Key points about similarity in 2D and 3D shapes

Two shapes are similarOne shape is an enlargement of another. The angles in each shape are the same, and the side lengths are in the same proportion. if one is an enlargementA transformation of a shape which results in a shape increasing or decreasing in size. of the other. When given two similar shapes, the scale factorThe ratio between corresponding sides in an enlargement. of the enlargement can be found.
For similar 2D and 3D shapes, there is a relationship between the length scale factor and the area, surface area or volume of the enlarged shapes.
Areas increase by a factor equivalent to the length scale factor squared.
Volumes increase by a factor equivalent to the length scale factor cubed.
Make sure you are confident with scale factors and enlargement before working with similarity in higher dimensions.
Watch – Calculating lengths, areas and volumes
Watch this video to find out how to calculate lengths, areas and volumes using scale factors.
Calculating lengths, areas and volumes.
Let's look at the relationship between length, area and volume.
This cube has side lengths of 1 unit.
That means the surface area of each one of its faces is 1 multiplied by 1, which is 1 square unit, and its volume is 1 multiplied by 1 multiplied by 1, which is 1 cubic unit.
What about this cube which has side lengths of 2 units?
This time, the area of each face is 2 multiplied by 2, which is 4 square units, and the volume is 2 multiplied by 2 multiplied by 2, which is 8 cubic units.
Notice that the side length has increased by a factor of 2, the area has increased by a factor of 4, or 2 squared, and the volume has increased by a factor of 8, or 2 cubed.
If instead you increase the side length by a factor of 3, this means the area will increase by a factor of 9, or 3 squared, and the volume will increase by a factor of 27, or 3 cubed.
In fact, if each side length of a 3D shape is increased by a scale factor of 𝑥, then the area of each face would increase by a scale factor of 𝑥 squared, and the volume of the shape would increase by a scale factor of 𝑥 cubed.
For example, shapes A and B are similar.
Question part a: find the missing lengths 𝑦 and 𝑧.
‘Similar’ means that although the two shapes are not the same size, their side lengths are in the same ratio.
In other words, shape B is the same shape as A, but a certain number of times bigger.
To find 𝑦 and 𝑧, you need to find a pair of corresponding lengths which you can use to calculate the length scale factor.
Corresponding sides in similar shapes have lengths that are in proportion to one another, and the angles at the vertices between the sides are the same in both shapes.
The longest side in shape A is 1 centimetre and the longest side in shape B is 4 centimetres, so the length scale factor is 4 divided by 1, which equals 4.
So, the side lengths in shape B are all 4 times bigger than the corresponding side lengths in shape A.
In other words, to get from lengths in shape A to lengths in shape B, you multiply by 4, and to get from lengths in shape B to lengths in shape A, you divide by 4.
Now use the length scale factor to find the missing lengths 𝑦 and 𝑧.
Starting with 𝑦, the corresponding side in shape B is 2 centimetres, so 𝑦 equals 2 divided by 4, which is 0.5 centimetres.
Likewise, for 𝑧, the corresponding side in shape A is 0.7 centimetres, so 𝑧 equals 0.7 multiplied by 4, which is 2.8 centimetres.
Now, shape A has a surface area of 1.9 centimetres squared and a volume of 0.12 centimetres cubed.
Question part b: find the surface area and volume of shape B.
Since the length scale factor is 4, the area scale factor is 4 squared, or 16, and the volume scale factor is 4 cubed, or 64.
This means the surface area of shape B is 1.9 multiplied by 16, which equals 30.4 centimetres squared, and the volume is 0.12 multiplied by 64, which equals 7.68 centimetres cubed.
How to calculate area scale factors and ratios
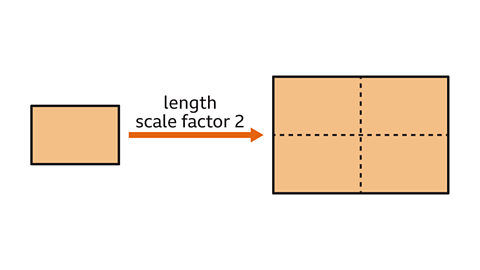
When given two similar shapes, a length scale factor can be worked out by dividing the corresponding sides.
