Key points about pyramids, cones and spheres

The volume of a 3D shape is the amount of space inside it. Volume is measured in cubic units such as cm³ and m³. The volume, or capacity, of liquids is measured in millilitres or litres.
The surface area of a 3D shape is the total area of all the faces of the shape. Surface area is measured in square units, including cm² or m².
A FormulaA fact, rule, or principle that is expressed in terms of mathematical symbols. The plural of formula is formulae. is used to calculate the volume and surface area of a coneA 3D shape with a flat, circular face at the bottom and a curved surface reaching to a vertex at the top. , pyramidA 3D shape with a polygon-shaped base and a pointed apex (top vertex). Named by the shape of its base, such as square-based pyramid or hexagon-based pyramid. or sphereA round ball-like shape where every point on the surface is an equal distance from its centre. . The formulas for cones and spheres will be provided in the exam.
Find the volume of compound shapeA shape formed by combining two or more shapes. by breaking the shape into two or more simpler shapes. The volume of the compound shape is the sum of the volume of each part.
Make sure you know how to find the area of triangles and rectangles, as this can help when working out the surface area of a pyramid.
How to calculate the volume and surface area of a pyramid
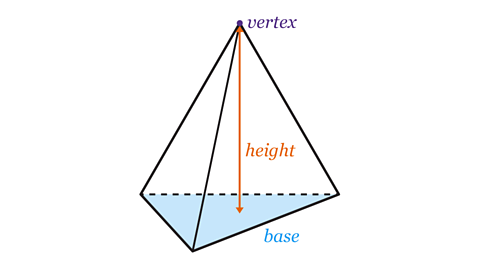
A pyramidA 3D shape with a polygon-shaped base and a pointed apex (top vertex). Named by the shape of its base, such as square-based pyramid or hexagon-based pyramid. is a 3D shape which can have differently shaped bases. Its other faceOne of the flat surfaces of a solid shape. are triangles which meet at a vertexThe point at which two or more lines cross. The corner of a shape. The plural form is vertices. .
The most common pyramids are square-based, rectangular-based and triangular-based pyramids.
A tetrahedron is a special pyramid where all the faces are equilateral triangles.

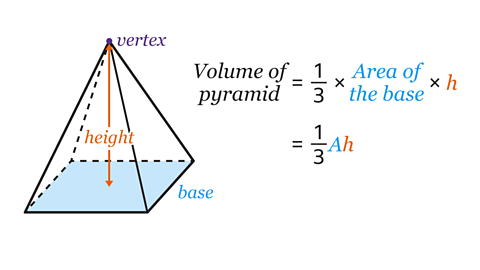
Calculate the volume The amount of space occupied by a 3D shape, measured in cubic units such as cm³, mm³, and m³. May also be referred to as capacity. of a pyramid using the formula:
Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 𝐴 × ℎ
- 𝐴 is the area of the base.
- ℎ is the perpendicular height between the base and the vertex.

