Key points
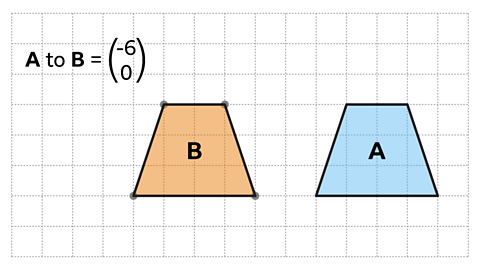
A translationThe movement of a shape from one place to another. The shape has the same orientation. is a type of transformationA change in position or size, transformations include translations, reflections, rotations and enlargements..
A translation moves a shape from one location to another.
The new shape is congruentA shape that has a mathematical change of appearance. to the original shape.
The size of the shape does not change, and the shape is not reflectionA reflection is a mirror image of the shape. An image will reflect through a line, known as the line of reflection. or rotationA 2D transformation which turns a shape about a fixed point called the centre of rotation. A rotation is described by specifying the centre of rotation and the angle of rotation..
To understand translation a good understanding of naming and plotting co-ordinates can be helpful.

Describing translation
A translation is described using horizontal and verticaldisplacementA change in position of a shape relative to its start point.. By counting squares on a grid or set of axesTwo reference lines, one horizontal and one vertical, that cross at right-angles. They are used to define the position of a point on a grid. Axes is the plural of axis. we can describe a translation. These displacements can then be represented using a column vectorA vector describes a movement from one point to another. A vector quantity has both direction and magnitude (size)..
A column vector uses two values and curly brackets:$$ \ (^x _y) $$
The \(x\) value describes the horizontalA line that is parallel to the horizon. displacement, moving to the right or left.
- A displacement right is a positive number and a displacement left is a negative number.
- If there is no horizontal movement a zero is used.
The \(y\) value describes the verticalA line that is perpendicular to the horizon. displacement, moving up or down.
- A displacement up is a positive number and a displacement down is a negative number.
- If there is no vertical movement, a zero is used.
Using a vertexA corner of a shape. The point at which two or more lines intersect. In 2D shapes, the adjacent sides of a polygon meet at a vertex. as a reference point helps track the translation of the shape.
Examples
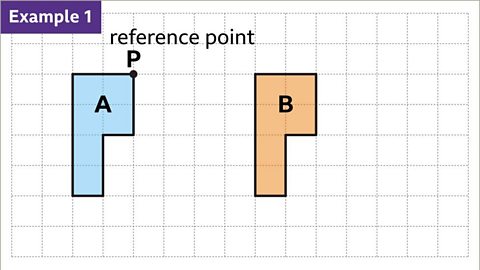
Image caption, Decide on a reference point to help describe the translation between shape A and shape B. Here, the reference point is labelled P.
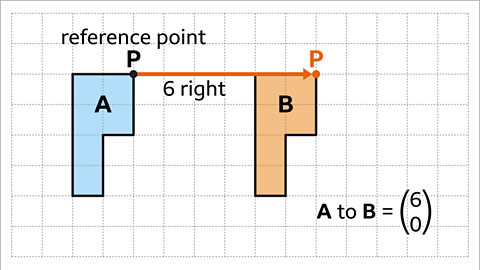
Image caption, From shape A to shape B the reference point P has moved 6 to the right. The translation of A to B is described using the vector shown in the image above.
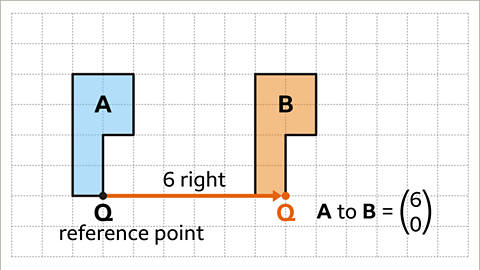
Image caption, Using a different point, such as reference point Q, the translation of A to B is still the same vector, or 6 right. This shows the choice of reference point does not matter.