Calculate the area scale factor by squaring the length scale factor.
Scale factors can also be represented using a ratioA part-to-part comparison..
If the length scale factor for two similar shapes, 𝐴 and 𝐵, is given by the ratio 𝑎 : 𝑏, then the area scale factor is
𝑎² : 𝑏².

Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
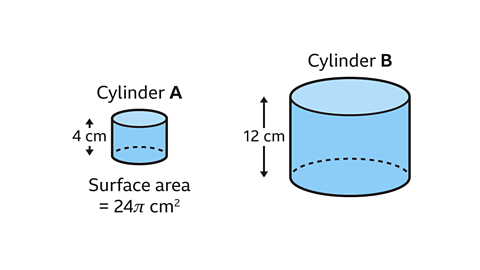
- Cylinders 𝐴 and 𝐵 are similar. Cylinder 𝐴 has a height of 4 cm and surface area of 24π cm².
The height of cylinder 𝐵 is 12 cm.
Calculate the surface area of cylinder 𝐵.
216π cm²
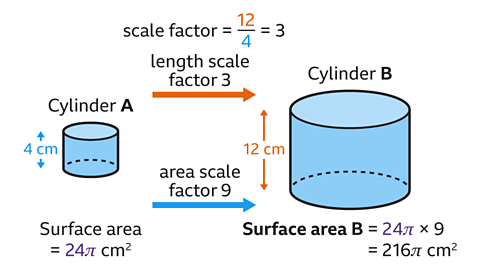
- Find the length scale factor, or length ratio, by comparing the corresponding heights of cylinders 𝐴 and 𝐵.
12 ÷ 4 = 3
The length scale factor equals 3.
The ratio of length 𝐴 to length 𝐵 simplifies to 1 : 3.
- Find the area scale factor, or area ratio, by squaring the length scale factor or ratio.
Area scale factor = 3² = 9
The ratio for the area of cylinder 𝐴 to the area of cylinder 𝐵 is 1 : 9.
- Find the surface area of cylinder 𝐵 by multiplying the surface area of cylinder 𝐴 by the area scale factor.
24π × 9 = 216π
- Shapes 𝑋 and 𝑌 are similar.
Shape 𝑋 has an area of 25 cm².
Shape 𝑌 has an area of 81 cm².
What is the length ratio 𝑥 : 𝑦?
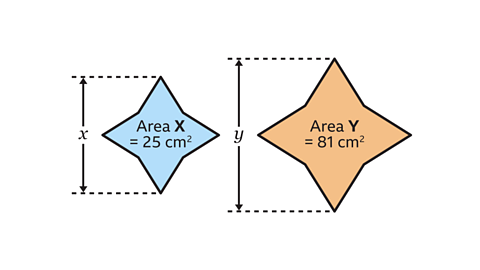
The length ratio is 5 : 9.
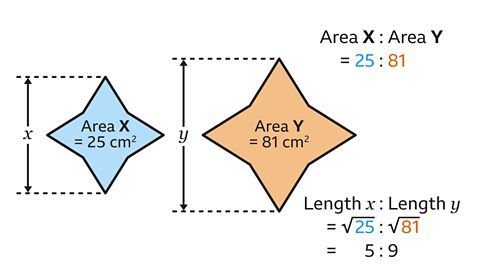
The area ratio of shape 𝑋 to 𝑌 is 25 : 81.
The area ratio is found by squaring the length ratio.
Find the length ratio by performing the inverse operation and square rooting the area ratio.
√25 = 5
√81 = 9
The length ratio is 5 : 9.
Calculating volume scale factors and ratios
When given two similar shapes, a length scale factor can be worked out by dividing corresponding sides.
Find the volume scale factor by cubing the length scale factor.
If the length scale factor for two similar shapes, 𝐴 and 𝐵, is given by the ratio
𝑎 : 𝑏, then the volume 𝑎³ : 𝑏³.
