Electrical components
There are a huge number of electrical components Something you solder into a circuit, eg a resistor or a diode. available to buy from specialist suppliers. Items such as bulbs, buzzerAn output device that produces a buzzing sound when current flows through it. and sensorA device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal to be read and interpreted. are all readily available, and prices decrease as more units of the product are bought. Items can be matched to ensure they are the right voltageThe potential difference across a cell, electrical supply or electrical component. It is measured in volts (V). and current rating The amount of current that can pass through a resistor. for the product being produced.

resistorAn electrical component that restricts the flow of electrical charge. Fixed-value resistors do not change their resistance, but with variable resistors it is possible to vary the resistance. limit the flow of current around a circuit and can prevent damage to components.
Resistors used in electrical circuits have a tolerance of how much power they allow into a circuit - the smaller that tolerance is, the less likely the circuit will be overloaded and damaged, but the more expensive the resistor will be.
Resistors are available in series - the series refers to the resistors tolerance. The most common two are called E12 and E24. Rather than have resistors available for every number possible, resistors are only available in what is called a ‘preferred value’. These values are indicated by the number created by the first two coloured bars on the resistor. The E12 and E24 series include resistors with the following preferred values:
| E12 | E24 |
| 10 | 10 |
| 11 | |
| 12 | 12 |
| 13 | |
| 15 | 15 |
| 16 | |
| 18 | 18 |
| 20 | |
| 22 | 22 |
| 24 | |
| 27 | 27 |
| 30 | |
| 33 | 33 |
| 36 | |
| 39 | 39 |
| 43 | |
| 47 | |
| 51 | |
| 56 | |
| 62 | |
| 68 | |
| 75 | |
| 82 | |
| 91 |
| E12 | 10 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 10 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 11 |
| E12 | 12 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 12 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 13 |
| E12 | 15 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 15 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 16 |
| E12 | 18 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 18 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 20 |
| E12 | 22 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 22 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 24 |
| E12 | 27 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 27 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 30 |
| E12 | 33 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 33 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 36 |
| E12 | 39 |
|---|---|
| E24 | 39 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 43 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 47 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 51 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 56 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 62 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 68 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 75 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 82 |
| E12 | |
|---|---|
| E24 | 91 |
Zeros from the third band of the resistor (the multiplier) can be added behind these numbers, eg 100 becomes 1,000 (× 10), 330 becomes 33,000 (× 100), etc.
The amount of toleranceThe range of accuracy in relation to the size of a resistor. a resistor has is shown with the colour of the fourth stripe down and is usually silver or gold. The E12 series resistors have a silver fourth band and the E24 series resistors have a gold fourth band.
E12 resistors have a tolerance of 10 per cent, meaning that the value of the resistor could be smaller or larger by 10 per cent, eg a 300 Ω E12 resistor could range from 270 Ω to 330 Ω.
E24 resistors have a tolerance of 5 per cent, meaning that the value of the resistor could be smaller or larger by 5 per cent, eg a 300 Ω E24 resistor could range from 285 Ω to 315 Ω.
Example
An E12 resistor has a tolerance of 10% and the value of the resistor is coded as 390 ohms (Ω). What is the range that the resistance could lie within?
Calculate the percentage difference:
(390 ÷ 100) × 10 = 39
390 - 39 = 351 ohms (Ω) would be the bottom of the range
390 + 39 = 429 ohms (Ω) would be the top of the range
Question
An E24 resistor has a tolerance of 5% and the value of the resistor is coded as 200 ohms (Ω). What is the range that the resistance could lie within?
(200 ÷ 100) × 5 = 10
200 - 10 = 190 ohms (Ω) would be the bottom of the range
200 + 10 = 210 ohms (Ω) would be the top of the range
Integrated circuits
dual in line (DIL) Legs of a chip or chip holder that are set in pairs. IC packages are integrated circuit (IC)A chip, used in many areas of electronic engineering including a computer CPU. that are protected inside a plastic housingAn exterior case or enclosure., with two rows of metal legs (which is why it’s called ‘dual’). The IC is usually placed inside a chip holder that is soldered to a circuit board A copper sheet used to attach electrical components. - each leg is numbered to identify their function. As they are small and lightweight they are often used in computers, cameras, microwaves and TVs.

microcontrollerA computer chip used instead of a CPU that contains a processor, memory and inputs/outputs. are controllable ICs. The most common type of microcontroller is a programmable interface controller (PIC)A common type of programmable microcontroller. that can be constantly reprogrammedTo program a computer again with different information. to complete a variety of tasks, such as controlling timing or temperature in a microwave or running specific wash cycles in a washing machine. PICs are available in a variety of memory sizes and with varying numbers of pins - each pin can attach to an input or output, so as pins increase so does the number of devices that can be attached. The more memory or pins available, the greater the cost of the PIC. They are used in most modern electrical products, such as TVs and stereos.