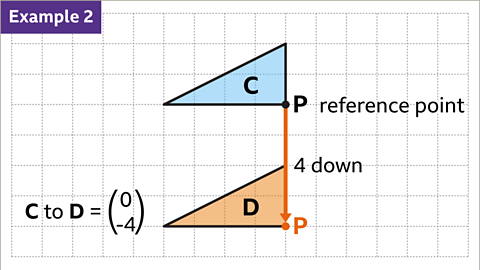
Image caption, From shape C to shape D, the reference point P has moved 4 squares down. The translation of shape C to shape D is described as the vector in the image.
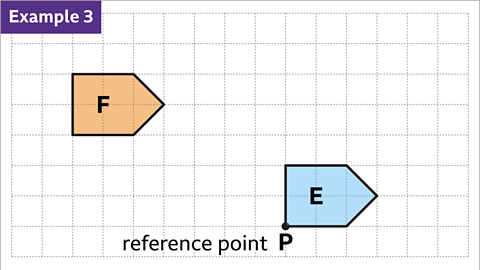
Image caption, This translation is a combination of horizontal and vertical displacements. Decide on a reference point to help describe the translation. This is labelled P.
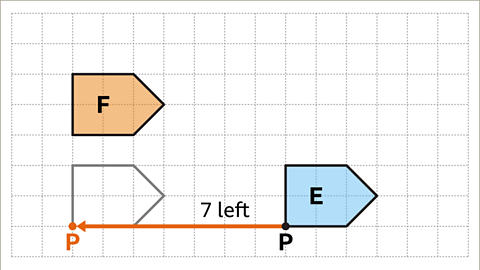
Image caption, From shape E to shape F, the reference point P has moved 7 squares to the left. This is a horizontal displacement of -7
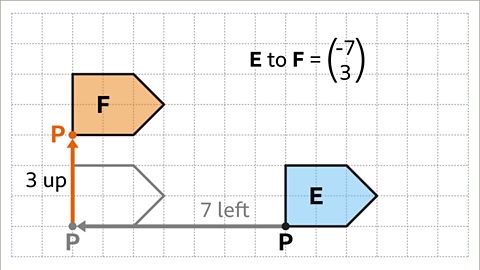
Image caption, It then moves 3 squares up. This is a vertical displacement of 3. Therefore, the translation from shape E to shape F is described as the vector in the image.
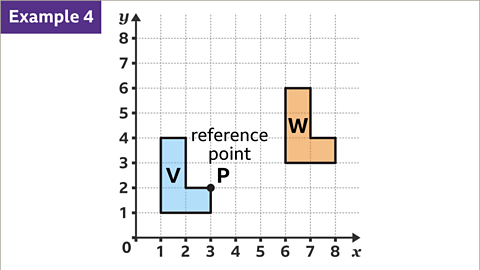
Image caption, Translations can also occur on sets of axes. This problem can be approached in the same way. Decide on a reference point to help describe the translation.
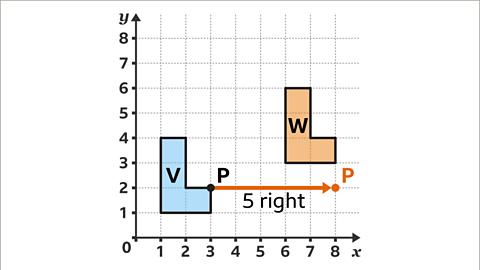
Image caption, From shape V to shape W, the reference point P has moved 5 squares to the right. Check the axes, each square is 1 unit. This is a horizontal displacement of 5
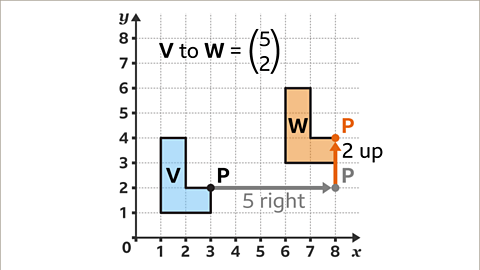
Image caption, It then moves 2 squares up. This is a vertical displacement of 2. Therefore, the translation of shape V to shape W is described as the vector in the image above.
1 of 10
Question
What is the translation between shape A and shape B?
