A short animation exploring the movement of tectonic plates, the cause of earthquakes and volcanoes.
Every thirty seconds, there's an earthquake somewhere in the world. Although, don't worry. Most are minor.
The Earth's surface is made up of a number of plates that are almost always moving.
Most earthquakes happen where these plates meet.
Some of these plates slide past each other, causing friction to build up.
While some move towards each other, causing a build up of pressure.
When these forces - friction or pressure - are released, they produce a violent jolt that shakes the land: an earthquake.
Although most are minor, a major earthquake can cause a lot of destruction.
So in parts of the world where earthquakes are common, people take precautions.
For example, they don't make buildings very tall, so they won't fall down easily.
Sometimes, they use rubber foundations to absorb some of the force coming from the earthquake's tremors.
Plastic is used in windows, rather than glass.
Schools in these countries practise what to do if an earthquake happens, like sheltering under a desk to protect yourself from falling objects.
The Earth's plates will keep moving and earthquakes will continue to occur.
All people living in countries affected by earthquakes can do, is be prepared to manage their destructive power.
Video summary
A short animation for KS2 pupils on the movement of Earth's tectonic plates - the cause of earthquakes and volcanoes - and what can be done to lessen their impact.
It explores the causes of earthquakes and illustrates the plate boundaries of the Earth, how these are constantly moving, and how earthquakes occur when these boundaries more past, into or away from each other.
It also explores possible precautions to minimise the damage caused by earthquakes and, in this way, illustrates to pupils the link between physical and human geography.
Teacher Notes
This short film introduces pupils to earthquakes and plate tectonics and plate boundaries. It explores the impact of earthquakes and the precautions that can be taken to minimise the damage they cause.
It can be used to introduce a unit of study on earthquakes or to review the key concepts behind them.
You can use the film to prompt discussion and an investigation about the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes and human responses to them.
Points for discussion:
- What are the causes of earthquakes?
- What are the three types of plate boundary?
- How might the plates move at each type of plate boundary?
- How do people living in earthquake-prone regions respond to the threat of earthquakes?
- What precautions can be taken to lessen the impact of earthquakes?
- Are there any positives to living in an earthquake-prone region?
Suggested activities:
After watching the film, you could work with pupils to further explore the structure of the Earth.
Pupils could investigate which plates are moving fastest and which parts of the world are the most earthquake prone.
You could also explore volcanoes with pupils and investigate the link between volcanoes and earthquakes.
You could initiate a more in-depth study of tectonic plates and the hazards of living in regions where they occur.
Suitable for teaching geography at KS1 and KS2 in England, Progression Step 2 and 3 in Wales, Early and 1st and 2nd level in Scotland and Foundation and KS1 in Northern Ireland.
Weather, climate and climate change. video
Exploring the difference between weather and climate, climate zones around the world and climate change.

Maps. video
Maps, mapping and navigation - including map keys, symbols, compass points and co-ordinates.
Cities, towns and villages. video
Exploring settlements to identify the key geographical features of villages, towns and cities, including their similarities and differences.

Rivers. video
Exploring the journey of water to the sea, including source, stream, river, meander, river mouth and estuary.

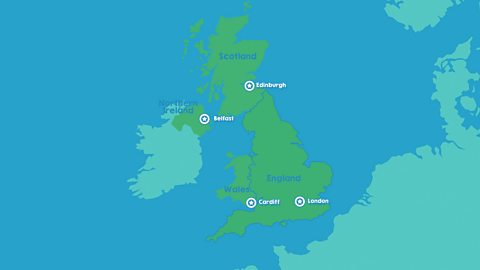
The United Kingdom. video
Identifying the four countries of the UK - England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland - and their capital cities: London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast.
The world. video
Exploring the regions of the Earth: the continents, oceans, Equator, Northern and Southern Hemispheres and the North and South Poles.

The seasons. video
Spring, summer, autumn, winter... Identifying the four seasons of the United Kingdom's temperate climate.

The water cycle. video
An short animation for KS2 pupils explaining the water cycle, including evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
