Key points about volume of cylinders and prisms

volume The amount of space occupied by a 3D shape, measured in cubic units such as cm³, mm³, and m³. May also be referred to as capacity. is measured in cubic units such as cm³ or m³. The volume, or capacity, of liquids is measured in millilitres or litres.
Use a FormulaA fact, rule, or principle that is expressed in terms of mathematical symbols. The plural of formula is formulae. to calculate the volume of shapes:
- cuboidA 3D shape with 6 rectangular faces. The opposite faces are congruent.: 𝑉 = 𝑙𝑤ℎ
- cylinderA 3D shape with a constant circular cross-section across its length. : 𝑉 = π𝑟²ℎ
- prismA 3D shape with a uniform polygon cross-section. : 𝑉 = 𝐴𝑙
𝐴 is the areaA measure of the size of any plane surface. Area is measured in square units. For example, square centimetres, cm². of the cross-sectionThe face that results from slicing through a solid shape. .
- The measurements of lengths used must be in the same units when finding volumes.
Make sure you know how to find the area of shapes as this can help when working out the volume of prisms.
Cubes and cuboids
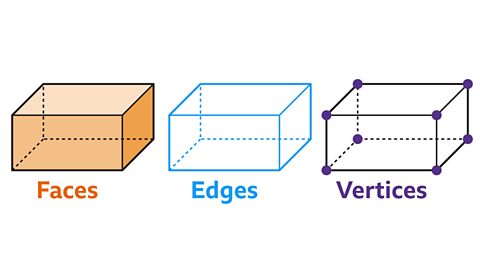
A cuboid is a three-dimensional (3D) shape with 6 faceOne of the flat surfaces of a solid shape. , 12 edgeThe line formed by joining two vertices of a shape. The line formed when two faces meet. and 8 vertexThe point at which two or more lines cross. The corner of a shape. The plural form is vertices. . Each face is a rectangle.
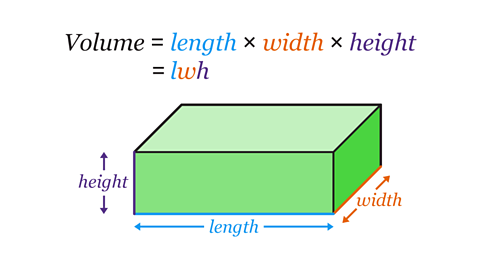
Calculate the volume of a cuboid by multiplying the length, width and height together.
This can be expressed using the formula 𝑉 = 𝑙𝑤ℎ
- 𝑉 is the volume of the cuboid.
- 𝑙 is the length of the cuboid.
- 𝑤 is the width of the cuboid.
- ℎ is the height of the cuboid.

