Key points about angles

An angle is the amount of turn between two lines. Angles are measured in degreesThe unit of measurement for the size of an angle. and denoted by the symbol °.
Angles can be sorted into types depending on their size. These are:
- .
When working out the size of missing angles it is important to recall and use the angles rules for , angles on a straight line, angles at a point, angles in triangles and angles in quadrilaterals.
Make sure you are confident with solving linear equations before working with angles written as algebraic expressions.
Check your understanding
What are the different types of angles?
Angles are based on fractions of a full turn or 360°.
- An acute angle is less then 90°.
- A quarter turn, which measures 90°, is called a right angle.
- An obtuse angle is between 90° and 180°.
- A reflex angle is between 180° and 360°.
Angles can be indicated by 3 letters, representing each point that make up an angle. The middle letter shows the point around which the angle is situated, eg ABC indicates an angle around point B.
can be named or labelled with two letters (eg EF) and describe the starting and finishing points of the line.
Find out more about the different angles below
GCSE exam-style questions
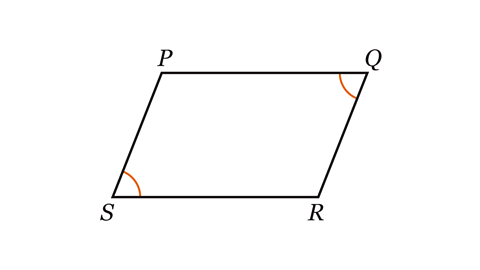
- Shape PQRS is a parallelogram. Which angles are acute?
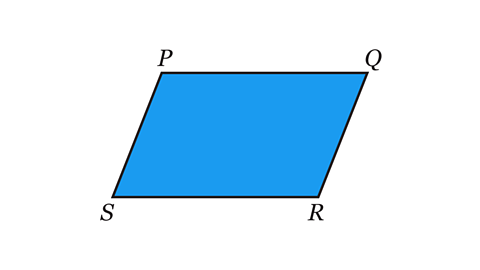
Angle PQR (or RQP) is an acute angle and is less than 90°.
Angle PSR (or RSP) is an acute angle and is less than 90°.
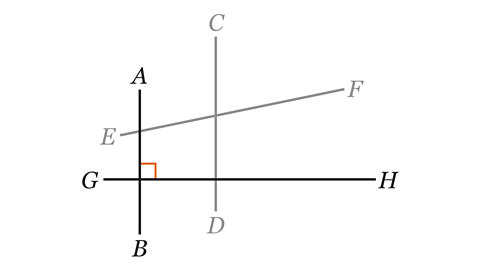
- Which line is perpendicular to AB?
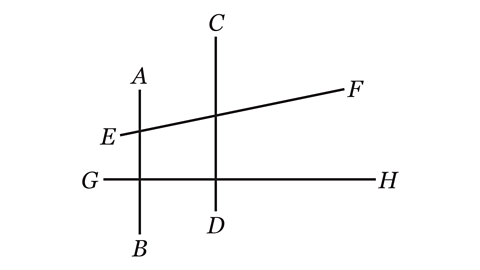
GH is perpendicular to AB. The lines cross at a right-angle.
Angles on straight lines and at a point
To work out the size of opposite angles, angles on a straight line and at a point, there are some important rules to remember.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- Calculate the sizes of angles 𝑏 and 𝑐.