Calculate the surface areaThe total area of all the faces of a 3D shape. Measured in square units, such as cm² and m². of a pyramid by finding the total area of all the faces of the shape.
If the base of the pyramid is a regular polygon, each of the triangular faces will be identical.
Calculate the total area of the triangular faces by finding the area of one face and multiplying by the number of triangular faces.
Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
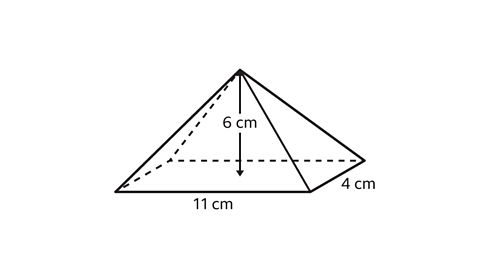
- Calculate the volume of the rectangular-based pyramid.
The volume of the pyramid is 88 cm³.
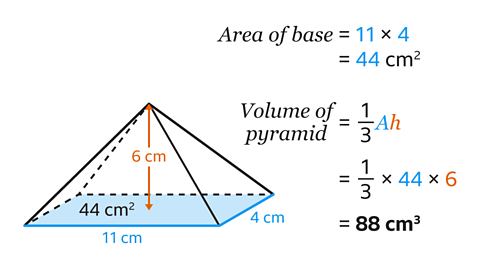
- First, find the area of the rectangular base.
Calculate the area of a rectangle by multiplying the length and width.
The area of the base is 11 × 4 = 44 cm².
The perpendicular height of the pyramid is 6 cm.
- Find the volume of the pyramid by substituting the values of 𝐴 = 44 and ℎ = 6 into the formula and work out the calculation:
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × 44 × 6 = 88
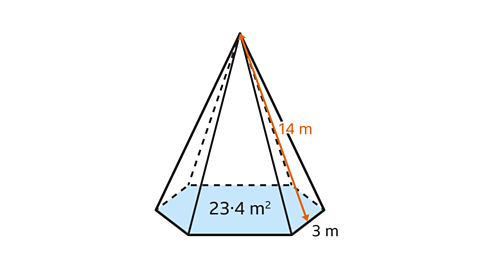
- A pyramid has a regular hexagon for its base with an area 23·4 m².
The height of each triangular face is 14 m.
Work out the total surface area of the pyramid.
The surface area of the pyramid is 149·4 m².
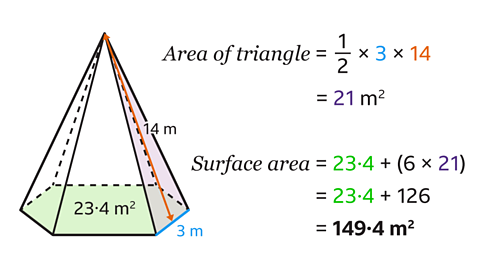
Find the surface area of a pyramid by adding the area of the base to the sum of the areas of the triangular faces. This pyramid has six triangular faces.
- Calculate the area of a triangle using the formula 𝐴 = \(\frac{1}{2}𝑏ℎ\)
The base and the height are at right-angles. The base is 3 m and the height is 14 m.
- Substitute the base and perpendicular height values into the formula.
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 3 × 14 = 21
The area of each triangle is 21 m².
- Find the surface area of the pyramid by adding the area of the hexagonal base and the area of the six triangular faces.
23·4 + ( 6 × 21) = 149·4
- A compound 3D shape is made by combining a cuboid and a pyramid.
Calculate the volume of the shape.
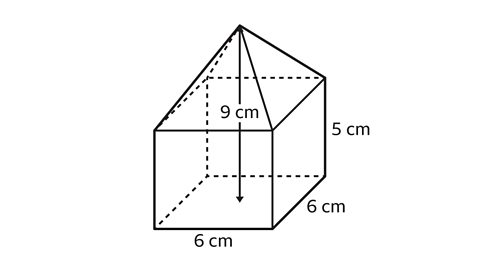
The volume of the compound shape is 228 cm³.
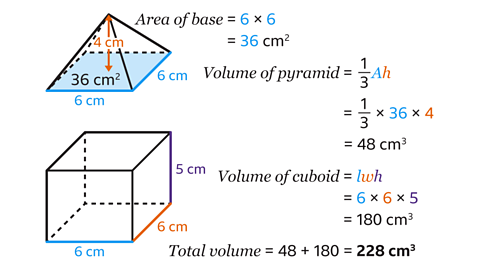
Find the volume of the compound shape by adding the volume of the cuboid to the volume of the pyramid.
- Find the volume of a pyramid by finding the area of the rectangular base.
Do this by multiplying the length and width.
6 × 6 = 36 cm²
- Work out the perpendicular height of the pyramid, which is the difference between the height of the whole shape and the height of the cuboid.
9 – 5 = 4 cm.
The perpendicular height of the pyramid is 4 cm.
- Find the volume of the pyramid by substituting the values of 𝐴 = 36 and ℎ = 4 into the formula 𝑉 = \(\frac{1}{3}𝐴ℎ\) and work out the calculation.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × 36 × 4 = 48
The volume of the pyramid is 48 cm³.
In the cuboid, the length and the width measure 6 cm and the height measures 5 cm.
- Using the formula, find the volume by multiplying the length, width and height.
6 × 6 × 5 = 180
The volume of the cuboid is 180 cm³.
- Find the volume of the compound shape by adding the volume of the cuboid to the volume of the pyramid.
48 + 180 = 228
How to calculate the volume and surface area of a cone
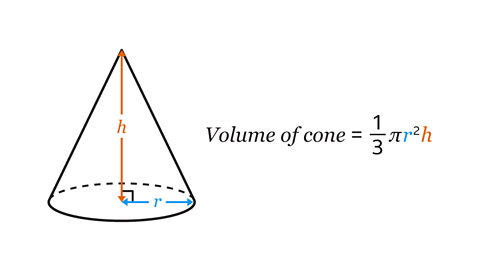
A coneA 3D shape with a flat, circular face at the bottom and a curved surface reaching to a vertex at the top. is a 3D shape with a circular base of radiusThe distance from the centre of the circle to the circumference. Plural of radius is radii. , 𝑟, which tapers up to a single vertex.
Calculate the volume of a cone using the formula:
\(\frac{1}{3}\)π𝑟²ℎ
- 𝑟 is the radius of the circle.
- ℎ is the perpendicular height of the cone.
- 𝑙 is the slanted height of the cone.