A cubeA 3D shape with 6 square faces. is a type of cuboid, with square faces and all dimensions equal in size.
Its volume can be expressed using the formula 𝑉 = 𝑙³.
Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
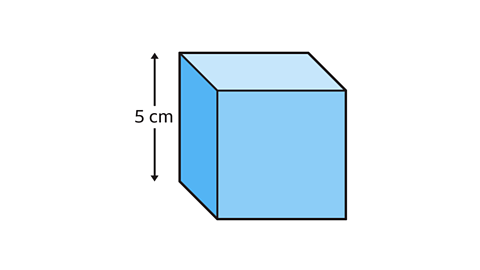
- What is the volume of the cube?
125 cm³
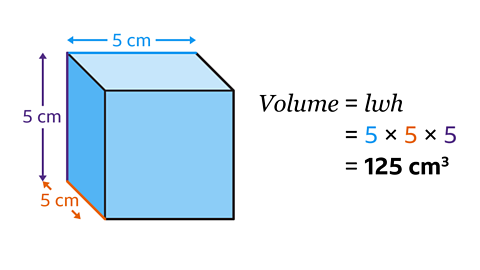
A cube is a type of cuboid where all of the dimensions are equal in size. The length, width and height all measure 5 cm.
Using the formula, find the volume by multiplying the length, width and height, or by cubing the length.
5³ = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125
The volume of the cube is 125 cm³.
- The diagram shows cuboid 𝑋 and cuboid 𝑌.
Cuboid 𝑋 has the same volume as cuboid 𝑌.
Calculate the height, ℎ, of cuboid 𝑌.
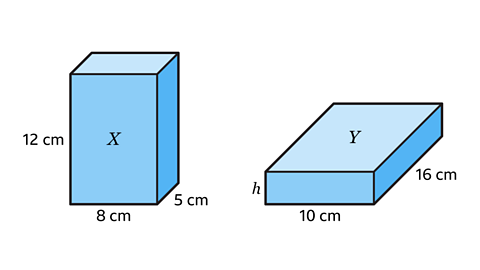
ℎ = 3 cm
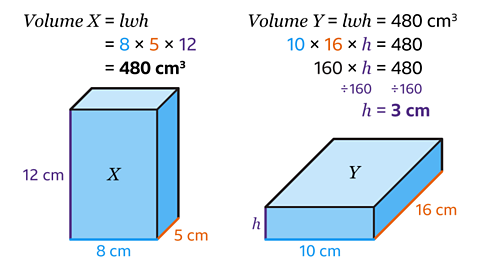
In cuboid 𝑋, the length measures 8 cm, the width 5 cm and the height 12 cm.
Using the formula, find the volume by multiplying the length, width and height.
8 × 5 × 12 = 480
The volume of cuboid 𝑋 is 480 cm³.
In cuboid 𝑌, the length measures 10 cm, the width 16 cm and the height is unknown.
Find the length of ℎ by setting up and solving an equation.
Find an expression for the volume of cuboid 𝑌 by multiplying the length, width and the height.
10 × 16 × ℎ
This must be the same as the volume of cuboid 𝑋 which gives the equation
10 × 16 × ℎ = 480
- Simplify this equation by multiplying the 10 and 16 to give
160 × ℎ = 480
- Find the value of ℎ by dividing both sides of the equation by 160 which gives the answer ℎ = 3 cm.
How to work out the volume of cylinders
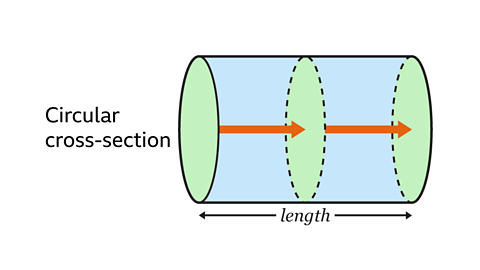
A cylinder is a three dimensional (3D) shape with a circular cross-section.
To find the volume of a cylinder, the radiusThe distance from the centre of the circle to the circumference. Plural of radius is radii. of the circular cross-section and the height of the cylinder must be known.
The height can also be described as the length of the cylinder.