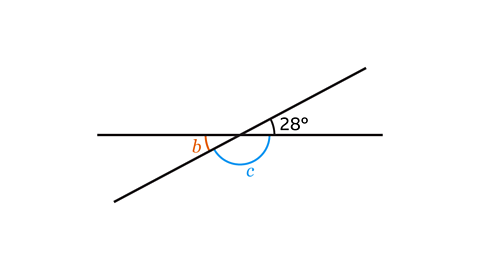
Angle 𝑏 = 28° and angle 𝑐 = 152°.
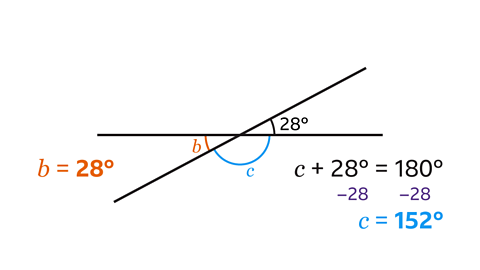
Angle 𝑏 is vertically opposite the 28°.
Angle 𝑐 and the 28° form a straight line.
𝑐 = 180 – 28 = 152°
- Calculate the size of angle 𝑥.
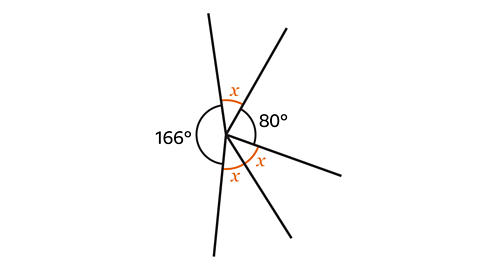
Angle 𝑥 = 38°.
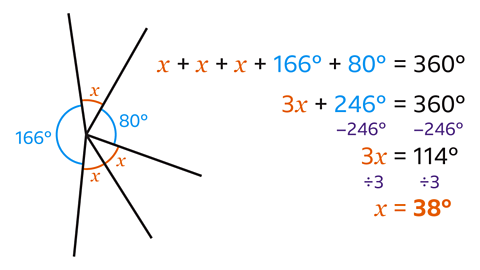
The angles that meet at a point add up to 360°, so 𝑥 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 + 166 + 80 = 360.
- To find the value of 𝑥, collect like terms.
3𝑥 + 246 = 360.
- Subtract 246 from both sides.
3𝑥 = 114
- Finally divide both sides by 3.
𝑥 = 38°
Interior angles
To work out the size of interior angles, there are some important rules to remember.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- Calculate the size of angle ABC.
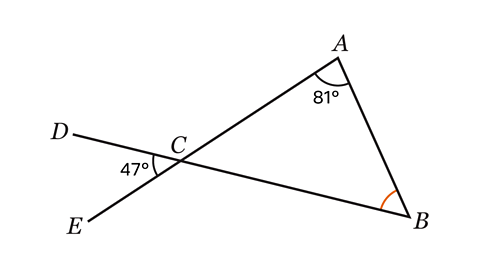
Angle ABC = 52°.
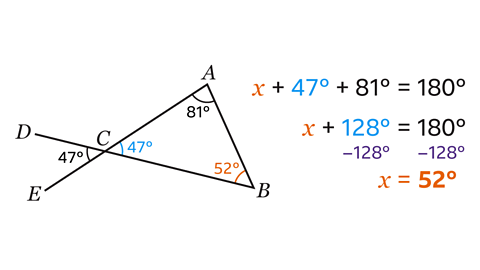
Angle ACB is vertically opposite angle DCE, so angle ACB = 47°.
The angles in triangle ABC add up to 180°. By denoting angle ABC with the letter 𝑥, then
𝑥 + 47 + 81 = 180.
- To find the value of 𝑥, add the angles.
𝑥 + 128 = 180
- Subtract 128 from both sides.
𝑥 = 52°
- Shape PQRS is a quadrilateral.
Set up and solve an equation to find 𝑦.
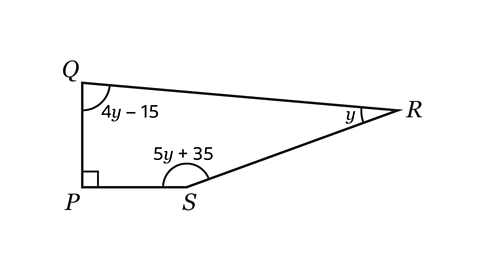
Angle 𝑦 = 25°.
Angle QPS is a right-angle, so equals 90°.
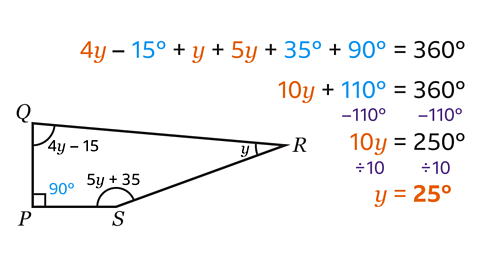
The angles in quadrilateral PQRS add up to 360° so
4𝑦 – 15 + 𝑦 + 5𝑦 + 35 + 90 = 360.
- To find the value of 𝑦, collect like terms.
10𝑦 + 110 = 360.
- Subtract 110 from both sides.
10𝑦 = 250
- Divide both sides by 10 to find the answer.
𝑦 = 25°
Quiz – Angles
Practise what you've learned about angles with this quiz.
Now you've revised angles, why not take a look at area?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 35

- count3 of 35

- count4 of 35

- count5 of 35
