Key points
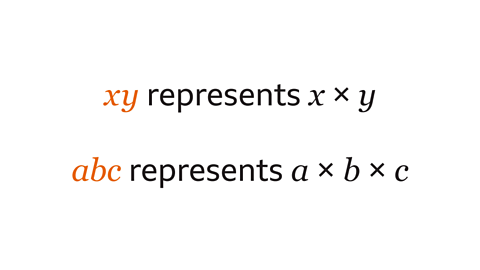
Algebra is a part of maths that uses letters and symbols in the place of numbers. Each letter or symbol is a variableA quantity that can take on a range of values. and can represent a range of values.
algebraic notationA series or system of written symbols used to represent numbers, amounts or elements in mathematics. is used to present information concisely.
An algebraic statement may be an expressionA mathematical sentence expressed either numerically or symbolically made up of one or more terms., an equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol =, a formulaA fact, rule, or principle that is expressed in words or in mathematical symbols. Plural: formulae., or an identity ≡An equation that is true no matter what values are chosen. The identity symbol ≡ links expressions that are identities..
Algebra uses arithmetic operations (+, –, ×, ÷) to simplify expressions, solve equations and rearrange formulae.
When writing or interpreting algebraic expressions, it is important to understand that addition and multiplication are commutativeAn operation is commutative if the order does not matter. Multiplication and addition are commutative, eg 4 × 3 = 3 × 4 and 4 + 3 = 3 + 4 and that subtraction and division are not.
To help your understanding of algebra, it may be useful to review negative number arithmetic.
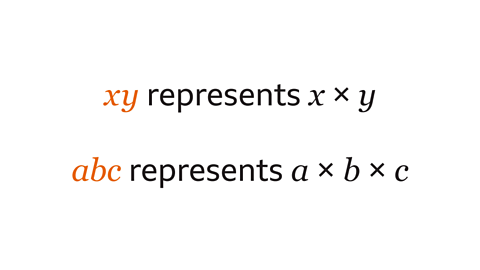
Understanding algebraic notation
Algebraic notation presents information in a concise way. For example, when variables are multiplied they are written next to each other in alphabetical order. Eg, 𝒙𝒚 represents 𝒙 × 𝒚
An algebraic sentence is known as an expression. Within an expression, each part is known as a termAn element within an algebraic sentence. Elements (terms) are separated by + or - signs. .
A term is one element in an algebraic sentence. It may be a constantA number or quantity that does not vary. A constant speed is a steady speed. Eg, the speed of light is constant. The speed of a car is not constant, it varies., a variableAn unknown value, usually represented by a letter like 𝒙 or 𝒚, or a combination of a coefficientA number or symbol multiplied with a variable or an unknown quantity in an algebraic term. Eg, 5 is the coefficient of 5𝒏 and one or more variables.
In algebra, division is written in fractional form. The dividend is the numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used. Eg, for 1⁄3, the numerator is 1 and the divisor is the denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts. Eg, for 1⁄3, the denominator is 3.
Examples
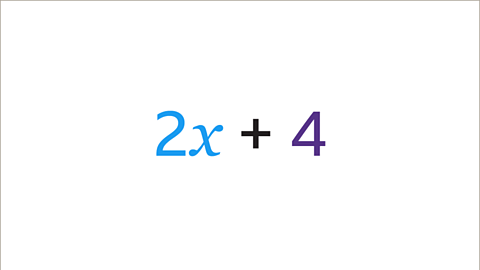
Image caption, 2𝒙 + 4 is an algebraic statement known as an expression. Each element in an expression is called a term. This expression has two terms (2𝒙 and 4).
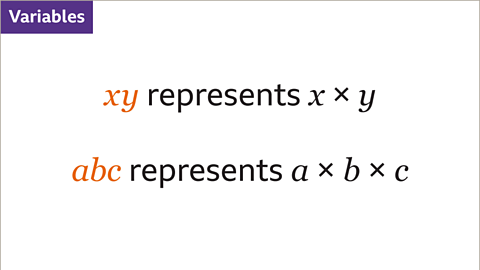
Image caption, A variable is a letter representing a quantity that can take on any value. When variables are multiplied, they are written next to each other in alphabetical order. The term 𝒙𝒚 represents 𝒙 multiplied by 𝒚. The term 𝒂𝒃𝒄 represents 𝒂 multiplied by 𝒃 multiplied by 𝒄

Image caption, Repeated multiplication by the same variable is written using index notation. The index of a number is positioned above and to the right of a number and says how many times to use the number in a multiplication. For example, 𝒑⁵ means 𝒑 x 𝒑 x 𝒑 x 𝒑 x 𝒑

Image caption, Coefficients are written at the front of a term. The coefficient of 5𝒏 is 5. The coefficient of 2𝒂𝒃𝒄 is 2. The coefficient shows how many of that variable or combination of variables there are. It can be the result of repeated addition or a single multiplication. If there is no coefficient given, the number is one.