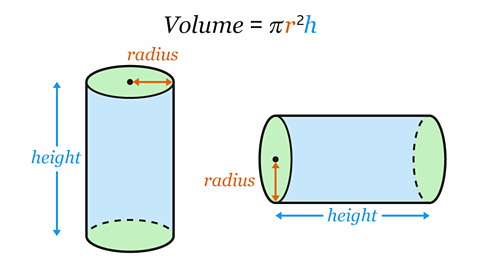
Multiply the area of the cross-section by the height of the cylinder to find the volume, using the formula:
𝑉 = π𝑟²ℎ
- 𝑉 is the volume of the cylinder.
- 𝑟 is the radius of the circular cross-section.
- ℎ is the height of the cylinder.
You should use the π on your calculator unless a question specifies an approximation to use.
3·14 is a common approximation.
Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
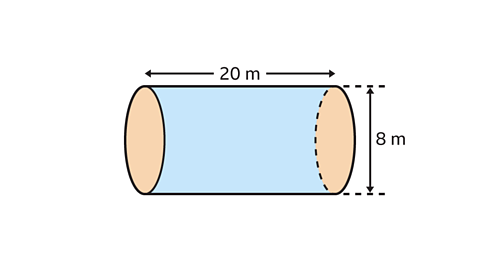
- Work out the volume of the cylinder?
Give your answer in terms of π.
The volume of the cylinder is 320 m³.
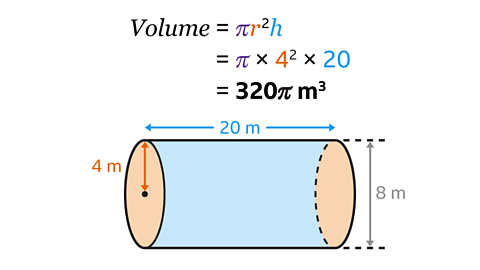
In the cylinder, the diameter measures 8 m and the length (height) measures 20 m.
The radius is half the diameter, so 𝑟 is 4 m.
Using the formula, find the volume by substituting the values of 𝑟 and ℎ.
𝑉 = π × 4² × 20 = 320π
The volume of the cylinder is 320π m³.
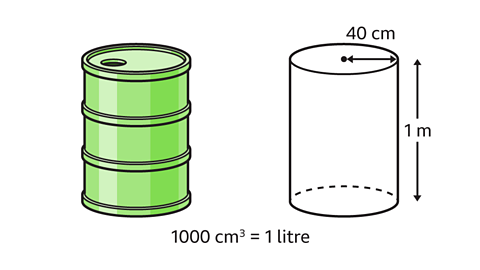
- Water collects in a rain barrel. The rain barrel is approximately a cylinder with a radius measuring 40 cm and a height measure 1 m.
What is the approximate capacity of the barrel in litres?
Use the conversion 1000 cm³ = 1 litre and π = 3·14
The approximate capacity is 502·4 litres
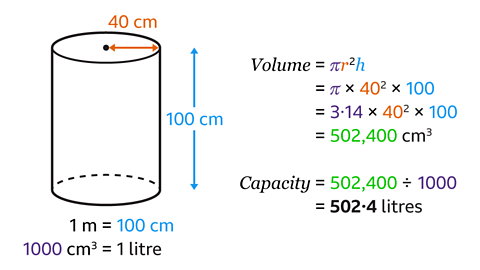
In the cylinder, the diameter measures 40 cm and the height measures 1 m.
When finding volumes, the measurements of lengths used must be in the same units.
- Convert the height measures in metres into centimetres by multiplying by 100.
1 m = 100 cm.
- Using the formula, find the volume by substituting the values for 𝑟 and ℎ.
𝑉 = 3·14 × 40² × 100 = 502,400
The volume of the cylinder is 502,400 cm³.
- Convert the measurement in cm³ to litres by dividing by 1000.
502,400 ÷ 1000 = 502·4
How to find the volume of a prism
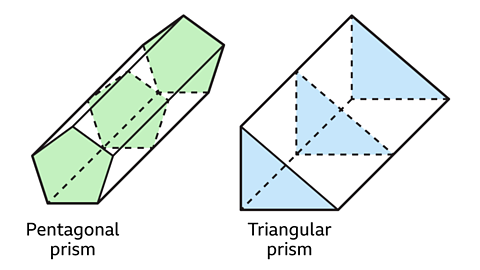
A prism is a three-dimensional (3D) shape that has the same cross-section throughout its length. The cross-section is a polygon.
The name given to the prism is dependent on the shape of the cross-section.
For example, a prism with a triangle shape as its cross-section is called a triangular prism.
A cuboid can also be called a rectangular prism.

