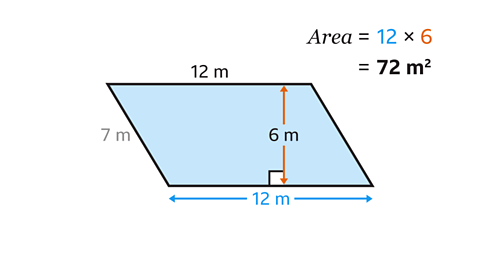
- The base and the perpendicular height are at right-angles.
- The base of the parallelogram is 12 m.
- The perpendicular height of the parallelogram is 6 m.
- The other side of the parallelogram which measures 7 m is not needed.
Substitute the base and perpendicular height values into the formula \(𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ\).
12 × 6 = 72 m².
- A parallelogram has a base measuring (2𝑥 + 3) and height 3 cm.
Its area is 24 cm².
Find the length of 𝑥 in centimetres.
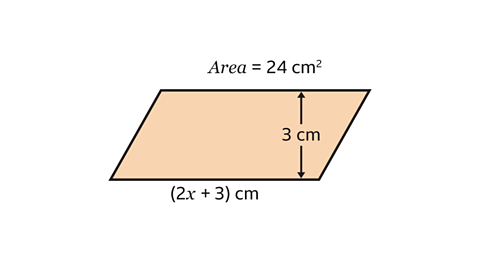
𝑥 = 2·5 cm
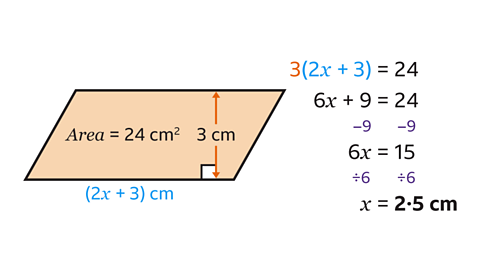
- Find the value of 𝑥 by forming and solving an equation.
- The base of the parallelogram is 2𝑥 + 3 cm.
- The perpendicular height of the parallelogram is 3 cm.
To find an expression for area, multiply the base and height.
An expression for the area is \(𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ\)
As the area equals 24 cm², this gives the equation
3(2𝑥 + 3) = 24
- Solve the equation by expanding the bracket which gives
6𝑥 + 9 = 24
- Work out the value of 𝑥 first by subtracting 9 from both sides of the equation, which gives
6𝑥 = 15
- Finally divide both sides by 6 to give
𝑥 = 2·5 cm.
Video – Area of a trapezium
Watch the video to learn how to work out the area of a trapezium.
Calculating the area of a trapezium is a little different to calculating the area of a rectangle, because a trapezium does not have two pairs of equal sides. But a trapezium can be looked at as half a parallelogram. The area of a parallelogram can be measured by multiplying its length by its perpendicular height.
Because if one end were chopped off, it would fit perfectly at the other end. When a triangle is chopped off a rectangle and moved to the other end, a parallelogram is formed. The area of the parallelogram is the same as the area of the rectangle.
Back to the trapezium, or trapeziums, since we have now created two by splitting the parallelogram in half.
Labelling the diagram to show each distinct edge demonstrates that an easy way to calculate the area of a trapezium is to calculate the area of the resulting parallelogram. That gives us the area for two trapeziums. So, to get the area for just the one, we divide that total by two.
In other words, the sum of 𝑎 + 𝑏 × 𝘩, all divided by two.
How do you work out the area of a trapezium?
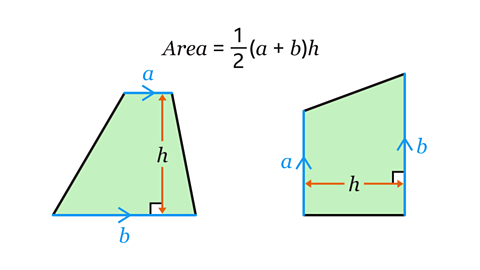
Calculate the area of a trapezium by adding the two parallelAlways equidistant. Parallel lines, curves and planes never meet however far they extend. sides. Halve this result and multiply by the perpendicular height.
\(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}(𝑎 + 𝑏)ℎ\)
- 𝐴 is the area of the trapezium.
- 𝑎 is the length of one of the parallel sides of the trapezium.
- 𝑏 is the length of the other parallel side of the trapezium.
- ℎ is the length of the perpendicular height between two parallel sides of the trapezium.
Identifying the parallel sides will help when substituting the numbers into the formula.
Find out more below, along with a worked example

