Key points about constructing triangles

A triangle has three sides and three angles. A uniqueA single solution that satisfies a given condition. triangle can be constructed when one set of the following properties is known:
- Two sides and the included angleAn angle between two given sides. (SAS)
- Two angles and the included sideA side between two given angles. (ASA)
- All three sides (SSS)
Use a ruler, protractor and a pair of compasses to construct a triangle accurately.
After the triangle has been constructed, leave the construction lines visible so each stage of the process is shown clearly. This is important in exams to maximise to marks.
To be certain your constructions are precise, make sure you are confident at measuring accurately with a ruler and a protractor.
How to construct SAS triangles
A Side, Angle, Side (SAS) triangle construction is needed when the lengths of two sides and the angle between them is known.
Watch the example about constructing a SAS triangle using a protractor and ruler.
Read the steps below on constructing SAS triangles.
- Draw one of the given sides of the triangle using the ruler.
- Use the protractor to measure the given angle at the correct end of the line segment. Mark the angle with a cross and draw a line from the endpoint through this cross.
- Measure with a ruler along the new line drawn from the vertexThe point at which two or more lines cross. The corner of a shape. The plural form is vertices. and mark the length of the other given side on it.
- Join the two ends of the given sides together to produce a triangle.
- Remember to label the sides, vertices and the angle, leaving in any construction lines.
Exam-style questions
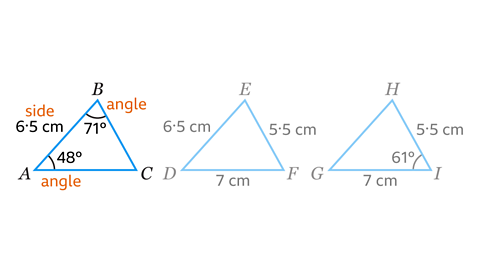
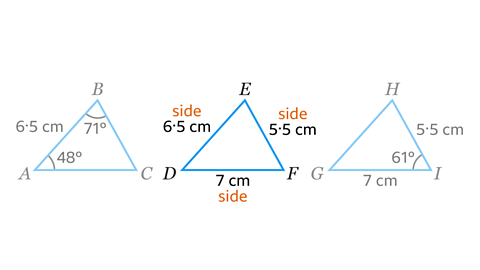
- Which triangle can be constructed using the SAS (Side, Angle, Side) method?
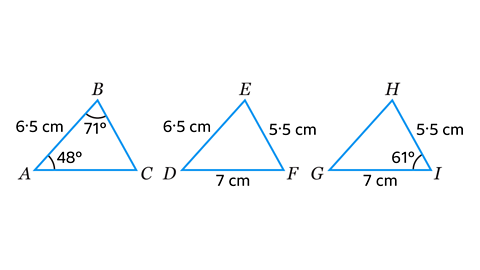
Triangle 𝐺𝐻𝐼
This is the only triangle where two sides and the included angle are given.

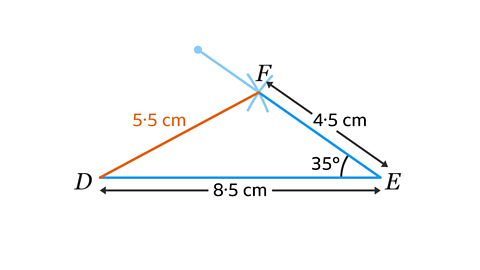
- In triangle 𝐷𝐸𝐹, 𝐷𝐸 = 8·5 cm and 𝐸𝐹 = 4·5 cm. Angle 𝐸 = 35°. Construct the triangle using paper, a pencil, protractor and ruler. By measuring 𝐷𝐹 on your diagram, find the length of 𝐷𝐹.
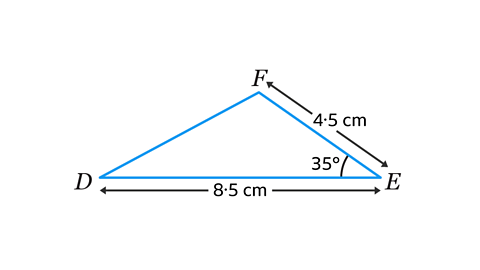
Side 𝐷𝐹 = 5·5 cm
Triangle 𝐷𝐸𝐹 is a SAS (Side, Angle, Side) triangle and can be constructed using a protractor and a ruler.
How to construct ASA triangles
An Angle, Side, Angle (ASA) triangle construction is needed when two angles and the side between them is known.
Watch the example about constructing a ASA triangle using a protractor and ruler.
Read the steps below on constructing ASA triangles.
- Draw the given side of the triangle using a ruler.
- Use a protractor to measure the given angle at the left-hand endpoint of the given side. Mark the angle and then draw a line from the endpoint through the mark.
- Use a protractor to measure the given angle at the right-hand endpoint of the given side. Mark the angle and draw a line from the endpoint through the mark.
- Where the lines intersect is the position of the third vertex.
- Remember to label the side, vertices and the angles, leaving in any construction lines.
Exam-style questions
- Which triangle can be constructed using the ASA (Angle, Side, Angle) method?
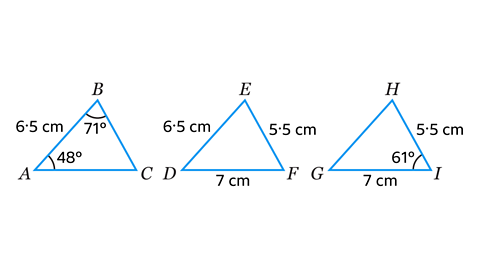
Triangle 𝐴𝐵𝐶
This is the only triangle where two angles and the included side are given.
- In triangle 𝐽𝐾𝐿, angle 𝐽 = 75°, angle 𝐾 = 40°, and 𝐽𝐾 = 7·5 cm.
Construct the triangle using paper, a pencil, protractor and a ruler. By measuring on your diagram, find the length of 𝐽𝐿.
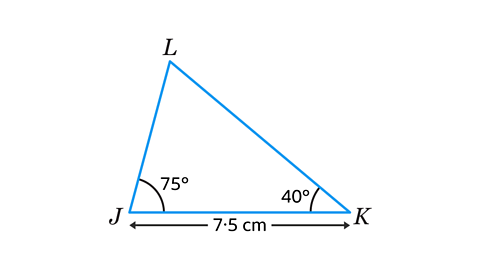
Side 𝐽𝐿 = 5·3 cm.
Triangle 𝐽𝐾𝐿 is a ASA (Angle, Side, Angle) triangle and can be constructed using a protractor and a ruler.

