Key points about polygons

A polygonA closed 2D shape made up of straight lines. is a 2D shape with at least three sides and is regularA regular shape has all sides equal and all angles equal. if all the sides are equal and all angles are equal.
In order to work out the size of missing Interior angleAn angle inside a shape. angles in polygons, it is important to know what the interior angles of each polygon add up to.
To find the size of one interior angle of a regular polygon, divide the sum of the interior angles by the number of sides.
Make sure you are confident in finding the value of missing angles before working with polygons.
Check your understanding
What are the different types of triangle?
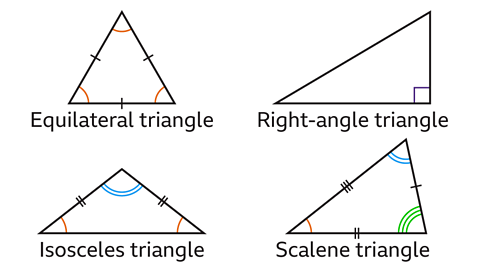
A triangle is a 2D shape or polygon with three sides.
There are four different types of triangle, with different properties.
- An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. All of the angles are 60°.
- An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and two equal angles.
- A right-angled triangle is a triangle that has one angle that is a right-angle or 90°.
- A scalene triangle has three sides of different lengths and unequal angles.


Remember
The angles in a triangle always add up to 180°.
Recognising the type of triangle can be useful in calculating the sizes of unknown angles.
Find out more about triangles, along with a worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Triangle PQR is an isosceles triangle.
Work out the size of angle 𝑎.
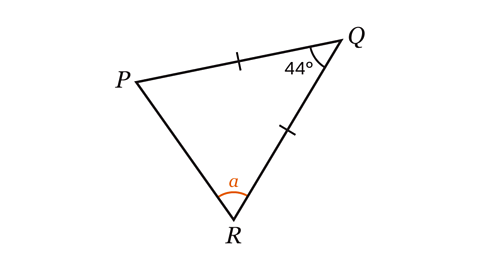
Angle 𝑎 = 68°.
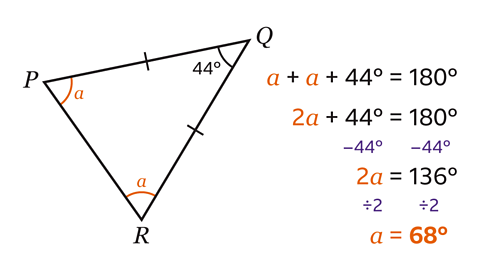
Triangle PQR is isosceles. Since the base angles in an isosceles triangle are equal, angle RPQ = 𝑎.
The angles in triangle PQR add up to 180°.
𝑎 + 𝑎 + 44 = 180
- To find the value of 𝑎, collect like terms which produces the equation
2𝑎 + 44 = 180
