Key points
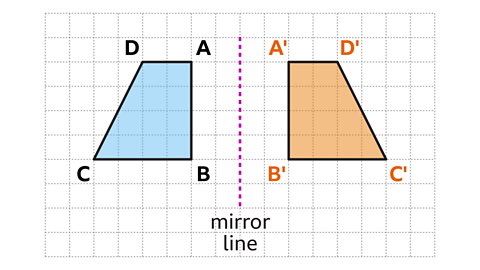
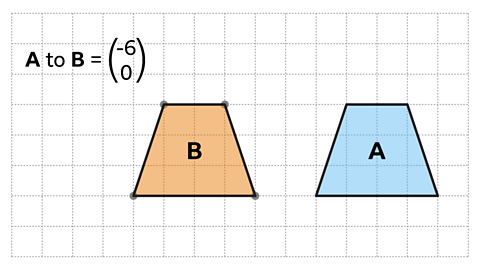
A reflectionA reflection is a mirror image of the shape. An image will reflect through a line, known as the line of reflection. is one of the four types of transformationA change in position or size, transformations include translations, reflections, rotations and enlargements.. A shape can be reflected across a line of reflection to create an image. The line of reflection is also called the mirror line.
Each vertexThe point at which two or more lines intersect (cross or overlap). The corner of a shape. The plural form is vertices. on the original shape is the same perpendicularPerpendicular lines are at 90° (right angles) to each other. distance from the mirror line to its corresponding vertex on the image.
The new shape is congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical. to the original shape.
When reflecting shapes in non-vertical mirror lines, rotating the paper to make the mirror line vertical can help to visualise a problem.
When reflecting shapes, a good understanding of symmetry and naming and plotting coordinates can be helpful.

Reflecting in vertical and horizontal lines
Reflections can be shown on a grid or on sets of axes.
To work out the position of the image after a reflection:
Pick a vertex on the shape (object).
Work out the perpendicular distance to the mirror line by counting the amount of squares on the grid.
Count the same perpendicular distance from the mirror line to the opposite side of the mirror line. This will be the position of the reflected vertex.
Repeat the process for additional vertices.
If a vertex is on the mirror line, it will be invariantA vertex or line segment that does not change after a transformation. under the reflection.
Examples
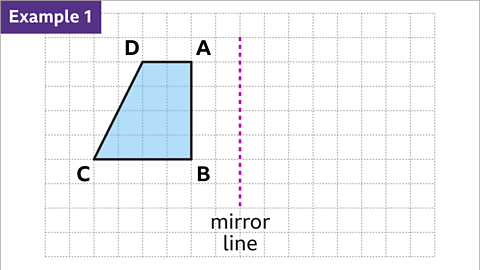
Image caption, Reflect shape ABCD in the vertical mirror line.
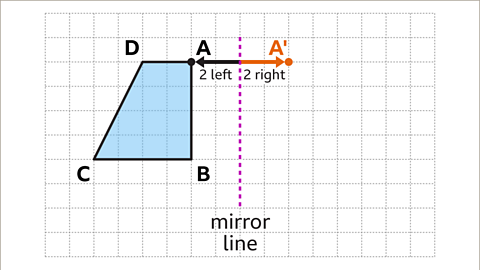
Image caption, Pick a vertex on the shape. In this example, Vertex A has been chosen as the first point to reflect. Vertex A is two squares left from the mirror line. The corresponding vertex will be plotted two squares to the right of the mirror line. Plot the point and label the new vertex A'. The new vertex is labelled with a similar letter to explain where the vertex has been reflected to.
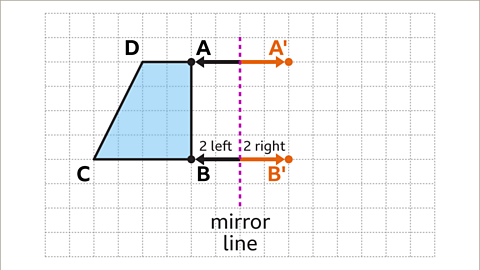
Image caption, Vertex B is also two squares to the left of the mirror line. The corresponding vertex B' is two squares to the right of the mirror line. Plot the point and label the new vertex B'.