The density of two similar 3D shapes is equal. The mass of a similar shape can be found by multiplying one mass by the volume scale factor.
Find out more below, along with a worked example
GCSE exam-style questions
- Cylinders 𝐴 and 𝐵 are similar.
Cylinder 𝐴 has a height of 4 cm and a volume of 32 cm³.
The height of cylinder 𝐵 is 16 cm.
Calculate the volume of cylinder 𝐵.
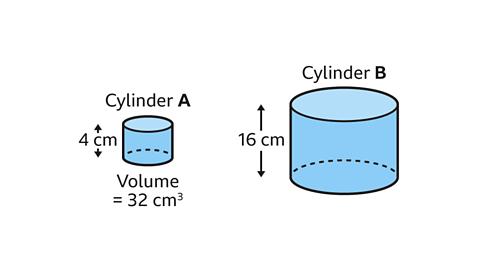
2048 cm³.
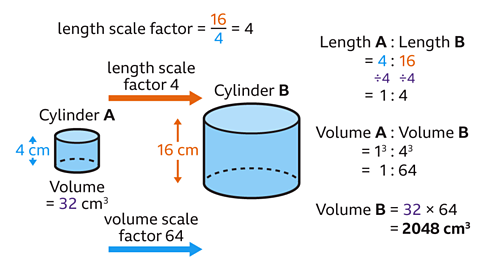
- Find the length scale factor, or length ratio, by comparing the corresponding heights of cylinders 𝐴 and 𝐵.
16 ÷ 4 = 4
The length scale factor equals 4.
The ratio of length 𝐴 to length 𝐵 simplifies to 1 : 4.
- Find the volume scale factor, or volume ratio, by cubing the length scale factor or ratio.
Volume scale factor = 4³ = 64
The ratio for the volume of cylinder 𝐴 to the volume of cylinder 𝐵 is 1 : 64.
- Multiply the volume of cylinder 𝐴 by the volume scale factor to find the volume of 𝐵.
32 × 64 = 2048
- Pyramids 𝑋 and 𝑌 are similar.
Volume of 𝑋 : Volume of 𝑌 = 125 : 8.
Work out the surface area of 𝑋 : surface area of 𝑌.
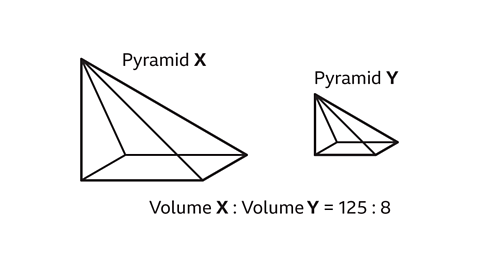
The surface area of 𝑋 : surface area of 𝑌 is 25 : 4.
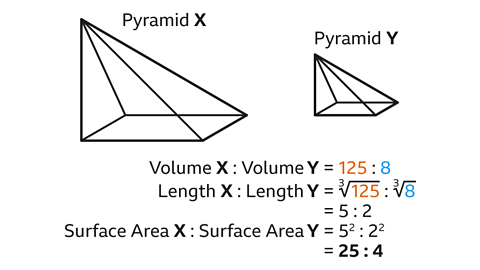
The volume ratio of pyramid 𝑋 to 𝑌 is 125 : 8. The volume ratio is found by cubing the length ratio.
- Find the length ratio by performing the inverse operation and cube rooting the volume ratio.
∛125 = 5
∛8 = 2
The length ratio is 5 : 2.
- Find the area ratio by squaring the length ratio.
5² = 25
2² = 4
The surface area ratio is 25 : 4.
Check your understanding
Quiz – Similarity in 2D and 3D shapes
Practise what you've learned about similarity in 2D and 3D shapes with this quiz.
Now you've revised similarity in 2D and 3D shapes, why not look at enlargement?
More on Geometry and measure
Find out more by working through a topic
- count27 of 35
- count29 of 35

- count30 of 35