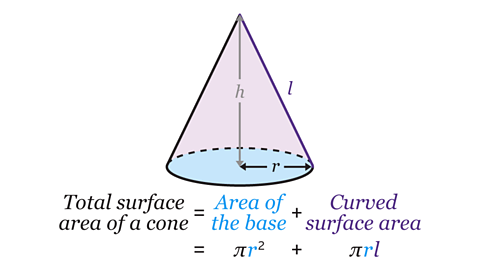
The surface area of a cone is made from a circle and a sector of a circle. The sector creates the curved surface of the cone.
Calculate the total surface area of a cone using the formula:
Surface area = π𝑟² + π𝑟𝑙

Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions

- Work out the volume of the cone.
Give your answer in terms of π.
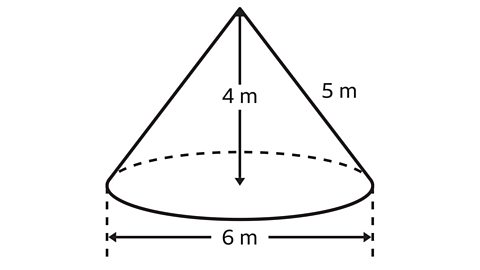
The volume of the cone is 12π m³.
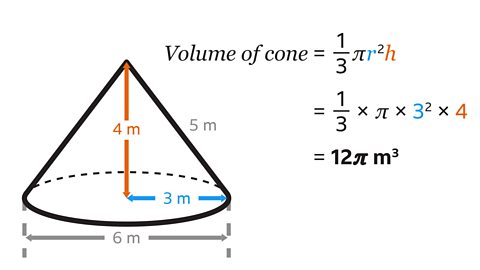
In the cone, the diameter is 6 m and the perpendicular height is 4 m.
- Find the radius by halving the diameter.
6 ÷ 2 = 3
The radius is 3 m.
- Find the volume of the cone by substituting the values of 𝑟 = 3 and ℎ = 4 into the formula 𝑉 = \(\frac{1}{3}π𝑟²ℎ \) and work out the calculation.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × π × 3² × 4 = 12π
- Work out the surface area of the cone.
Give your answer in terms of π.
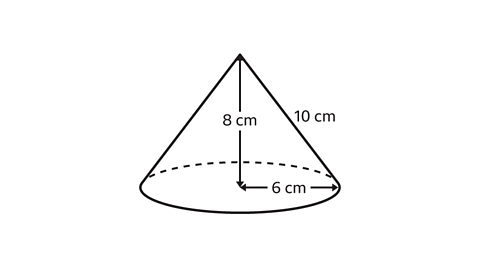
The surface area of the cone is 96π cm².
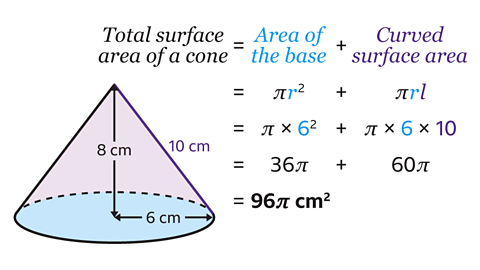
In the cone, the radius is 6 cm and the slant height is 8 cm.
Find the surface area of the cone by substituting the values of 𝑟 = 6 and 𝑙 = 10 into the formula π𝑟² + π𝑟𝑙.
π × 6² + π × 6 × 10 = 36π + 60π = 96π
- A frustum is created by removing the upper part of a cone.
Work out the volume of the frustum.
Give the answer in terms of π.
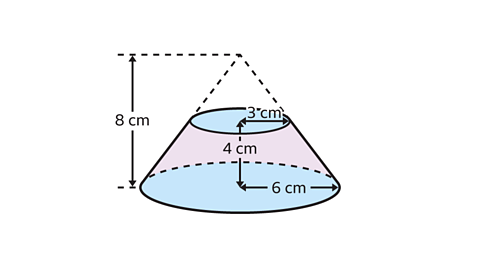
The volume of the frustum is 84π cm³.
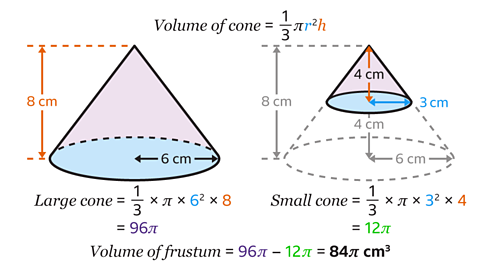
- Find the volume of the frustum by finding the volume of the full, larger cone and subtracting the volume of the smaller cone.
In the larger cone the radius is 6 cm and the perpendicular height is 8 cm.
- Find the volume of the cone by substituting in the values 𝑟 = 6 and ℎ = 8 into the formula.
𝑉 =\(\frac{1}{3}π𝑟²ℎ \)
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × π × 6² × 8 = 96π
In the small cone, the radius is 3 cm and the perpendicular height is 4 cm.
- Substitute the values of 𝑟 = 3 and ℎ = 4 into the formula, which gives
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × π × 3² × 4 = 12π
- Find the volume of the frustum by subtracting the volume of the small cone from the large cone.
96π – 12π = 84π
How to calculate the volume and surface area of a sphere
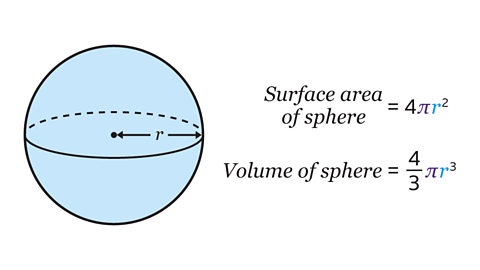
A sphere is a round 3D shape with every point on its surface equidistantEqual distance between two objects. from its centre.
Calculate the volume and surface area of a sphere using the formula.
Volume = \(\frac{4}{3}π𝑟³\)
Surface area = 4π𝑟²
In these formulae, 𝑟 is the radius of the sphere, the distance of every point from its centre.