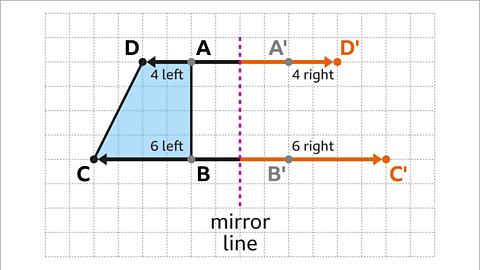
Image caption, Repeat the process for the final two vertices. Vertex C is six squares to the left of the mirror line, so the corresponding vertex C' is six squares to the right of the mirror line. Vertex D is four squares to the left of the mirror line, so the corresponding vertex D' is four squares to the right of the mirror line.
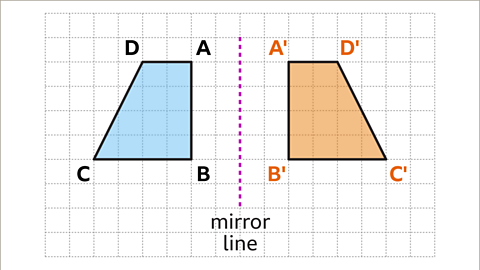
Image caption, Draw a line to connect each new vertex. The reflection of the shape is complete. Shape A'B'C'D' is congruent to shape ABCD.
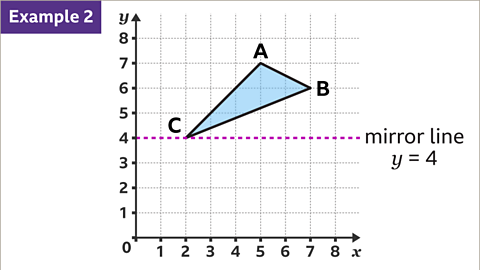
Image caption, Reflections can also occur on sets of axes. This problem can be approached in the same way as on a grid. Reflect triangle ABC in the horizontal line, 𝒚 = 4
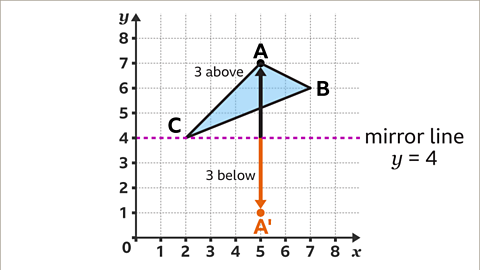
Image caption, Vertex A, at (5, 7), is three squares above the mirror line. The corresponding vertex, A' is three squares below the mirror line. A' has the coordinates (5, 1).
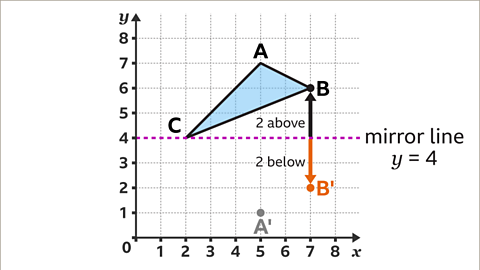
Image caption, Vertex B, at (7, 6), is two squares above the mirror line. The corresponding vertex, B' is two squares below the mirror line. B' has the coordinates (7, 2). Shape A'B'C'D' is congruent to shape ABCD.
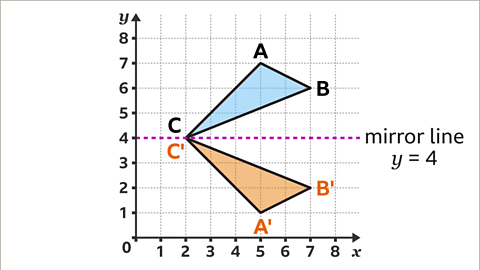
Image caption, Vertex C is on the mirror line. Therefore, this vertex it will remain unchanged (invariant) in the reflection. Draw a line to connect each new vertex. The reflection of the shape is complete. Triangle A'B'C' is congruent to triangle ABC.
1 of 9
Question
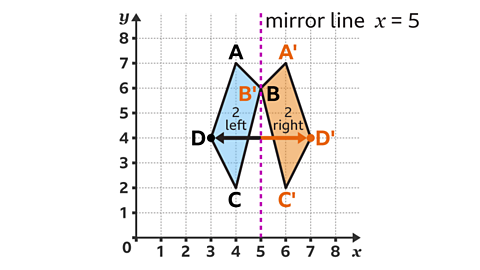
Quadrilateral ABCD is reflected in the vertical line \(x\) = 5. What are the co-ordinates for the reflection of vertex D?

Vertex D, at (3, 4), is two squares left of the mirror line.
The corresponding vertex D' is two squares right of the mirror line.
Vertex D' has the co-ordinates (7, 4).
