Key points about congruent and similar shapes

Two shapes are congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical. when both their sides and angles are identical.
Prove two triangles are congruent by showing they satisfy one of four criteria.
Two shapes are similarOne shape is an enlargement of another. The angles in each shape are the same, and the side lengths are in the same proportion. if one is an enlargementA transformation of a shape which results in a shape increasing or decreasing in size. of the other. When given two similar shapes, the scale factorThe ratio between corresponding sides in an enlargement. of the enlargement can be found.
Find missing lengths by using the scale factor.
The relationship between similar shapes may be expressed as a ratio. Make sure you are confident at working with ratios to help understand similarity.
What are the conditions for congruence?
Two shapes are described as congruent if they are identical.
reflectionA transformation of a shape which results in a mirror image of the shape with respect to a line.or rotationA transformation of a shape which results in a turning effect on the shape. change the orientation of a shape, but they are still congruent to the original shape.
Congruence conditions for triangles
Two triangles can be shown to be congruent by matching one of the four conditions.
Side, side, side (SSS) – If two triangles have three pairs of matching length sides, they are congruent.
Side, angle, side (SAS) – If two triangles have corresponding sides and the included angleAn angle between two given sides. that are equal, they are congruent.
Angle, side, angle (ASA) – If two triangles have two corresponding angles and the included sideA side between two given angles. that are equal, they are congruent.
Right-angle, hypotenuse, side (RHS) – If two right-angled triangles have a matching hypotenuseThe longest side in a right-angled triangle. and a matching length side, they are congruent.
The first three conditions are equivalent to the information required to construct a triangle.
Follow the worked examples below
GCSE exam-style questions
- What condition do these two congruent triangles meet?
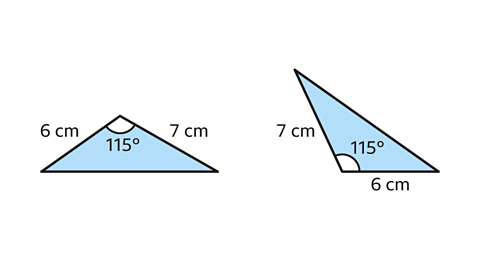
The triangles are congruent by the side, angle, side (SAS) condition.
The triangles have two corresponding sides and the included angle that are equal.
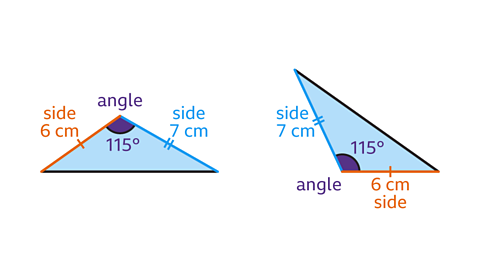
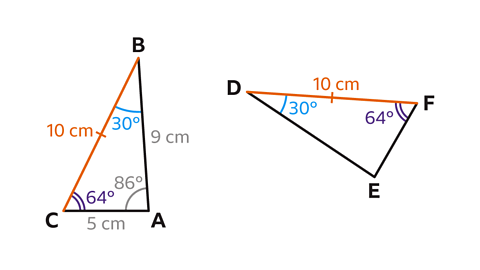
- These two triangles are congruent.
What is the size of angle 𝐹?
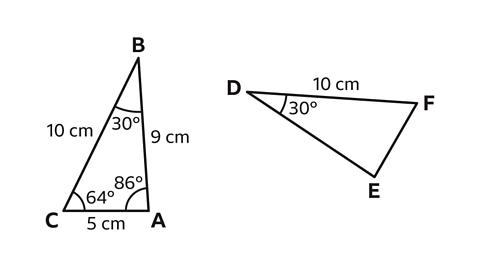
Angle 𝐹 = 64°
The side measuring 10 cm, 𝐵𝐶, corresponds to the side 𝐷𝐹 in the second triangle.
Angle 𝐵, measuring 30°, corresponds to angle 𝐷.
Angle 𝐹, must correspond to angle 𝐶, which measures 64°.
