NARRATION:Algorithm, you’ve probably heard it been thrown about. Algorithm this, algorithm that. But what does it mean?
Actually, it's really quite simple and not as scary as it sounds… and breathe.
An algorithm is just a set of instructions to make something happen. Let me explain.
Say you wanted to make a cake - you couldn't just throw in any ingredients whenever you wanted. Otherwise, you'd end up with a giant messy looking pile of mush.
That's why you have to follow a recipe with a step by step method. This step by step method is just like an algorithm. If we follow it word for word in the correct order then, voila. You get the perfect cake.
This is what an algorithm is. It is a set of specific and detailed instructions that lead to an outcome, and it is the first step in writing a program to control a computer. Each of the steps needs to be followed just like the recipe, otherwise we end up with a scrambled mess, just like our cake.
Let's look at this - an electronic door lock. The idea is that we want the door only to unlock if someone uses a card with the correct door key code stored on it. So, what instructions will we need to give to the door lock device to solve this problem? An algorithm will help us decide on the steps we need and the order we need to put them in. Let's use a flow chart diagram to help us organise our instructions.
At the start, we want the door to be locked. When someone uses a card key in the door lock, we want the computer inside the lock to check the card key and see if it has the correct code. If the answer is yes then the light should flash green and the door will unlock. If the answer is no then the light should flash red and the door should stay locked.
By writing our instructions for the door lock down as an algorithm, we can make sure our instructions are correct and in the right order before we actually write the computer program to use in the door lock device.
People use algorithms everywhere you can think of when it comes to technology. Every click, every interaction, every button press, every swipe… an algorithm was used to help create the programs that make everything work.
Algorithms can even help to write computer programs that make decisions about what you see on social media, or what internet search results go to the top of the list.
What problem are you going to solve with an algorithm?
So you see they aren’t so scary after all… they are a piece of cake!
Video summary
This short film for primary schools outlines how algorithms are sets of instructions to make something happen, before explaining further using a recipe analogy.
The film outlines how algorithms are the starting points for computer programs that solve problems.
It then looks at the example of using an electronic card key to open a door, using a flow diagram to organise the instructions and steps needed to make sure the door only unlocks when the correct card key is used.
The film finishes with more examples of how algorithms are used in computer-based tools and systems like social media feeds and search engine rankings.
This short film is from the BBC Teach series, Cracking Computing.
Teacher Notes
A good way to introduce the idea of algorithms is to focus on familiar lists of instructions that organise everyday life - for example, taking the register, getting ready for a school lesson, packing up at the end of the day - and turning them into flow charts.
The next step is to explore problems or dilemmas that include a question, and create a list of instructions or statements that solve the problem. Again, flow charts can be used to clarify the steps and sequence lists for pupils.
It is important that, before pupils start to write a program to solve a problem or achieve a specific outcome, they have a clear idea of what they want the program to achieve, in the form of an algorithm, either as a flow chart or list of instructions.For example, when programming a computer game character the algorithm might look like this:
- When left arrow clicked character moves left 10 steps
- When right arrow clicked character moves right 10 steps
- When space bar clicked character jumps up
Other subjects
English: Understanding algorithms fits well with work on instruction writing, or explanation texts that explain a process or sequence of events. Similar vocabulary is used: for example, firstly, then, when, next, finally, etc.
Maths: In Maths the word algorithm is used to describe the series of steps carried out to complete a calculation or solve a problem. For example, to solve 3 x 7 we need to carry out the following steps:
- Start with zero
- Add 7
- Add 7 to the new total
- Add 7 to the new total
This short film is suitable for teaching:
- KS2 computing curriculum in England
- Technologies curriculum area at 2nd Level in Scotland
- KS2 digital competence framework in Wales
- KS2 using ICT cross-curricular skill in Northern Ireland
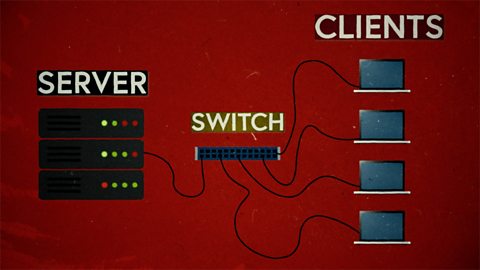
Computer networks. video
This short film explains computer networks. It looks at different types of computer network and the elements that make up a basic network including clients, servers, switches and hubs.
Creating with computing. video
This short film explores the many creative computing tools we have access to, with a focus on how they are used to create new creative content and media.

Debugging. video
This short film uses computer games to explain debugging, which is the process of finding and correcting errors in computer programs.

Decomposition. video
This short film explains how decomposition involves breaking one big problem down into smaller, more manageable problems that can be tackled step by step.

Input and output. video
This short film gives a brief history of input and output methods with examples, and brings us up to date with examples of familiar input and output devices that we use every day.

Logical reasoning. video
This short film outlines logical reasoning as ‘sensible thinking’ when following rules, and explains how a problem with a computer program can be solved using logical reasoning.

Repetition. video
This short film for primary schools explains how repetition within computing allows a command to be repeated to make a computer program more efficient.

Search technologies. video
This short film gives a brief history of the development of the internet and the invention of the world wide web by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, and explains the role of a search engine.

Selection. video
This short film covers the use of selection in simple computer programs, and shows how this idea of yes/no questions can allow computers to respond to external conditions and select different paths.

Sequencing. video
This short film covers the concept of sequencing, or making sure things are in the right order, and explores what might happen if things are done in the wrong order, or sequence.

Variables. video
This short film explores how computers use variables to store things that change, like names, numbers and scores.

Working with data. video
This short film explores how data is collected using digital devices in response to questions, and how it is organised into tables, records and fields on a computer system.
