Key points about bearings

A bearing An angle measured in degrees, that is used to describe a direction clockwise from north. is an angle used to describe a direction.
A bearing is always:
- given as a three-digit number
- measured clockwiseTravelling in the same direction as the hands on a clock. from the north line
- measured in degreesThe unit of measurement for the size of an angle.
For example, the bearing of B from A is the direction needed to travel from A to B.
Make sure you are confident in measuring and calculating angles when working out bearings.
More challenging bearings questions may also combine knowledge of right-angled trigonometry.
How to measure a bearing
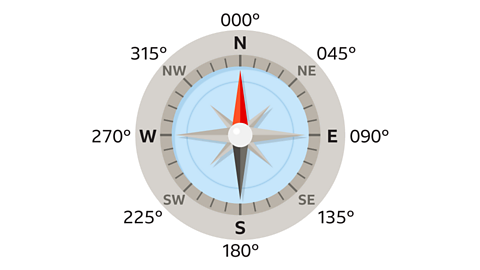
A compass is a tool used to describe a direction. There are four main directions on a compass: north, south, east and west.
Each direction on a compass is equivalent to a bearing.
For angles smaller than 100°, zeros are placed in front of the angle to ensure the bearing has three digits. For example, the bearing for the direction of north-east is 045°.
Bearings are used in real life, for example in helping to navigate aircraft and ships.

Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- Work out the bearing of D from C.
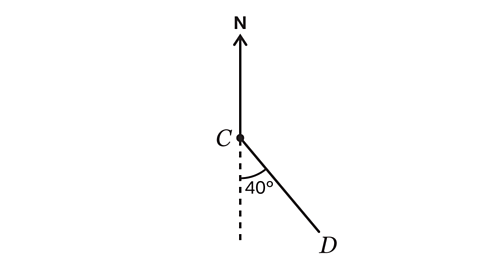
The bearing of D from C is 140°.
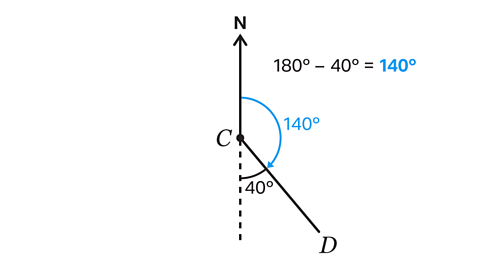
The bearing of point D from point C is the direction required to travel from C to D.
This is the angle measured clockwise from the north line to the line segment CD.
Angles on a straight line add up to 180°.
180° – 40° = 140°
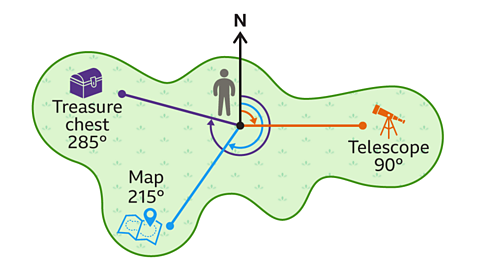
- A person is collecting three items on an island: a telescope, map and treasure chest.
Approximate the bearings they must travel on, each time from the starting location, to collect each item.
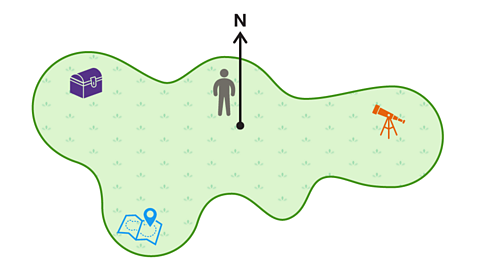
From the starting point each time:
The telescope is on an approximate bearing of 090°.
The map is on an approximate bearing of 215°.
The treasure chest is on an approximate bearing of 285°.
What are back bearings?
A back bearingA bearing opposite to a given bearing. is a direction which is the opposite to a given bearing.
It is calculated by adding or subtracting 180° from the given bearing.
For example, the bearing of 315° (north-west) is opposite to 135° (south-east). These angles have a difference of 180°.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
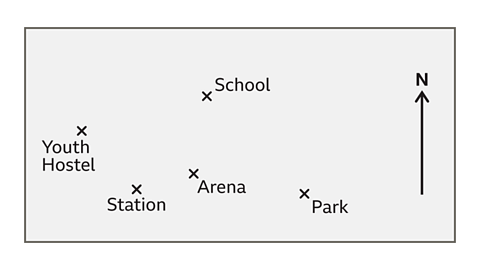
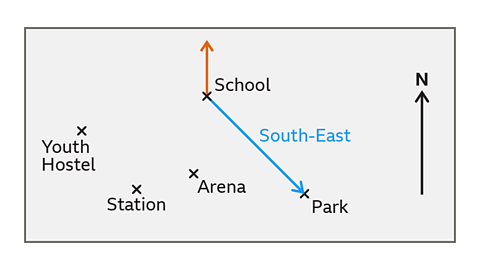
- What is south-east of the school?
The park is south-east of the school.
- Approximate the three-figure bearing of the school from the station.