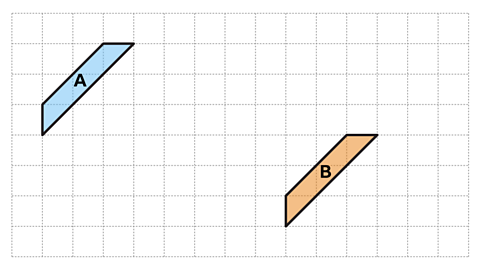
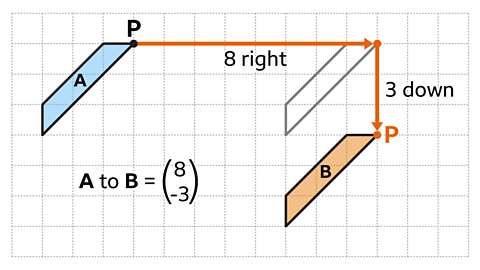
From shape A to shape B the reference point (labelled P) has moved 8 squares to the right and 3 squares down.
This is horizontal displacement of 8 and a vertical displacement of -3
The translation of shape A to shape B is described as the vector in the image.
Plotting translations
When given a translation, it is possible to plot a shape in its new position.
This can be done by translating each vertexA corner of a shape. The point at which two or more lines intersect. In 2D shapes, the adjacent sides of a polygon meet at a vertex. of the shape in turn. These points can then be joined together to create the shape.
Alternatively, since the new shape is congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical., it is possible to pick one vertex as a reference point. If this reference point is moved to the correct position, the whole congruent shape can be drawn.
Examples
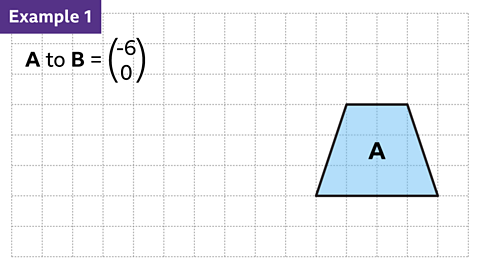
Image caption, Translate shape A by the vector in the image. Label the new shape B.
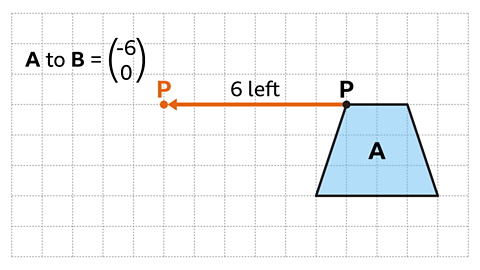
Image caption, The vector in the image means shape A is translated 6 squares to the left. Starting with reference point P, the vertex is translated 6 squares horizontally to the left.
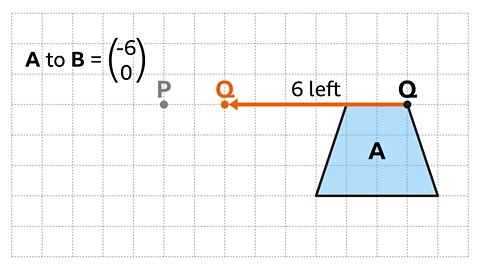
Image caption, Reference point Q is translated 6 squares horizontally to the left.
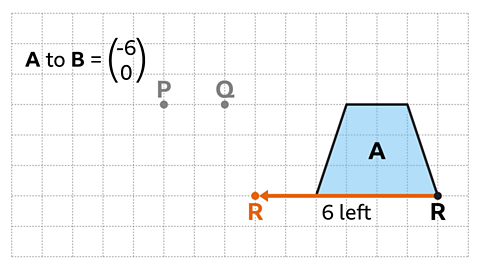
Image caption, Reference point R is translated 6 squares horizontally to the left.
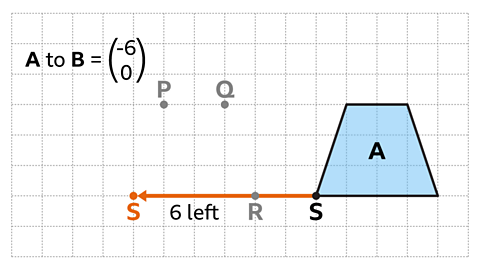
Image caption, Finally, reference point S is translated 6 squares horizontally to the left.