Reflecting in diagonal lines
To reflect a shape in a diagonal line, a small adjustment to the method needs to be made. Since the mirror line is a diagonal, the perpendicular distance is also diagonal.
To reflect a shape on a diagonal line:
Pick a vertex on the object shape.
Work out the perpendicular distance to the mirror line. This is done by drawing a line from the vertex which passes through the diagonal of each square on the grid until the mirror line is reached.
Count the same perpendicular distance from the mirror line to the opposite side of the mirror line. This will be the position of the reflected vertex.
Repeat the process for additional vertices.
Examples
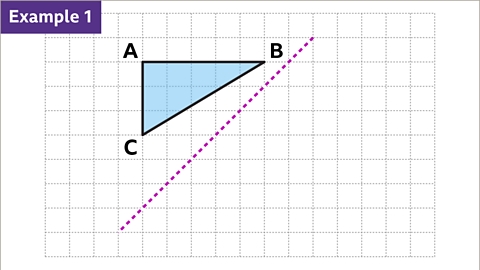
Image caption, Reflect triangle ABC in the diagonal mirror line.
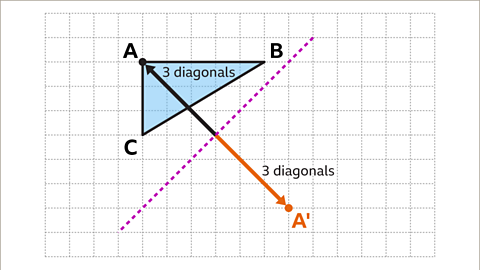
Image caption, Find the perpendicular distance from the vertex to the mirror line. Start at the vertex and draw a line which passes through the diagonal of each square on the grid until the mirror line is reached. The line from vertex A to the mirror line passes through 3 squares. The corresponding vertex A' passes through 3 squares from the mirror line on the opposite side.
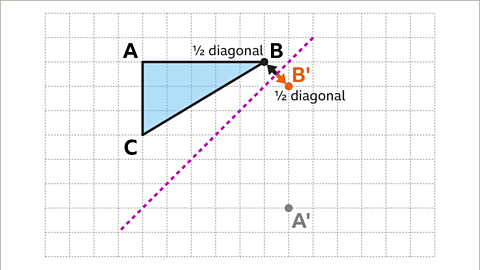
Image caption, The perpendicular distance from vertex B to the mirror line is half of the diagonal of a square. The corresponding vertex B' is the distance of half a diagonal square away from the mirror line on the opposite side.
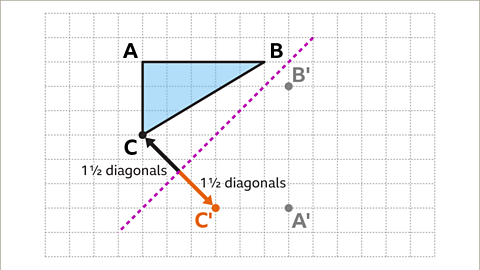
Image caption, The perpendicular distance from vertex C to the mirror line is one and a half diagonals of a square. The corresponding vertex C' is one and a half diagonals of a square from the mirror line on the opposite side.
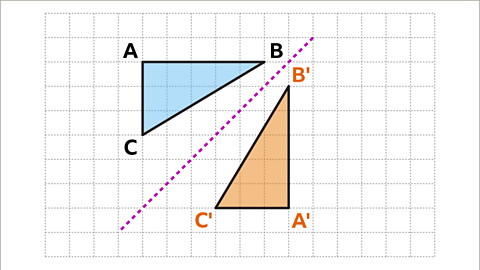
Image caption, Draw a line to connect each new vertex. The reflection of the shape is complete. Triangle A'B'C' is congruent to triangle ABC.
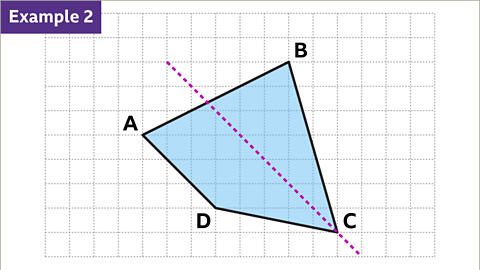
Image caption, Reflections can also occur where vertices are either side of the mirror line. This problem can be approached in a similar way. Reflect quadrilateral ABCD in the diagonal mirror line.