Follow the worked example below
GCSE exam-style questions
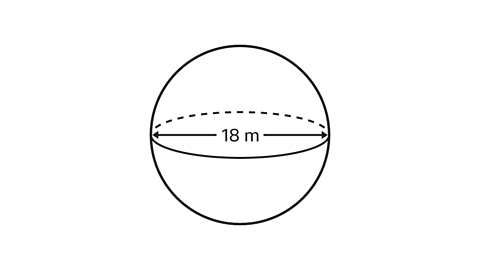
- A sphere has a diameter measuring 18 metres. What is its surface area in terms of π?
The surface area of the sphere is 324π m².
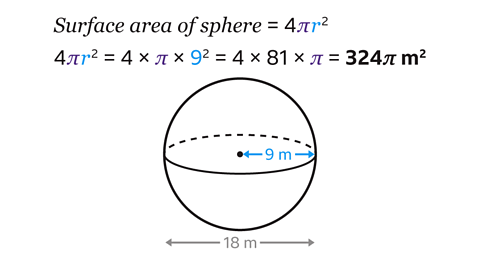
The surface area of a sphere is calculated using the formula
𝑆𝐴 = 4π𝑟²
The diameter of the sphere is 18 m.
Find the radius by halving the diameter.
18 ÷ 2 = 9
The radius is 9 m.
The surface area of the sphere is 4 × π × 9² = 324π m².
- A hemisphere, which is half a sphere, has a radius measuring 4 cm.
Work out the volume of the hemisphere.
Use the approximation π = 3·142
Give an answer to 3 significant figures.
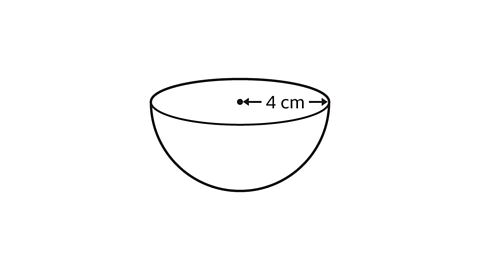
The volume of the hemisphere to 3 significant figures is 134 cm³.
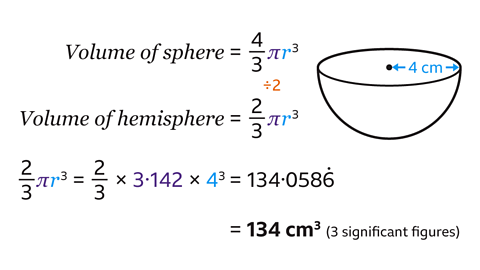
Find the formula for the volume of a hemisphere by halving the formula for the volume of a sphere.
The formula for the volume of a hemisphere is
\( 𝑉 = \frac{2}{3}π𝑟³\)
The radius of the hemisphere is 4 cm.
\( \frac{2}{3}\) × 3·142 × 4³ = \(134·058\dot{6}\)
The volume of the hemisphere to 3 significant figures is 134 cm³.
Check your understanding
Quiz – Pyramids, cones and spheres
Practise what you've learned about pyramids, cones and spheres with this quiz.
Now you've revised pyramids, cones and spheres, why not have a look at polygons?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count14 of 35

- count15 of 35

- count16 of 35
