This film introduces pupils to maps and how to use them - including map keys, symbols, compass points and co-ordinates.
When we go somewhere new, it’s not easy to find our way around.
CARA – Let’s find the beach!
RIO – It's this way!
ARJUN – No, it's this way!
That’s why we use maps.
A map is a picture of a place, usually drawn from above.
We have big giant maps … and small maps with lots of detail.
Maps can be printed on paper and folded, they can be three dimensional like this globe or even on a phone.
The closer you look at a map, the more detail you see. Those green areas are national parks.
If you get even closer, you’ll be able to see the roads.
To help us find the important places - like the train station - we use symbols.
There are all sorts of symbols used on maps, like an envelope for a post office, a shopping trolley for a market and even a paw print for a zoo!
A good map will show you everything a place has to offer.
CARA - And then the beach should be…
RIO – This is not the beach.
ARJUN – I don’t understand.
CARA – We had it upside down!
To help make sure you don’t get the map upside down most maps have one of these…
It shows you which way is north, south, east and west on the map.
Maps also use co-ordinates to help you find what you’re looking for.
Co-ordinates work by drawing lines over the map and dividing it into sections which are numbered or lettered.
This line is called the X axis and this is where you find the first number or letter from a co-ordinate.
This line is the Y axis and this is where you find the second number or letter from a co-ordinate.
Think of it as crossing the hallway and then climbing the stairs. You need to cross the hallway first before you climb up the stairs.
CARA – Where do we go now.
ARJUN - I would quite like to go to the waterfall.
RIO – The waterfall is here, which is B7.
CARA – Alright then, lets go that way!
Video summary
This film introduces pupils to maps, mapping and navigation. It examines how we use maps, including compass points, keys, symbols and co-ordinates.
It has been developed in a child-centred way to allow pupils to visualise themselves using maps in their everyday lives.
Download/print a transcript of the video.
NB: The video refers to the lines on a map as the 'x axis' and 'y axis'. The more technical term for these lines are 'northings' and 'eastings'. The northings are the horizontal lines - they increase in value as you travel north. The eastings are the vertical lines - they increase in value as you travel east.
Teacher Notes
Download/print the Teacher Notes for this episode (pdf).
Teacher Notes prepared in partnership with the Geographical Association.
Central or big idea
- Maps are used to show what features can be found in a place and how to navigate between them.
Think, work and apply like a geographer
- Observe
- Interpret
- Explore
- Scale
Questions to explore
- What do maps show?
- Are all maps the same?
- When might we need to use maps?
- How should we hold a map?
- What do the symbols represent?
Key learning outcomes
- Know that maps can be different sizes and at different scales.
- Know how to use symbols, keys, grid references and compass rose to read a map.
Suitable for teaching geography at KS1 and KS2 in England and Wales, Early and 1st and 2nd level in Scotland and Foundation and KS1 in Northern Ireland.
Key geographical vocabulary and definitions
- Symbol
- Grid reference (co-ordinate)
- Key
- Navigate
Suggested learning opportunities
- Use an OS to follow, and then create, a virtual treasure hunt across the local area.
- Use collection of symbol cards and their meanings for matching and sorting activities.
- Create a set of instructions on how to use a map.
- Explore the school grounds and create symbols for key features. These could be added to a base map, together with a key.
NB: The video refers to the lines on a map as the ‘x axis’ and ‘y axis’ to create ‘co-ordinates’. The more technical geographical terms for these lines are ‘northings’ and ‘eastings’ to find a grid reference. The northings are the horizontal lines - they increase in value as you travel north. The eastings are the vertical lines - they increase in value as you travel east.
Ideas for going further and links
- The video introduces maps and pupils could develop and practice using maps to plan routes, locate features or create their own maps of familiar places incorporating symbols, a key, a compass rose and an approximate scale.
KS1/KS2 Primary Geography: The United Kingdom
KS2 Geography: UK settlements and navigating using maps
Weather, climate and climate change. video
Exploring the difference between weather and climate, climate zones around the world and climate change.

Cities, towns and villages. video
Exploring settlements to identify the key geographical features of villages, towns and cities, including their similarities and differences.

Rivers. video
Exploring the journey of water to the sea, including source, stream, river, meander, river mouth and estuary.

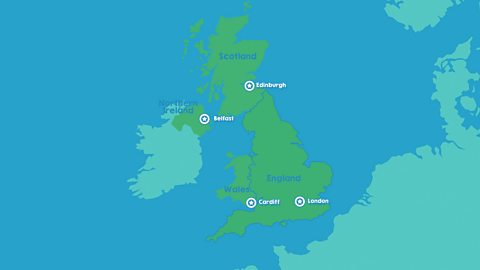
The United Kingdom. video
Identifying the four countries of the UK - England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland - and their capital cities: London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast.
The world. video
Exploring the regions of the Earth: the continents, oceans, Equator, Northern and Southern Hemispheres and the North and South Poles.

The seasons. video
Spring, summer, autumn, winter... Identifying the four seasons of the United Kingdom's temperate climate.

Earthquakes. video
An animation for KS2 pupils on tectonic plate movement and steps to lessen the impact of earthquakes.
The water cycle. video
An short animation for KS2 pupils explaining the water cycle, including evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