Exam-style questions
- Calculate the area of the trapezium.
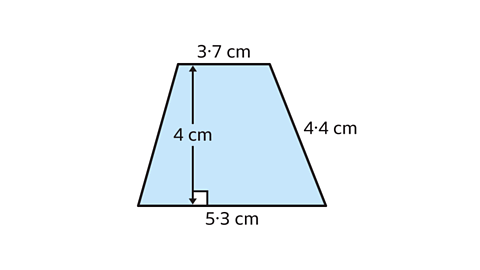
The area of the trapezium is 18 cm².
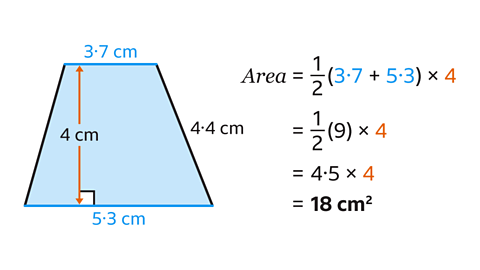
- Identify the two parallel sides.
In the trapezium, the two parallel sides measure 3·7 cm and 5·3 cm.
The perpendicular distance between them measures 4 cm.
The side of the trapezium which measures 4·4 cm is not needed.
- Using the formula, find the area by substituting the values for 𝑎, 𝑏 and ℎ.
The two parallel sides add up to 9 cm.
Half of 9 is 4·5.
- Multiply this by the perpendicular height:
4·5 × 4 = 18
The area of the trapezium is 18 cm².
- The area of the trapezium is 65 m².
Work out the value of 𝑥.
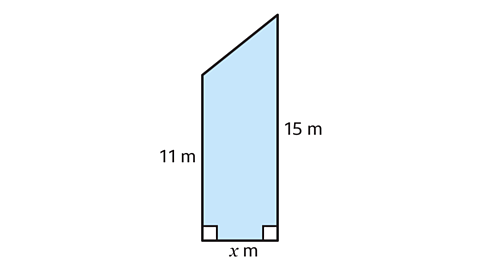
𝑥 = 5 m
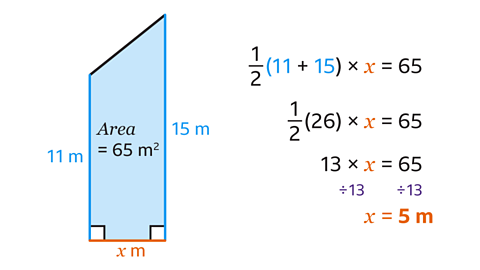
Find the value of 𝑥 by forming and solving an equation.
- First identify the two parallel sides.
In this trapezium, the two parallel sides measure 11 m and 15 m.
The perpendicular distance between them measures 𝑥 m.
The given area is 65 m².
- Next, using the formula, create an equation by substituting the values for 𝑎, 𝑏 and ℎ and the area.
\(\frac{1}{2}\)(11 + 15) × 𝑥 = 65
The two parallel sides add up to 26 m.
Half of 26 is 13.
This gives the equation 13 × 𝑥 = 65
- Finally, work out the value of 𝑥 by dividing both sides by 13.
This gives the answer 𝑥 = 5 metres.
Check your understanding
Quiz – Area
Practise what you've learned about area with this quiz.
Now you've revised area, why not have a look at line and rotational symmetry?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count11 of 35

- count12 of 35

- count13 of 35

- count14 of 35
