Key points about equations of direct and inverse proportion

- Proportion is a relationship between two variableA quantity that can take on a range of values, often represented by a letter, eg 𝑛, 𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧, 𝑡 … etc. based on multiplication and division.
- The two types of proportion are direct proportion and inverse proportion.
- If two variables, 𝑥 and 𝑦, are direct proportionA relationship between values where one value increases at the same rate as another, eg as one value doubles, the other value doubles. to each other, they can be written as an equation in the form 𝑦 = 𝑘𝑥.
- If two variables, 𝑥 and 𝑦, are inverse proportionA relationship between values where one value increases and the other decreases at the same rate, eg as one value doubles, the other value halves. to each other, they can be written as an equation in the form 𝑦 = \(\frac{𝑘}{𝑥}\) .
- Higher only – Proportion equations can be constructed for more complex relationships such as 𝑦 = \(\frac{𝑘}{𝑥² }\).
Make sure you know how to solve equations with fractions to be confident with this topic.
Video – Direct and inverse proportion
Watch this video to learn about equations of direct and inverse proportion, with worked examples.
Direct and inverse proportion.
In this graph, 𝑥 and 𝑦 are directly proportional.
This means that when 𝑥 doubles, 𝑦 also doubles, and when 𝑥 triples, so does 𝑦.
In fact, for all coordinates on this line, you could multiply or divide 𝑥 by any scale factor, and 𝑦 would also be multiplied or divided by the same scale factor.
As well as this, when 𝑥 is 0, 𝑦 also equals 0.
All of this means that the graph linking two directly proportional variables is always a straight line through the origin, which is the point at which both 𝑥 and 𝑦 are equal to 0.
This has the equation 𝑦 equals 𝑘𝑥, where 𝑘 is the constant of proportionality, or the gradient.
In this next graph, 𝑥 and 𝑦 are inversely proportional, or in other words, 𝑦 is proportional to 1 over 𝑥.
This means that, for example, when 𝑥 doubles, 𝑦 halves, and when 𝑥 triples, 𝑦 is divided by 3.
So, multiplying 𝑥 by any scale factor will divide 𝑦 by the same scale factor, and dividing 𝑥 by any scale factor will multiply 𝑦 by the same scale factor.
With inverse proportion, the equation of the graph is 𝑦 equals 𝑘 over 𝑥.
You can use these general equations for direct and inverse proportion in real life situations.
For example, say the cost of wool is directly proportional to the length of wool purchased, and that 10 metres of wool cost £2.
Algebraically, this could be written as 𝐶 equals 𝑘𝑙, where 𝐶 is the cost in pounds, 𝑙 is the length in meters, and 𝑘 is the constant of proportionality.
Then, to work out the constant of proportionality, substitute 𝑙 equals 10 and 𝐶 equals 2 into the equation.
Doing this tells you that 2 equals 𝑘 times 10. So, 𝑘 equals 2 divided by 10 which is 0·2.
Then, putting 𝑘 equals 0·2 back into the equation 𝐶 equals 𝑘𝑙, tells you that 𝐶 equals 0·2𝑙.
You can use this equation to find the values of missing costs or lengths of wool if you know one of these variables.
For example, to find the cost of 5 metres of wool, you can use the equation 𝐶 equals 0·2 multiplied by 5, which equals £1, and the cost of 23 metres of wool is 0·2 multiplied by 23, which equals £4.60.
How about this question?
The number of weeks, 𝑤, it takes to build a house is inversely proportional to the number of builders, 𝑏, where 5 builders take 25 weeks to build a house.
Since the variables are inversely proportional, firstly, write 𝑤 equals 𝑘 over 𝑏, where 𝑤 is the number of weeks and 𝑏 is the number of builders.
Then, substituting 𝑤 equals 25 and 𝑏 equals 5 into the equation tells you that 25 equals 𝑘 over 5.
Multiplying both sides by 5 gives 25 times 5 equals 𝑘, so 𝑘 equals 125.
You can now use the equation 𝑤 equals 125 over 𝑏 to work out the number of weeks it takes to build a house with 10 builders, or how many builders are needed to build a house in 5 weeks, for example.
Check your understanding
Proportional relationships
Example 1 - Direct proportion
When two variableA quantity that can take on a range of values, often represented by a letter, eg 𝑛, 𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧, 𝑡 … etc. are directly proportional to each other, they increase at the same rate. If the first is doubled, the other is also doubled.
In direct proportion, one variable is always the same multipleWhen one set of values is a multiple of another, it can be multiplied by a specific number to give the other set. of the other.
