Explores key features of water's journey to the sea: source, stream, river, meander, river mouth and estuary.
Rivers are home to a whole host of different types of animal and plant life.
But where do rivers come from?
RIO – Up there?
Many rivers start high up in hills or mountains.
This is where its ‘source’ is found.
AVA – So what are we looking for anyway?
RIO – The source of the river.
ARJUN – Well we can’t see much around here!
RIO – Come on…
There are a few different types of river source. It can be a lake, a bog, rainfall or a spring.
AVA - I think I found it!
A spring is where water is released from under the ground but the same thing happens whatever the source.
Water from the source trickles downhill forming a small stream, which joins another stream to make a bigger stream.
This happens all the way down the hill until you get…
RIO, ARJUN & AVA: A river!
The flow of the water slows as a river twists and bends, meandering its way through the countryside.
But where does it go?
RIO, AVA & ARJUN – The sea?
Yes! Rivers lead to the sea or a lake, and the place where it enters the sea or lake is called the river mouth
Rivers that flow into the sea form an estuary where fresh water from the river mixes with the salty water from the sea.
It’s not just animals that choose to live near rivers. People love to live near rivers too.
RIO – Nice house!
AVA – Yeah, I'd like to live here.
ARJUN – Not me!
AVA – Why not?
ARJUN – Floods!
Yeah, floods can be a problem for people living near rivers.
Building river defences, or diverting the path of the river to a safe area, can help to minimise the risk.
ARJUN – Okay, well maybe it wouldn’t be so bad then.
Video summary
This film explores the journey of a river from its source to the sea. It covers the following: water source, stream, river, meander, river mouth and estuary.
Teacher Notes
This short film shows pupils how a river changes as it moves from source to mouth.
It can be used to describe what happens at each stage of the river journey and to explore how the river changes over the course of that journey.
Pupils could discuss where they have seen examples of features shown in the film.
They could also discuss why they think the river changes as it moves from source to mouth.
Points for discussion:
- What is a river?
- What are the key parts of a river?
- What is a meander?
- How do humans benefit from rivers?
- What are the potential negative things about living near a river?*
Suggested activities:
After watching this short film, pupils could develop a report to explore the key features of a river and how it changes from source to mouth.
They could use base maps of the United Kingdom and the world to plot major rivers and investigate how humans have used rivers to their benefit over time.
Teachers could plan fieldwork activities to investigate a local river and how it works. Pupils could collect data and plot their results to show how the river operates, e.g. what the speed and size of the river is, and then deduce how this affects wildlife in the locality.
Pupils could investigate how human activity has damaged rivers over time and also what is being done today to conserve rivers.
Pupils could discuss changes they could make to their lives to help conserve rivers.
Suitable for teaching geography at KS1 and KS2 in England, Progression Step 2 and 3 in Wales, Early and 1st and 2nd level in Scotland and Foundation and KS1 in Northern Ireland.
Weather, climate and climate change. video
Exploring the difference between weather and climate, climate zones around the world and climate change.

Maps. video
Maps, mapping and navigation - including map keys, symbols, compass points and co-ordinates.
Cities, towns and villages. video
Exploring settlements to identify the key geographical features of villages, towns and cities, including their similarities and differences.

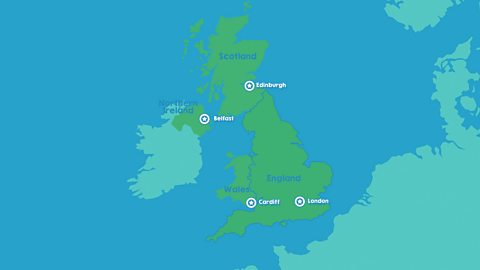
The United Kingdom. video
Identifying the four countries of the UK - England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland - and their capital cities: London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast.
The world. video
Exploring the regions of the Earth: the continents, oceans, Equator, Northern and Southern Hemispheres and the North and South Poles.

The seasons. video
Spring, summer, autumn, winter... Identifying the four seasons of the United Kingdom's temperate climate.

Earthquakes. video
An animation for KS2 pupils on tectonic plate movement and steps to lessen the impact of earthquakes.
The water cycle. video
An short animation for KS2 pupils explaining the water cycle, including evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