- Next subtract 44 from both sides to give the equation
2𝑎 = 136
- Finally, divide both sides by two, which gives the answer
𝑎 = 68°
- ACE is a straight line.
Triangle ABC is isosceles.
Triangle CDE is equilateral.
Work out the size of angle 𝑘.
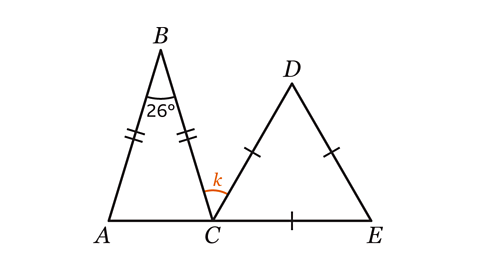
Angle 𝑘 = 44°
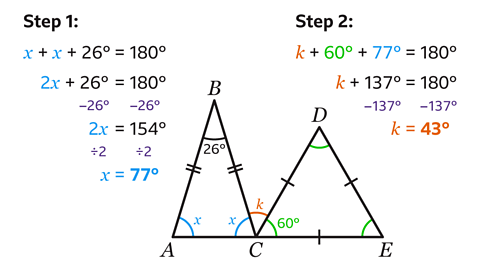
Triangle CDE is equilateral. Since all angles in an equilateral triangle are equal, angle DCE = 60°.
Triangle ABC is isosceles. Since the base angles in an isosceles triangle are equal, if angle BAC equals 𝑥 then angle ACB equals 𝑥.
- Work out the value of 𝑥.
- The angles in triangle ABC add up to 180°.
𝑥 + 𝑥 + 26 = 180
- To find the value of 𝑥 collect like terms. Collecting like terms produces the equation
2𝑥 + 26 = 180
Next subtract 26 from both sides. Subtracting 26 from both sides gives the equation
2𝑥 = 154
- Finally, divide both sides by two. Dividing both sides by two gives the answer
𝑥 = 77°
- Work out the value of 𝑘.
- ACE is a straight line. Angles on a straight line add up to 180°.
𝑘 + 60 + 77 = 180
- To find the value of 𝑘 add the angles which produces the equation
𝑘 + 137 = 180
- Next subtract 137 from both sides giving the answer
𝑘 = 43°
What are quadrilaterals?
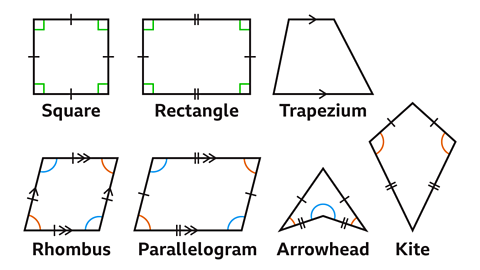
A quadrilateral is a 2D shape or polygon with four sides. There are different types of quadrilaterals, each with different properties.
These include square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezium, kite and arrowhead.
Properties of a quadrilateral include the length of their sides, size of their angles, their diagonalA line joining two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of a polygon. and their symmetry.
A specific property may apply to more than one quadrilateral.
Angles in a quadrilateral always add up to 360°.
Recognising the type of quadrilaterals can be useful in calculating the sizes of unknown angles.