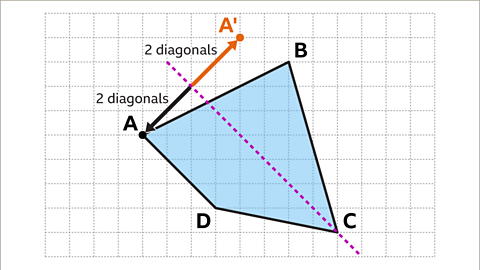
Image caption, The perpendicular distance from A to the mirror line is two diagonals of a square. The corresponding vertex A' is two diagonals of a square away from the mirror line on the opposite side.
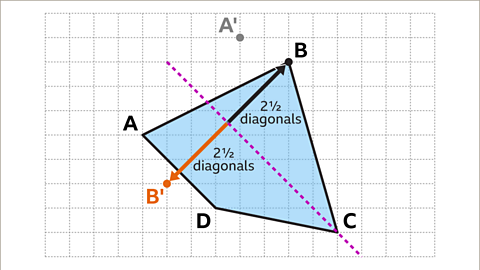
Image caption, The distance from vertex B to the mirror line is two and a half diagonals of a square. The corresponding vertex B' is two and a half diagonals of a square away from the mirror line on the opposite side.
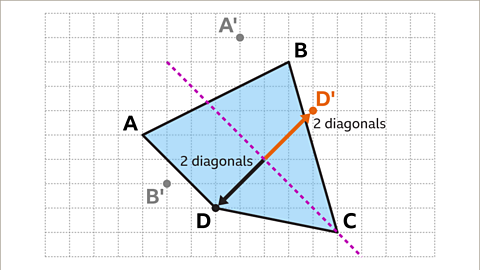
Image caption, Vertex C is on the mirror line. Therefore, under the reflection, it will stay the same (invariant). Vertex D is the distance of two diagonal squares from the mirror line. The corresponding vertex D' is the distance of two diagonal squares from the mirror line on the opposite side.
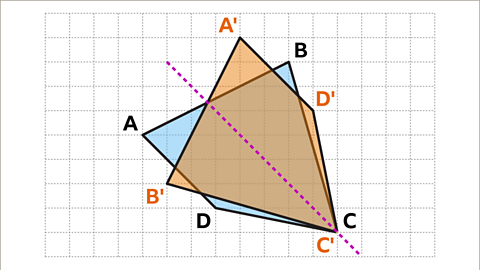
Image caption, Draw a line to connect each new vertex. The reflection of the shape is complete. Shape A'B'C'D' is congruent to shape ABCD.
1 of 10
Question
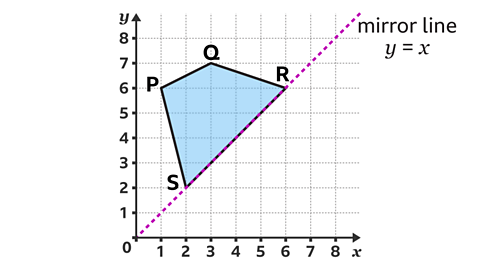
Shape PQRS is reflected in the diagonal line, \(y\) = \(x\). In the reflected image, which coordinates would be invariant?
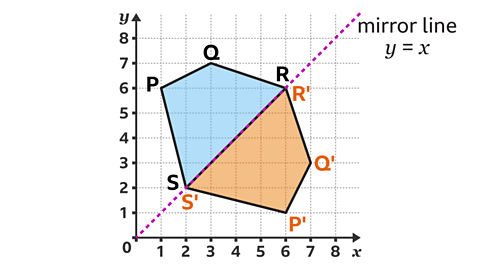
If a vertex is on the mirror line, it will be invariant under the reflection.
Vertices R (6, 6) and S (2, 2) are on the mirror line. Therefore, under the reflection they would be invariant.
Practise reflecting shapes
Quiz
Practise reflecting shapes with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you work out your answers.
Real-life maths
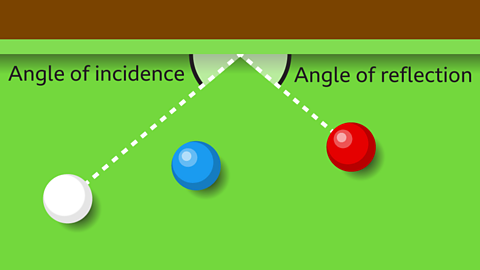
In the game of snooker, a player may choose to bounce the cue ball off the edge of the table (cushion) to strike the ball they need to hit.
The trajectoryThe path a moving object takes. of the ball after it hits the cushion is a reflection. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Symmetry and transformations
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 6
- count1 of 6
- count2 of 6
- count3 of 6