Who dey in charge for Iran?

Wia dis foto come from, EPA
Di death of Iran President Ebrahim Raisi for helicopter crash, don open road for fresh presidential elections for di kontri.
But di cleric sudden death no go really affect politics for di Islamic Republic, especially as e be say for di kontri, power las las rest wit di supreme leader.
Wetin go happun for Iran now?
Iran constitution dey straightforward, if di president no fit carry out im duties sake of sickness, death, or impeachment and removal by parliament.
Following Oga Raisi death, Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei don appoint First Vice-President Mohammad Mokhber to run di affairs of di kontri.
Na Oga Mokhber go organise di election for di new president – im go work wit di heads of parliament and di judiciary – and dem go hold election within 50 days.
For di last election, dem bin ban all serious challengers of di president from running, e clear di way for Oga Raisi to enta office wit di lowest number of voters.
Majority bin boycott wetin dem see as a fixed election.
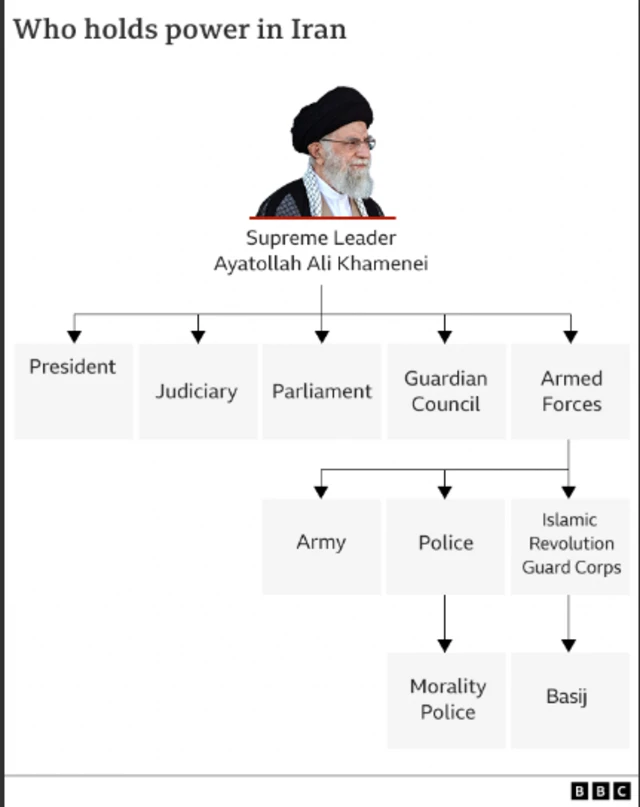
Which powers di supreme leader get?
Di most powerful figure for Iran na Ayatollah Khamenei, na im don be di kontri supreme leader since 1989.
End of Di one wey oda users dey read well well
Im be di head of state and commander-in-chief.
Na im also get authority ova di national police and di morality police.
Ayatollah Khamenei dey control di Islamic Revolution Guard Corps (IRGC), wey dey im charge of internal security, and im volunteer wing the Basij Resistance Force - dem dey use to end disagreement for Iran.
Which powers di president get?
Di president na di top elected official and second in rank to di supreme leader.
Im dey responsible for di day-to-day running of di goment and na im get significant influence ova domestic policy and foreign affairs.
However, im powers dey limited - especially wen e get to do wit security matters.
Na di president interior ministry dey run di national police force. However, im commander na di supreme leader appoint am and im dey answerable directly to am.
Na di same tin wit di commander of di Islamic Revolution Guard Corps and di Basij.
Parliament fit also check di president powers, na dem dey introduce new laws.
In turn, di Guardian Council – wey conatin close allies of di supreme leader - job na to approve new laws and dem fit veto dem.
Dem don challenge state power bifor for Iran?
For 2022, di Islamic Republic bin shake wit ogbonge protests sake of di death of 22-year old Mahsa Amini, wey di morality police bin detain for allegedly violating Iran strict dress code.
Human rights groups say hundreds bin die for di kasala and dem detain thousands.
Di protests bin spread ova time from discontent ova di dress code to anger with di regime as a whole.
Wetin be di morality police?
Di morality police - or Guidance Patrols - na part of di national police.
Na for 2005 dem establish di force to uphold Islamic morals and laws on "proper" dressing wey dem introduce afta di Islamic Revolution of 1979.
Tori be say about 7,000 male and female officers get power to issue warnings, impose fines or arrest suspects.
Weeks bifor di unrest for di summer of 2022, President Raisi bin give order to tighten Iran "hijab and chastity law" wey force women to behave and dress modestly.
Dem introduce surveillance cameras to help spot women wey no wear veil and dem introduce mandatory prison for pipo wey oppose di hijab rules on social media.
Who be di Revolution Guards?
Di IRGC na Iran main organisation for maintaining internal security, and now na major military, political and economic force for di kontri, wit more dan 150,000 personnel.
Wit dia own ground forces, navy and air force, na dem dey oversee Iran strategic weapons.
Dem get overseas arm wey dem dey call di Quds Force wey secretly dey provide money, weapons, technology and training to allies throughout di Middle East.
Na dem dey also control di Basij Resistance Force.
Wetin be di Basij?
Di Basij Resistance Force, wey many bin know as di Organisation for di Mobilisation of di Oppressed, na for1979 dem form am as a volunteer paramilitary organisation.
Dem get branches for every province and city for Iran, and within many of di kontri official institutions.
Di male and female members, dey referred to as "Basijis", dem be loyalists to di revolution and dem dey under di orders of di IRGC.
Many believe say about 100,000 dey perform internal security duties.
Dem dey heavily involved in suppressing anti-government protests since di 2009 presidential election.