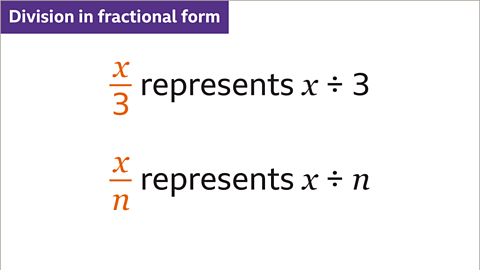
Image caption, In algebra, division is written in fractional form. The dividend (𝒙) is the numerator and the divisor (3 and 𝒏) is the denominator.
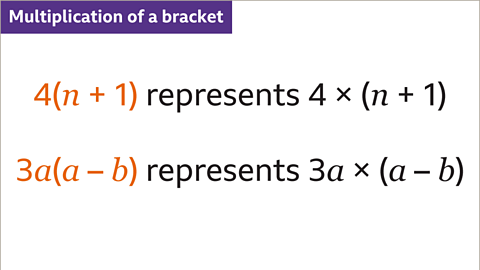
Image caption, A term in front of the bracket means that the expression in the bracket is being multiplied by that term, whether a constant, variable or combination.

Image caption, When coefficients are not integers, they are usually written in fractional form rather than as decimals.
1 of 7
Question
Write this expression using the correct algebraic notation:
𝒃 x 𝒃 x 𝒄 x 2
Repeated multiplication by the same variable is written using index notation. 𝒃 × 𝒃 is 𝒃²
When variables are multiplied, they are written next to each other. The 𝒃² and 𝒄 are written next to each other, 𝒃²𝒄
The coefficient (2) is written at the front of the term and gives the number of this combination of variables. The 2 is written first, 2𝒃²𝒄
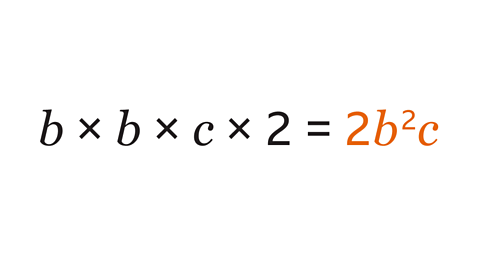
Video
Watch the video to hear Kim, a textiles designer, talk about how algebra plays a part in her work.
Bobby:The word algebra might make you think of equations and formulas that you only hear about in a maths lesson.
Bobby: So Kim, tell me about your work in fashion.
Kim: I’m a textiles designer for my own company and we make silk scarves that feature endangered animals.
Bobby: That sounds really cool. So, how would you work out how much you can sell your products for?
Kim: There’s a lot of things I need to consider. There’s the materials, the size of the scarf, the manufacture and also the finishing of the scarf.
Bobby: So, you listed some variables to me. Your sales price, that’s an unknown variable. Your cost of production is a known variable. And the other factors, they are known variables. So, we can set up an algebraic equation for that.
Kim: Exactly, and when I work seasonally, I know how much I need to make and when I need to make, but I don’t know the cost. That’s because the price of materials could change from season to season or year to year.
Bobby: Ah, even again, there’s more algebra there because your cost of production, that’s an unknown variable and then your known variables are your time frame and how much to produce - Algebra!
Kim: Exactly.
Writing and interpreting algebraic expressions
To interpret an expressionA mathematical sentence expressed either numerically or symbolically made up of one or more terms., each variableA quantity that can take on a range of values. is defined as representing a number of items.
The correct operation must be used in an expression.
- An amount is added on to show that the result is more. Addition is used to total values.
- An amount is subtracted to show that the result is less. Subtraction is also used to find a difference.
- An amount is multiplied to show that the result is that amount times larger. Multiplication is also used for repeated addition.
- An amount in a divisor is used to show that the result is that amount times smaller. This can include finding a fractional amount. Eg, to find a half, divide by 2
Examples
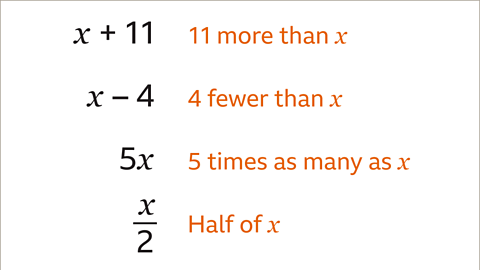
Image caption, Algebraic expressions can show different amounts.