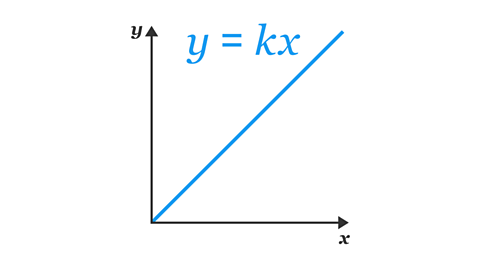
- The equation 𝑦 = 𝑘𝑥 represents two variables (𝑥 and 𝑦) that are in direct proportion.
- 𝑘 is a constantA number that does not vary. Constants are different to variables such as 𝑥 and 𝑦 that can take many values. number.
- Graphs that show direct proportion are straight lines that go through the point (0, 0).
Example 2 - Inverse proportion
When two variables are inversely proportional to each other, as one increases, the other decreases at the same rate. So, if one variable is doubled, the other is halved.
The relationship is reciprocalWritten as 1 divided by the number, eg the reciprocal of 2 is ½ and the reciprocal of ½ is 2. The reciprocal is also called the multiplicative inverse. Any non-zero number multiplied by its reciprocal is equal to one..
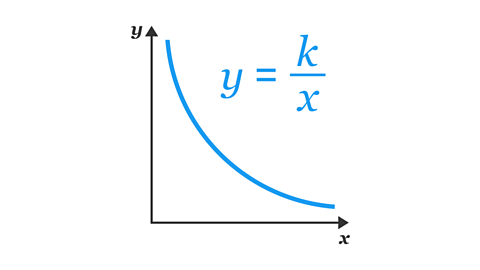
- The equation 𝑦 = \(\frac{𝑘}{𝑥}\) represents two variables (𝑥 and 𝑦) that are in inverse proportion.
- 𝑘 is a constant number.
- Graphs that show inverse proportion are curved and do not cross the 𝑥 or 𝑦 axis.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- 𝑥 is directly proportional to 𝑦.
𝑥 = 3, 𝑦 = 12.
Work out the value of 𝑦 when 𝑥 = 8.
𝑦 = 32
- If 𝑥 is directly proportional to 𝑦, then one is always the same multiple of the other.
- 3 has been multiplied by 4 to give 12.
- 𝑥 is always multiplied by 4 to give 𝑦.
If 𝑥 = 8, then 𝑦 = 8 × 4 = 32.
- 𝑥 is inversely proportional to 𝑦.
Complete the table by working out the missing value.
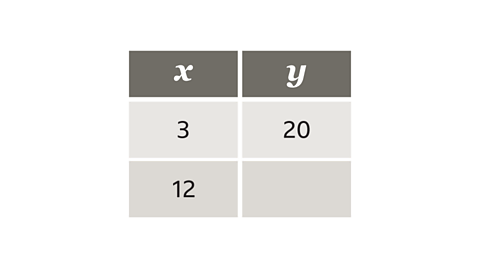
The missing value is 5.

If 𝑥 is inversely proportional to 𝑦, as 𝑥 increases, 𝑦 decreases at the same rate.
To get from 3 to 12, 𝑥 has been multiplied by 4.
Therefore 𝑦 needs to be divided by 4:
20 ÷ 4 = 5
- The graph shows the conversion between litres and gallons.
Use the graph to estimate 90 litres in gallons.
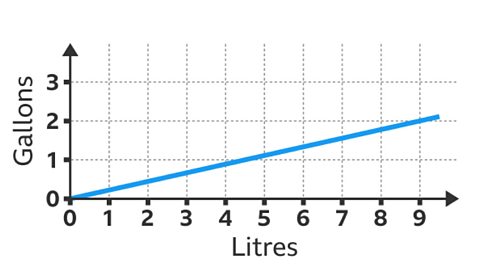
20 gallons
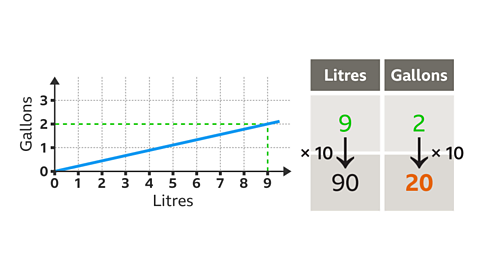
The graph does not reach 90 litres, so read off the conversion for 9 litres:
- 9 litres is roughly 2 gallons.
The number of litres needs to be multiplied by 10 to make 90.