What are similar shapes?
Two shapes are described as similarOne shape is an enlargement of another. The angles in each shape are the same, and the side lengths are in the same proportion. if one is an enlargementA transformation of a shape which results in a shape increasing or decreasing in size. of the other.
The sizes of corresponding angles must be equal between the two shapes.
If one side of the enlarged shape doubles in length, all sides must be double the original size shape.
The increase in size from one shape to another is called a scale factorThe ratio between corresponding sides in an enlargement..

When given two similar shapes, divide the corresponding sides to work out the scale factor.
The relationship between corresponding sides can also be expressed as a ratio.
Similar shapes must also be proportionally the same.
For example, if the length of a rectangle is three times its width, a similar shape must also satisfy this property.
Find missing lengths on similar shapes by calculating and using the scale factor.
Find out more below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Which two rectangles are similar?
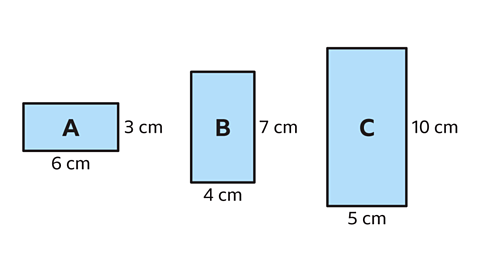
Rectangles 𝐴 and 𝐶 are similar.
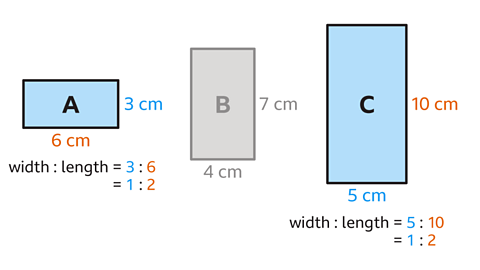
In both rectangles 𝐴 and 𝐶, the length of the rectangle is double the size of the width.
These rectangles are proportionally the same.
The ratio of width to the length simplifies to 1 : 2.
- These boxes are similar.
What is the ratio of the volume of box 𝑋 to box 𝑌?
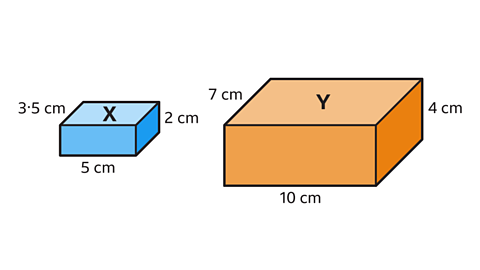
1 : 8
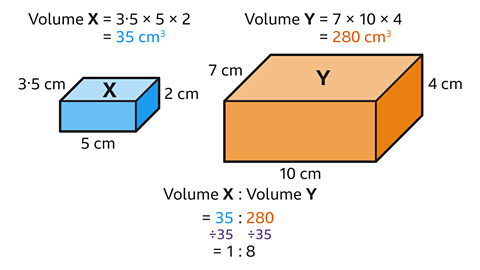
- Find the volume of a cuboid by multiplying the three dimensions.
The volume of box 𝑋 is 3·5 × 5 × 2 = 35 cm³.
The volume of box 𝑌 is 7 × 10 × 4 = 280 cm³.
The ratio of volume 𝑋 to volume 𝑌 is 34 : 280.
- Divide both sides by 35.
The ratio simplifies to 1 : 8.
Using equations to calculate missing sides in similar shapes
Missing lengths on similar shapes can be calculated by forming and solving an equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol =., using the ratio of the sides of each shape.
Use this method when the sides of the shape are expressed using algebra.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- Triangles 𝑃𝑄𝑅 and 𝑆𝑇𝑈 are similar.
Work out the value of 𝑥.