The bearing of the school from the station is 037°.
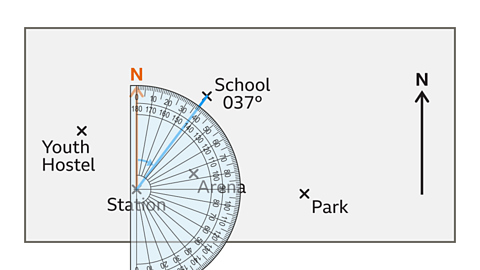
Join the two points with a line segment.
The bearing of the school from the station is the direction required to travel from the station to the school.
Draw a north line at the station.
The bearing is the angle measured clockwise from the north line to the line segment.
The angle measures 37°.
- The bearing of Harrogate from York is 275°. What is the bearing of York from Harrogate?
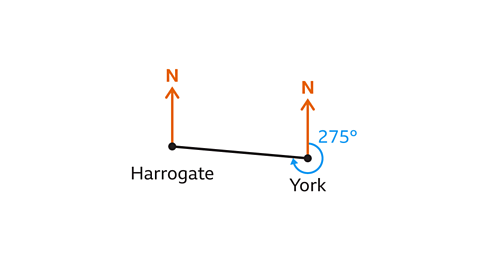
The bearing of York from Harrogate is 095°.
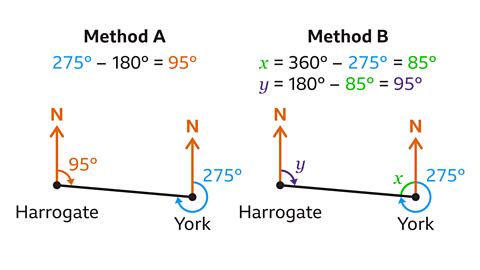
It can be calculated using two different methods.
Method A
The bearing of York from Harrogate is a back bearing. It can be calculated by adding or subtracting 180° from the given bearing. In this case 180° must be subtracted from the given bearing.
275° – 180° = 95°
Method B
The bearing of York from Harrogate can be calculated using geometry.
Angles at a point add up to 360°, therefore:
Angle 𝑥 = 360° – 275° = 85°
The two north lines are parallelandco-interior angles add up to 180°, therefore:
Angle 𝑦 = 180° − 85° = 95°
Bearings and trigonometry
When compass directions are used to describe a journey, the resulting path can create right-angled triangleA triangle with one right angle. .
Use trigonometry to calculate the size of unknown angles.
Draw a diagram to help visualise the problem.
Remember, a bearing must be the angle measured clockwise from a north line.

Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
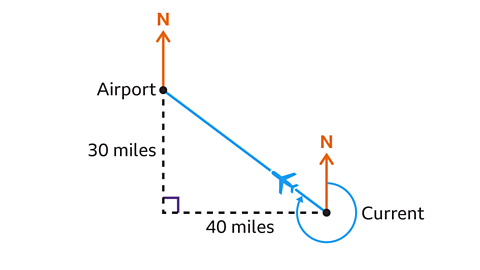
- X is 7 km due north of Y and 8 km due east of Z.
Work out the bearing of Y from Z.
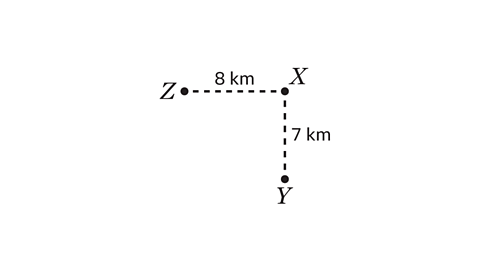
The bearing of Y from Z is 131° to the nearest whole number.
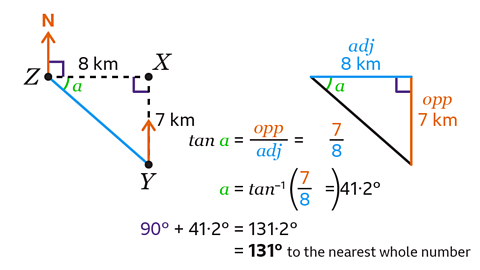
The size of the bearing is equal to 90° + 𝑎.
Calculate angle 𝑎 using trigonometry. In the triangle, both the opposite and adjacent are known.
Use tan 𝑎 = opp/adj to work out the missing angle.
Use the inverse function:
𝑎 = tan⁻¹ (7 ÷ 8) = 41·2°
The size of the bearing is 90° + 41·2° = 131° to the nearest whole number.
- A ship sails 40 kilometres on a bearing of 125°.
How far east has the ship sailed?
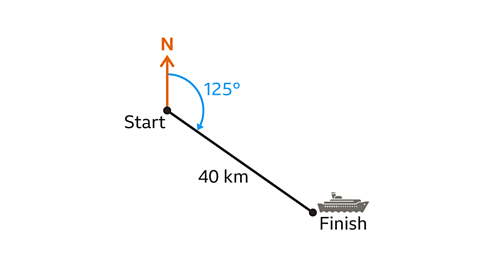
The ship has sailed 32·8 km.
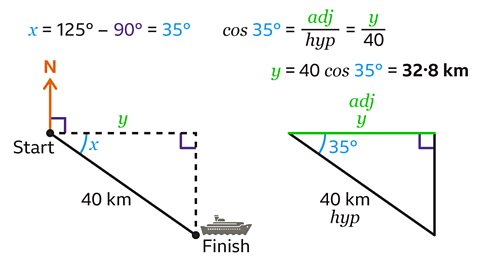
Draw a horizontal and vertical line from the start to the finish to create a right-angled triangle. The distance travelled east is the horizontal distance labelled 𝑦.
Calculate angle 𝑥 using geometry.
𝑥 = 125° – 90° = 35°.
In the triangle, both the angle and hypotenuse are known. The side labelled 𝑦 is the adjacent.
- Use cos 𝑥 = adj ÷ hyp to work out the missing side.
Therefore cos 35° = 𝑦 ÷ 40
- To work out the length of 𝑦, multiply both sides by 40, which gives:
𝑦 = 40 cos 35° = 32·8
Quiz – Bearings
Practise what you've learned about bearings with this quiz.
Now you've revised bearings, why not take a look at angles in parallel lines?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 35

- count10 of 35

- count11 of 35

- count12 of 35