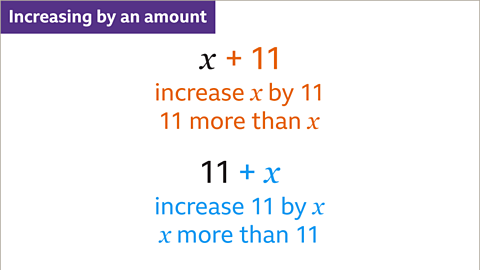
Image caption, An amount is added to show that the result is more. To increase an amount (𝒙) by 11, 11 is added on to 𝒙. 𝒙 + 11 is eleven more than 𝒙. To increase 11 by an amount (𝒙), 𝒙 is added to 11. 11 + 𝒙 means 𝒙 more than 11. 11 + 𝒙 and 𝒙 + 11 give the same total.
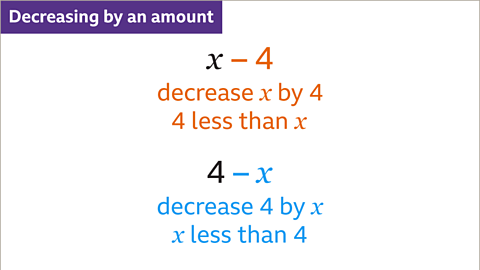
Image caption, An amount is subtracted to show that the result is less. To decrease an amount (𝒙) by 4, 4 is subtracted from 𝒙. 𝒙 – 4 is four less than 𝒙. To decrease 4 by an amount (𝒙), 𝒙 is subtracted from 4. 4 – 𝒙 is 𝒙 less than 4. 𝒙 – 4 and 4 – 𝒙 are not the same.
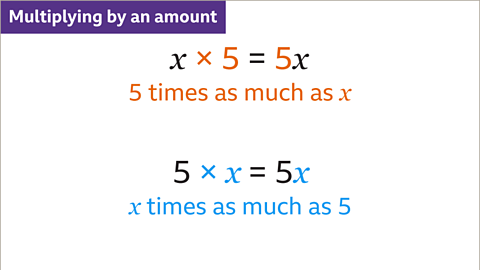
Image caption, An amount is multiplied to show that the result is that amount times larger. Five times as many as 𝒙 is 5 multiplied by 𝒙, written as 5𝒙. 𝒙 times as many as 5 is 𝒙 multiplied by 5, written as 5𝒙. When variables and constants are multiplied, the coefficient (number) is written to the left of the variable. The expressions give the same total.
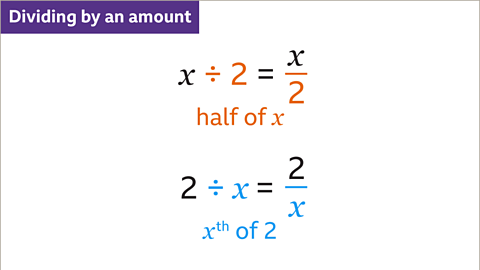
Image caption, To find a half, divide by 2. To find a third, divide by 3. To find an 𝒙th divide by 𝒙. 𝒙 divided by 2 is written as a fraction. The dividend (𝒙) is the numerator, the divisor (2) is the denominator. 2 divided by 𝒙 is written as a fraction. The dividend (2) is the numerator, the divisor (𝒙) is the denominator.
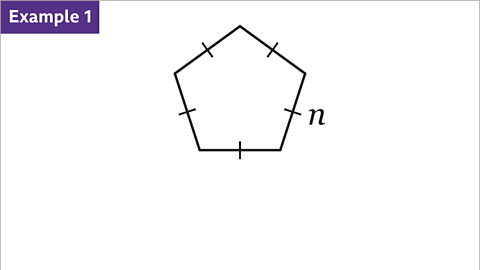
Image caption, This is a regular pentagon. Each side is the same length (𝒏). An expression can be written for the perimeter of the regular pentagon.