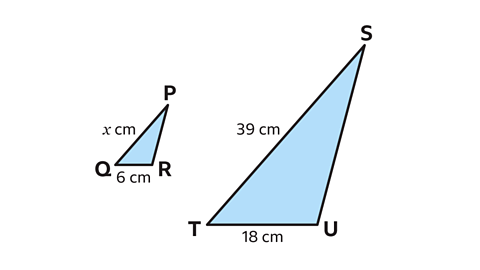
𝑥 = 13 cm
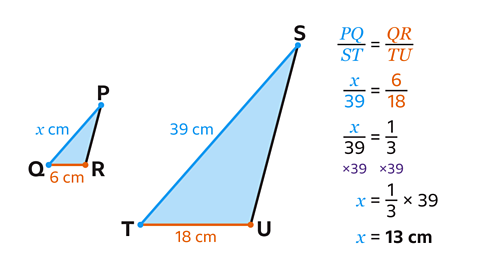
- Find 𝑥 by writing an equation using two pairs of corresponding sides.
For these triangles \(\frac{𝑃𝑄}{𝑆𝑇} \) = \(\frac{𝑄𝑅}{𝑇𝑈} \)
\(\frac{𝑥}{39} \) = \(\frac{6}{18} \)
The fraction \(\frac{6}{18} \) simplifies to \(\frac{1}{3} \) so the equation becomes
\(\frac{𝑥}{39} \) = \(\frac{1}{3} \)
- Multiply both sides by 39 to solve the equation.
𝑥 = \(\frac{1}{3} \) × 39 = 13
- 𝐴𝐵 and 𝐶𝐷 are parallel lines.
𝐴𝐷 and 𝐵𝐶 meet at 𝑃.
Work out the length of 𝐴𝑃.
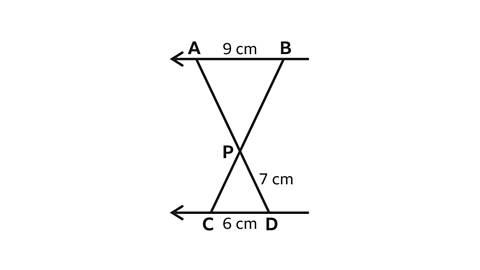
𝐴𝑃 = 10·5 cm
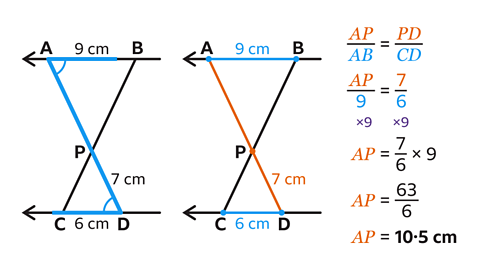
In the triangles, the opposite angles 𝐶𝑃𝐷 and 𝐴𝑃𝐵 are equal.
The parallel lines, 𝐴𝐵 and 𝐶𝐷, means angle 𝐵𝐴𝐷 and angle 𝐶𝐷𝐴 are alternate angles and are equal.
Similarly, angle 𝐴𝐵𝐶 and angle 𝐷𝐶𝐵 are also alternate and are equal. Two triangles are similar is all three angles are the same.
The alternate angles showing implies sides 𝐴𝐵 and 𝐶𝐷 are corresponding, and sides 𝐴𝑃 and 𝑃𝐷 are corresponding.
- Find 𝐴𝑃 by forming an equation using two pairs of corresponding sides.
For these triangles \(\frac{𝐴𝑃}{𝐴𝐵} \) = \(\frac{𝑃𝐷}{𝐶𝐷} \).
\(\frac{𝐴𝑃}{9} \) = \(\frac{7}{6} \)
- Multiply both sides by 9 to solve this equation.
𝐴𝑃 = \(\frac{7}{6} \) × 9 = \(\frac{63}{6} \)
Written as a mixed number, the fraction \(\frac{63}{6} \) is 10 \(\frac{1}{2} \).
Check your understanding
Quiz – Congruent and similar shapes
Practise what you've learned about congruent and similar shapes with this quiz.
Now you've revised congruent and similar shapes, why not look at reflection?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count26 of 35

- count27 of 35
- count29 of 35