Mechanical components
Mechanical components are available to buy in a variety of shapes and sizes. Chains, used to turn sprocket The toothed wheel a chain attaches to. in items such as pulleys and bicycle wheels, are sold by width and pitch (distance between the pins). They are available in standard lengths that can be adjusted by adding and removing link The piece that joins chain together. .

gearA wheel with teeth that can change the speed of a mechanism. are available in many different sizes and with a varying number of teethProjecting part of a component such as a gear.. Gears have different tooth shapes that lock together in different ways and are used in cars, bicycles and clocks. The size of the gear controls the speed at which it turns. Stock gears are sold in diameter measurements or number of teeth.
There are two main types of spring A fixed coil that is usually made of metal and can store energy when compressed.:
- compression springs - hard to compress
- extension springs - hard to extend
They can be bought with a variety of rates of ‘springiness’ and can be ordered by the length of spring, number of coil A word used to describe the shape of a spring or rotation of wire round a cylindrical object. or distance they can be stretched or compressed. They are usually made from hardened steel as it has the properties most needed to maintain a spring’s shape. Other materials such as plastic or copper can also be used.

Circuit boards
Circuit boards are used in most electronic systems as they ensure reliable connections between componentA part that when put together makes a product.. Components must be connected accurately for the circuit to work properly and different types of circuit boards are available for different tasks. Circuit boards can be designed by using a computer aided design (CAD)The process of creating a 2D or 3D design using computer software. program to create a circuit that can be input into a computer numerical controlled (CNC) routerA method by a computer to execute a pre-programmed sequence. Machines move via numerical values along X, Y and Z axes. and accurately etched Creating designs on metal or glass by corroding the surface with acid. into the surface.
Stripboard is a copper board and is often used for prototyping as it is the simplest type of board to create circuits on without the use of expensive machinery. Stripboard circuits are not printed as they have pre-laid tracks on which to lay the circuit.
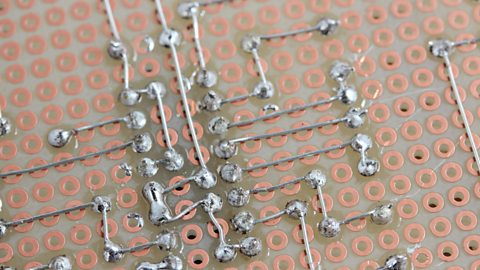
While stripboard is made of copper, it is different to copper-clad board, which is used particularly for small, simple electronic circuits. It is a type of printed circuit board where the connections are either cut in with a CNC router or etched onto the surface using a photoresist pen. This is then placed in an etching bath, leaving the pen drawn areas in place. This is a cheap way of creating a circuit without the use of expensive materials, although it isn’t very accurate and can be time-consuming.
Photoresist, printed circuit board (PCB) prints a photosensitive Reacts to UV rays. layer above the copper from a computer aided design (CAD), which is then exposed to ultraviolet lightElectromagnetic radiation with a greater frequency than visible light but less than X-rays. Humans cannot see it but it can damage eyes and skin in high doses.. developer Chemical used to develop an image. solution is then used to rinse away the exposed parts, leaving only the circuit ready for use. This is an accurate way to create complex and easy-to-use circuit boards with only the copper areas, where the components will be attached, left exposed.
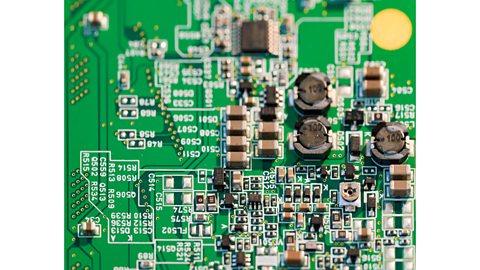
These circuit boards are made from glass-reinforced plastic (GRP)A composite material (resin and glass mixed together) commonly known as fibreglass. , this material is light in weight and strong. GRP is an insulator to electricity and resists corrosion well. One side of the circuit board is often printed with labels, so that each component can be placed in the correct place. PCBs can be produced in large numbers, quickly and accurately, but the machinery to produce them is expensive, so it can be more cost-effective to buy them in from a specialist factory.