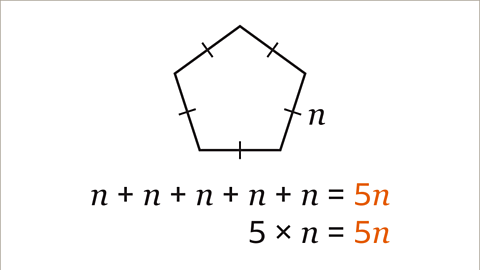
Image caption, The perimeter of the pentagon is the total distance around the shape. The perimeter is worked out either by adding all the sides (𝒏 + 𝒏 + 𝒏 + 𝒏 + 𝒏) or by multiplying the length of one side by 5, (5 × 𝒏). The resulting expression is 5𝒏
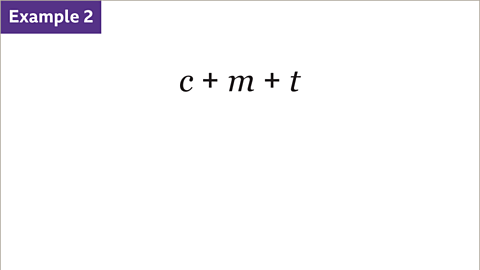
Image caption, A vegetable box contains carrots, mushrooms and tomatoes. 𝒄 is the number of carrots. 𝒎 is the number of mushrooms. 𝒕 is the number of tomatoes. Find the meaning of the expression 𝒄 + 𝒎 + 𝒕
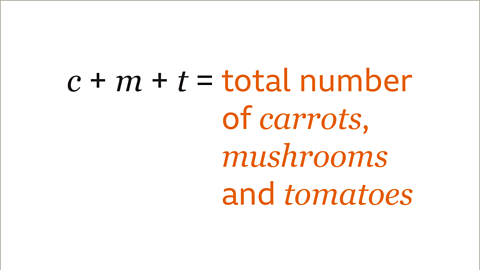
Image caption, The variables have been added to give a total. This expression is the total number of carrots, mushrooms and tomatoes in the vegetable box.
1 of 9
Match the statement to the correct expression
Practise using algebraic expressions by matching the correct statement to each algebraic expression.
Recognising different algebraic statements
There are four types of algebraic statements:
- An expression is a mathematical statement with no equals symbol.
- An equation links two expressions with an equals symbol.
- A formula is a statement linking two or more variables.
- An identity means that the left-hand side of the equation is identically equal to the right-hand side, for all values of the variables. The identity symbol links expressions that are identities.
Examples

Image caption, An algebraic statement can be an expression, an equation, a formula or an identity.
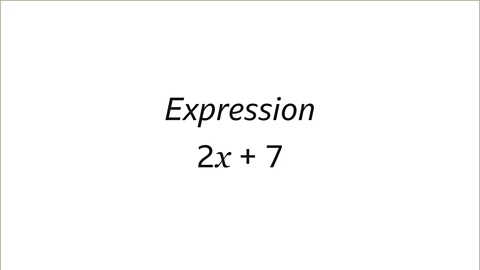
Image caption, An expression is a mathematical statement with no equals symbol. It is made up of individual terms that are being added or subtracted.
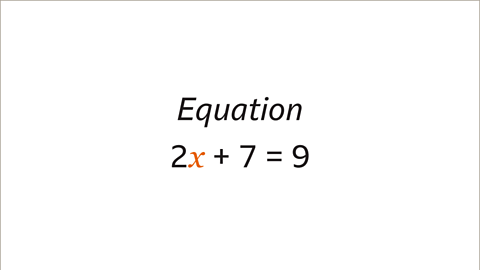
Image caption, An equation links two expressions with an equals symbol. In this equation, the variable is unknown.
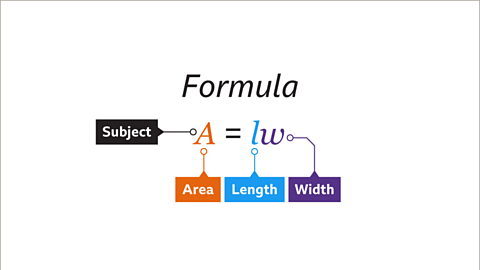
Image caption, A formula is a statement linking two or more variables. Values are substituted into a formula to find the value of the subject. The formula for the area (𝑨) of a rectangle is 𝑨 = 𝒍𝒘. The subject of the formula is 𝑨. The area is worked out by multiplying the length (𝒍) by the width (𝒘).
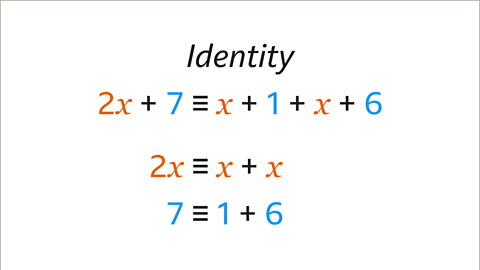
Image caption, An identity is an equation which is always true, no matter what values are substituted. The expressions on each side of the identity symbol (≡) are equivalent. 2𝒙 + 7 is identical to 𝒙 + 1 + 𝒙 + 6 because 𝒙 + 𝒙 is 2𝒙 and 1 + 6 is 7
1 of 5
Practise algebraic notation
Quiz
Practise recognising, writing and interpreting algebraic notation with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you.
Real-life maths

Knowing algebraic notation is necessary when working with certain types of computer software.
Software engineers rely on a solid understanding of algebraic notation and processing. They create codes that make computer interfaces more user-friendly, which other software developers then make use of to enhance games or Computer-Aided Design (CAD) packages.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Expressions and formulae
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 8
- count3 of 8
- count5 of 8