- The two variables (gallons and litres) are directly proportional to each other, so multiply the number of gallons by 10 as well.
90 litres is roughly 2 × 10 = 20 gallons.
Quiz - Equations of direct and inverse proportion
Practise what you've learned about equations of direct and inverse proportion with this quiz.
Rates of change - interactive activity
This interactive activity will help you understand how relationships are presented on a graph.
The height of the fluid in a container is affected by the shape of the container and the amount of time a liquid is poured into it at a constant rate.
Higher – Algebraic proportion
When two variables are directly proportional to each other, one is a multiple of the other.
When two variables are inversely proportional to each other, they have a reciprocalWritten as 1 divided by the number, eg the reciprocal of 2 is ½ and the reciprocal of ½ is 2. The reciprocal is also called the multiplicative inverse. Any non-zero number multiplied by its reciprocal is equal to one. relationship.
The symbol ∝ means ‘is proportional to’.
Direct proportion
This table shows how different direct proportion relationships are shown, and their proportion equations for a constant, 𝑘.
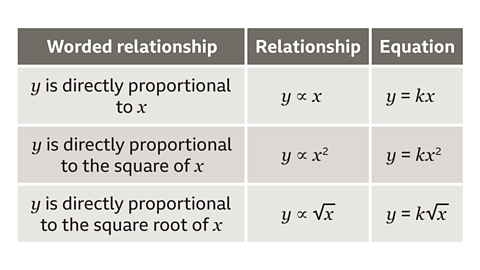
If a pair of values for 𝑥 and 𝑦 are known, it is possible to substitute them into the correct proportion equation to work out the value of 𝑘.
The proportion equation containing a value for 𝑘 can then be used to work out different pairs of 𝑥 and 𝑦 values.
Follow the working out below
Inverse proportion
This table shows how different inverse proportion relationships are shown, and their proportion equations for a constant, 𝑘.
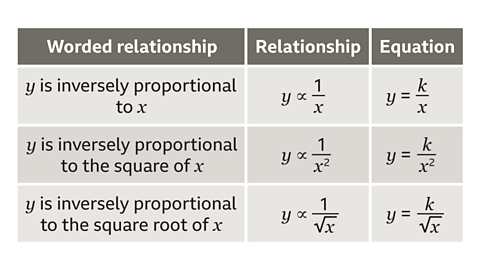
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions

- A ball is dropped from a roof. The distance it falls (𝑑 metres) is proportional to the square of the time (𝑡 seconds). The ball falls 45 m after 3 seconds.
Write an equation for 𝑑 in terms of 𝑡.
𝑑 = 5𝑡²
- Write a proportion equation involving 𝑘:
𝑑 = 𝑘𝑡² - Substitute the given values for 𝑑 (45) and 𝑡 (3):
45 = 𝑘 × 3² - Rearrange to find the value of 𝑘:
45 = 𝑘 × 9
𝑘 = 5 - Rewrite the proportion equation with 5 as the value of 𝑘:
𝑑 = 5𝑡²
- The distance a ball falls in metres (𝑑) for the amount of time taken (𝑡 seconds) can be found using the equation 𝑑 = 5𝑡².
Find the time taken for the ball to fall 20 metres.
𝑡 = 2 seconds
- Substitute the value of 20 in place of 𝑑 in the equation 𝑑 = 5𝑡².
20 = 5𝑡² - Divide both sides by 5.
4 = 𝑡² - Square root both sides.
2 = 𝑡
- The power of a kettle (𝑃 watts) is inversely proportional to the time taken (𝑡 minutes) for it to boil water.
When 𝑃 = 1200, 𝑡 = 3.
Find an equation for 𝑃 in terms of 𝑡.
𝑃 = \(\frac{3600}{𝑡}\)
- Write a proportion equation involving 𝑘:
𝑃 = \(\frac{𝑘}{𝑡}\) - Substitute the given values for 𝑃 (1200) and 𝑡 (3):
1200 = \(\frac{𝑘}{3}\) - Multiply both sides by 3 to find the value of 𝑘:
1200 × 3 = 𝑘
3600 = 𝑘 - Rewrite the proportion equation with 3600 as the value of 𝑘:
𝑃 = \(\frac{3600}{𝑡}\)
Higher - Quiz – Equations of direct and inverse proportion
Practise what you've learned about equations of direct and inverse proportion with this quiz for Higher tier.
Now you've revised equations of direct and inverse proportion, why not look at how to factorise expressions?
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Ratio, proportion and rates of change
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 8
- count4 of 8