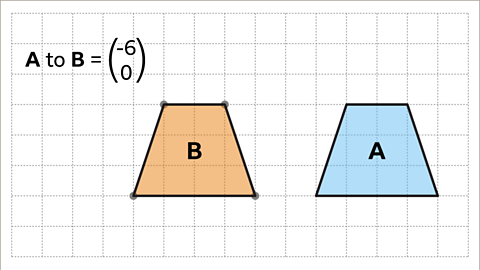
Image caption, Joining the points up, the new shape is finished. Label the new shape B.
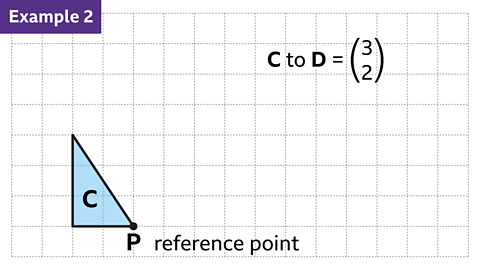
Image caption, Shape D is a translation of shape C by the vector in the image. It is possible to draw shape D in its new position. Decide on a single reference point (labelled P). Here, the bottom right corner has been chosen.
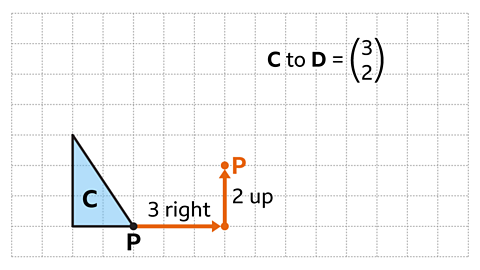
Image caption, The vector in the image means shape C is translated 3 squares to the right and 2 squares up. Reference point P is translated 3 squares horizontally to the right and 2 squares up.
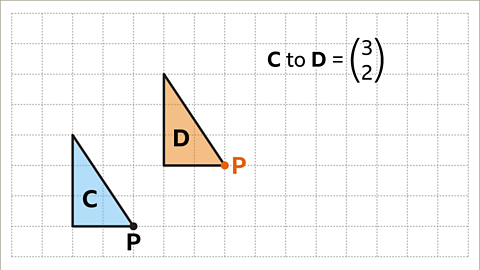
Image caption, Since shape D is congruent (identical) to shape C, an identical triangle can be plotted with the bottom right corner at the new location. Label the new shape D.
1 of 9
Question
Shape A is translated by vector, which is shown in the image below. The new shape is called B.
What is the corresponding coordinate of P on shape B?
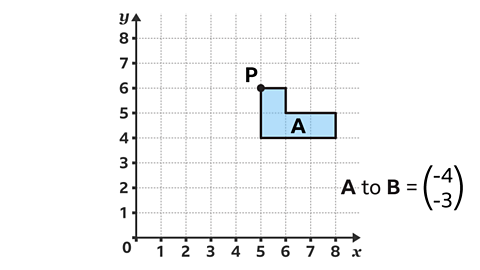
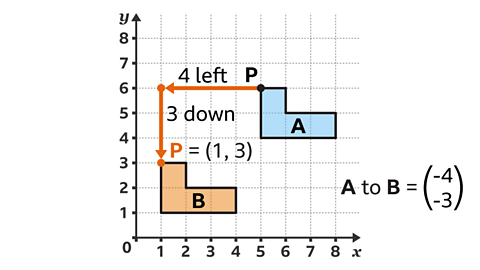
The vector means shape A is translated 4 squares to the left and 3 squares down.
Reference point P moves 4 squares horizontally to the left and 3 squares down from (5, 6).
Point P on shape B has the coordinate (1, 3).
Practise translating shapes
Practise translating shapes with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Quiz
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Symmetry and transformations
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 6
- count5 of 6
- count6 of 6
- count1 of 6