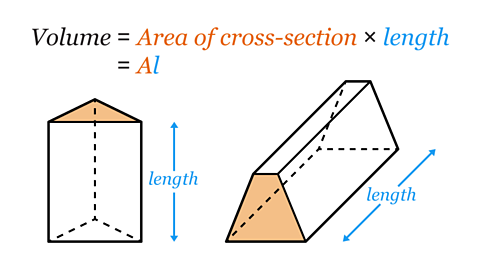
Find the volume of a prism by using the formula 𝑉 = 𝐴𝑙
- 𝑉 is the volume of the prism.
- 𝐴 is the area of the cross-section.
- 𝑙 is the length of the prism.
The formula needed to find the area of the cross-section will depend on the shape.
Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Find the volume of the triangular prism.
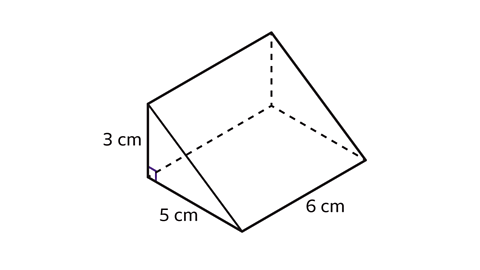
The volume of the triangular prism is 45 cm³.
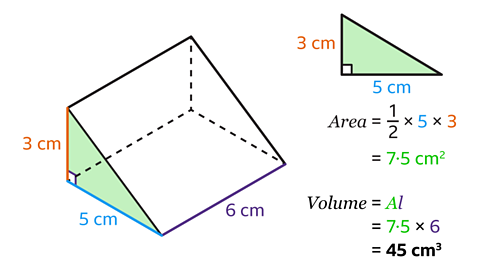
The cross-section is a triangle.
- Calculate the area by using the formula for the area of a triangle.
\(𝐴 = \frac{1}{2}𝑏ℎ\)
The base and the height are at right angles. The base is 5 cm and the height is 3 cm.
- Substitute the base and perpendicular height values into the formula.
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 × 3 = 7·5
The area of the cross-section is 7·5 cm².
The length of the prism is 6 cm.
- Find the volume of the prism by multiplying the area of the cross-section by the length.
7·5 × 6 = 45
The volume of the prism is 45 cm³.
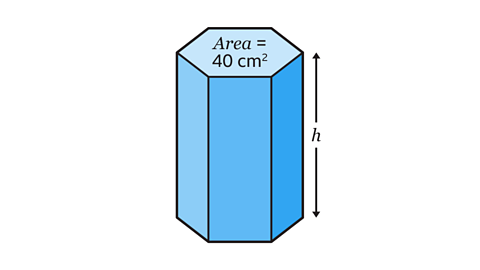
The diagram shows a solid hexagonal prism. The area of the cross-section is 40 cm². The volume of the prism is 340 cm³.
Calculate the height, ℎ.
ℎ = 8·5 cm
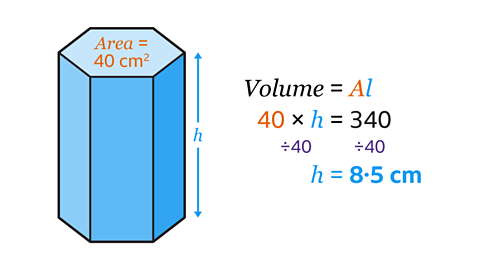
- Find the volume of the prism by multiplying the area of the cross-section by the length.
In this prism, the length is equivalent to the height, ℎ.
- Using the formula, create an equation by substituting the values for 𝐴, ℎ and the volume.
40 × ℎ = 340
- Work out the value of ℎ by dividing both sides by 40, which gives the answer 8·5 cm.
- Find the volume of the L-shaped prism.
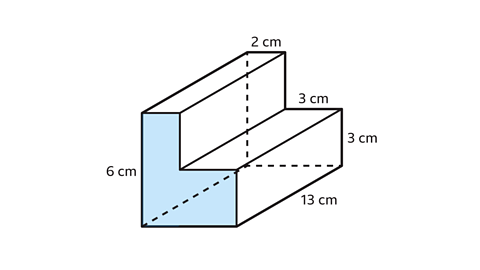
The volume of the L-shaped prism is 273 cm³.
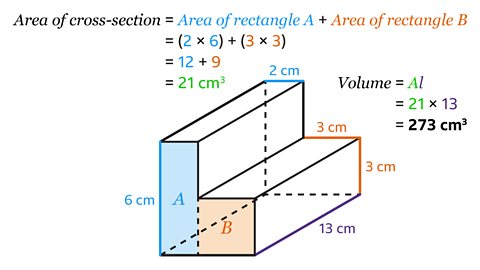
The cross-section is a compound shape made up of two rectangles. The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying the length and width.
- Work out the areas of the two rectangles, calling them 𝐴 and 𝐵, that make up the cross-section.
The area of rectangle 𝐴 is 2 × 6 = 12 cm².
The area of rectangle 𝐵 is 3 × 3 = 9 cm².
- Find the area of the cross-section by adding the areas of the two rectangles together.
The area of the cross section is 12 + 9 = 21 cm².
The length of the prism is 13 cm.
- Find the volume of the prism by multiplying the area of the cross-section by the length.
21 × 13 = 273
The volume of the prism is 273 cm³.
Check your understanding
Quiz – Volume of cylinders and prisms
Practise what you've learned about the volume of a prism with this quiz.
Now you've revised volume of cylinders and prisms, why not look at constructing triangles?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count12 of 35

- count13 of 35

- count14 of 35

- count15 of 35