How to construct SSS triangles
A Side, Side, Side (SSS) triangle construction is needed when all three sides are known.
Watch the example about constructing SSS triangles using a compass and ruler.
Read the steps below on constructing SSS triangles
To construct a SSS triangle:
- Draw the longest side of the triangle using a ruler.
- Place the compass along the ruler and measure out the length of one of the other sides. Draw an arcPart of the circumference. Named as ‘major’ for over half of the circumference and ‘minor’ for less than half of the circumference. from an endpoint of the line you have drawn.
- Repeat the previous step for the remaining side.
- Draw a line from the endpoint of each side of the base to the point where the arcs intersectWhen lines cross or overlap. .
- Remember to label the sides, leaving the construction lines (arcs).
Exam-style questions
- Which triangle can be constructed using the SSS (Side, Side, Side) method?
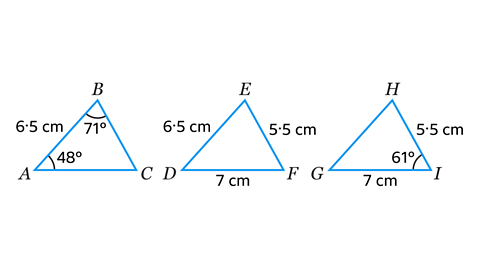
Triangle 𝐷𝐸𝐹
This is the only triangle where all three sides are given.
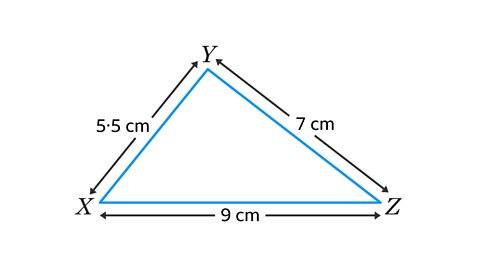
- In triangle 𝑋𝑌𝑍, 𝑋𝑌 = 5·5 cm, 𝑌𝑍 = 7 cm, and 𝑍𝑋 = 9 cm. Construct the triangle using paper, a pencil, pair of compasses and a ruler. By measuring on your diagram, work out the size of angle 𝑋.
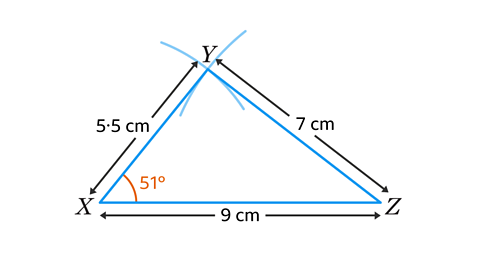
Angle 𝑋 = 51°
Triangle 𝑋𝑌𝑍 is a SSS (Side, Side, Side) triangle.
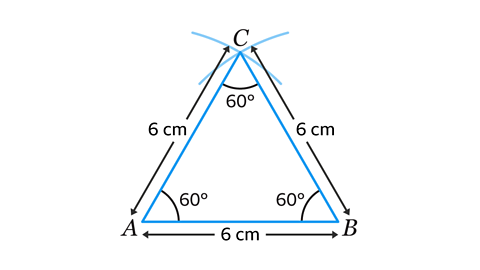
- Use a pencil, paper and a pair of compasses to construct an angle of 60°.
You may not use a protractor.
Hint: What type of triangle has angles measuring 60°?
The SSS (Side, Side, Side) construction method can be used to construct an equilateral triangle.
An equilateral triangle is where all three sides are the same length, and all angles are 60°.
This equilateral triangle has been constructed where each of the sides measures 6 cm.
Check your understanding
Quiz – Constructing triangles
Practise what you've learned about constructing triangles with this quiz.
Now you've revised constructing triangles, why not look at nets, plans and elevations?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 35

- count7 of 35

- count8 of 35

- count9 of 35