Find out more about quadrilaterals and their properties below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Ben is describing a shape.
Which shape is it?
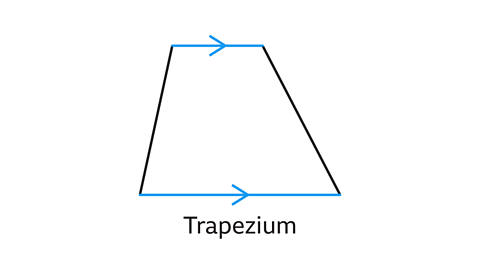
The shape is a trapezium.
A trapezium has one pair of parallel sides.
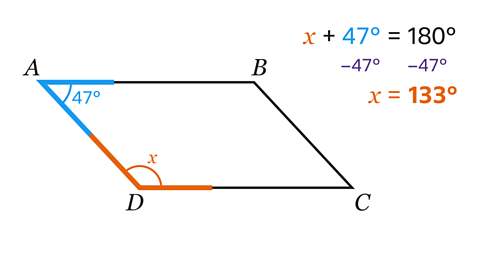
- Shape ABCD is a parallelogram.
Work out the size of angle 𝑥.
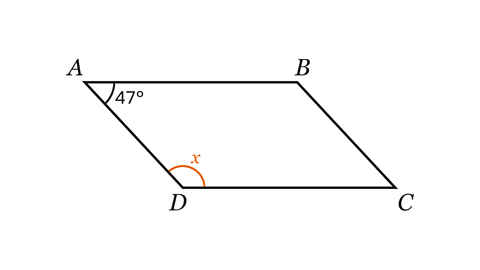
Angle 𝑥 = 133°
Angles 𝑥 and 47° are co-interior. Co-interior angles add up to 180°, so angle 𝑥 = 180 – 47 = 133°.
Polygons - interior and exterior angles
A polygon is a 2D shape with three or more sides.
The polygon is regular if all its sides and angles are the same size. For polygons:
- an Interior angleAn angle inside a shape. and an exterior angleAn angle created on the outside of a shape by extending an edge. add up to 180°
- the interior angles of any polygon add up to (number of sides – 2) × 180°
For a regular polygon the size of one exterior angle = 360 ÷ 𝑛, where 𝑛 is the number of sides.
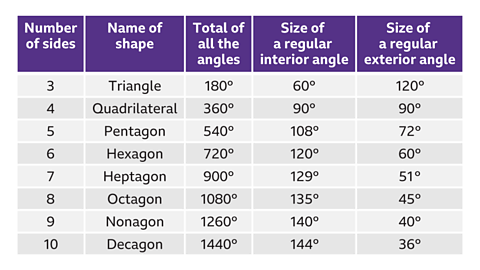
The table below shows the sum of interior angles for some regular polygons. It also shows the sizes of their interior and exterior angles.
The interior and exterior angles for the heptagon are rounded to the nearest degree.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- A regular decagon has 10 sides.
Work out the sizes of angles 𝑥 and 𝑦.
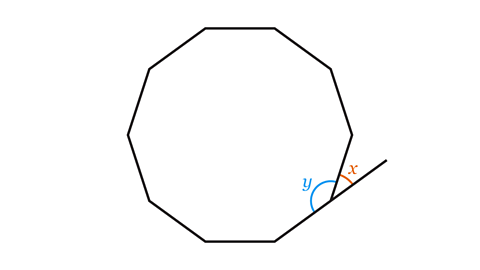
Angle 𝑥 = 36° and angle 𝑦 = 144°
A decagon has 10 sides so 𝑥 = 360 ÷ 10 = 36°.
The interior angle and exterior angle of a polygon add up to 180°.
𝑦 = 180 – 36 = 144°.
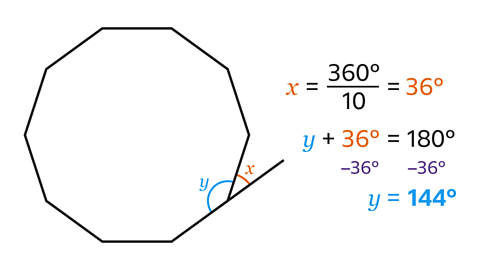
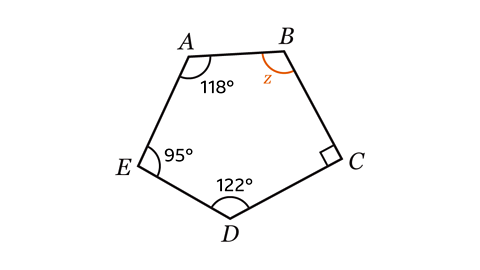
- Shape 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷𝐸 is an irregular pentagon.
Work out the size of angle 𝑧.
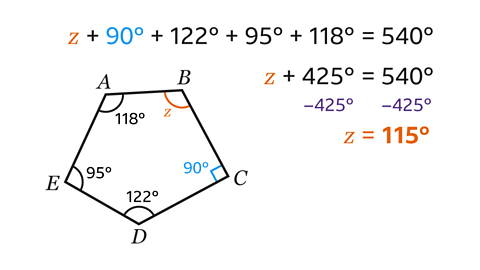
Angle 𝑧 = 115°
Angle 𝐶 is a right-angle measuring 90°.
A pentagon has five sides.
The sum of the interior angles in a pentagon is
(5 – 2) × 180 = 3 × 180 = 540°.
𝑧 + 90 + 122 + 95 + 118 = 540
To find the value of 𝑧, add the angles, which produces the equation
𝑧 + 425 = 540
Next subtract 425 from both sides which gives the answer:
𝑧 = 115°
Quiz - Polygons
Practise what you've learned about polygons with this quiz.
Now you've revised polygons, why not look at nets, plans and elevations?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 35

- count5 of 35

- count6 of 35

- count7 of 35
