Key points
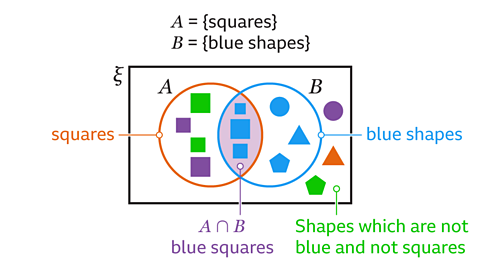
The combination of two or more setA collection of information or letters or numbers. The members of the set can be listed inside curly brackets, { }. A set may be described in words inside curly brackets { }. On a Venn diagram a set is shown as a circle. is the union (of sets) (∪)On a Venn diagram, the region of two or more sets when they are combined. 𝑷∪𝑸 is the union of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∪𝑸 = {elements just in 𝑷, in both 𝑷 and 𝑸, just in 𝑸}. of the sets.
The notationAn agreed form of presentation for mathematical information. for union is ᴜ.
For example, the union of set \(A\) and set \(B\) is written as \(A\)ᴜ\(B\). The union of set \(X\), set \(Y\) and set \(Z\) is written as \(X\)ᴜ\(Y\)ᴜ\(Z\).
The union contains the elementA piece of information, a letter or a number, in a set. Also described as a member of the set. that are in each set and any elements that are common to the sets being considered.
The lowest common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers can be found using the union of sets. For this it is important to know about common factors.

Using the union of two sets
To list the elements in \(A\)ᴜ\(B\), list those that are:
- In both set \(A\) and set \(B\)
- In only set \(A\)
- In only set \(B\)
The elements can be listed in any order, and starting with the intersection (of sets) (∩)On a Venn diagram, the region where sets overlap. 𝑷∩𝑸 is the intersection of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∩𝑸 = {elements in 𝑷 that are also in 𝑸}. elements can help in avoiding duplication of elements.
To identify \(A\)ᴜ\(B\) on a Venn diagram:
- Use the regionAn identified area on a diagram or graph. that is made up of the combined set circles for set \(A\) and set \(B\).
Remember that all the data being considered is contained inside the rectangle. This is called the universal set (ξ)The set of all the elements being considered. The Greek letter ξ (Xi) is used to represent the universal set. and is represented by the Greek letter ξ (Xi). Each circle represents a setA collection of information or letters or numbers. The members of the set can be listed inside curly brackets, { }. A set may be described in words inside curly brackets { }. On a Venn diagram a set is shown as a circle..
Examples
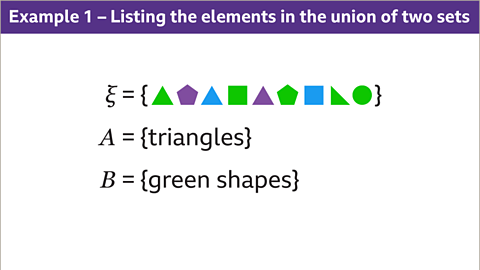
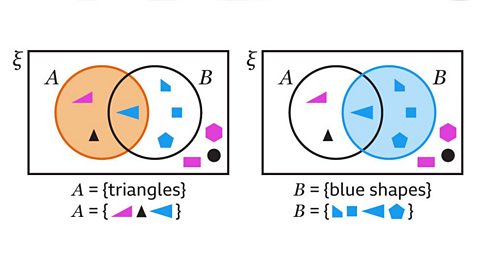
Image caption, List the elements of 𝑨ᴜ𝑩, the union of set 𝑨 and set 𝑩.
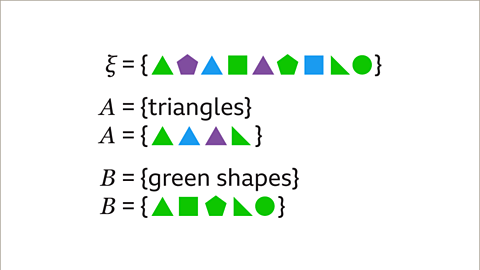
Image caption, The elements of each set are listed. 𝑨ᴜ𝑩 contains the elements that are in both set 𝑨 and set 𝑩, the elements only in set 𝑨 and elements only in set 𝑩.
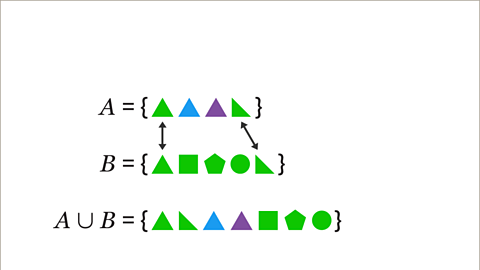
Image caption, The elements that are in both set 𝑨 and set 𝑩 are two green triangles. The elements that are only in set 𝑨 are a blue triangle and a purple triangle. The elements that only in set 𝑩 are a green square, a green pentagon and a green circle. 𝑨ᴜ𝑩 contains this set of shapes.
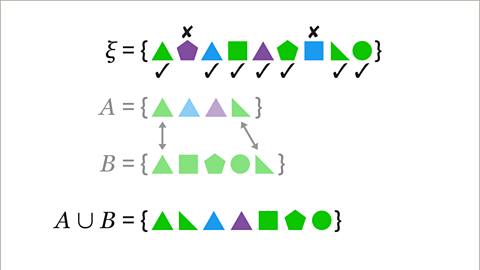
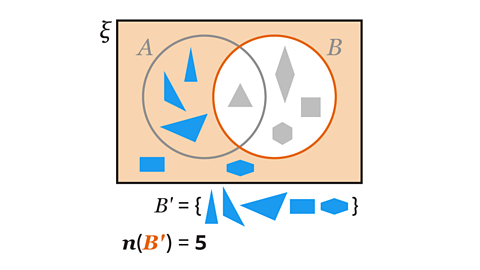
Image caption, The union of sets does not necessarily contain all the elements in the universal set. In this example, the union of set 𝑨 and set 𝑩 does not include the purple pentagon and the blue square.
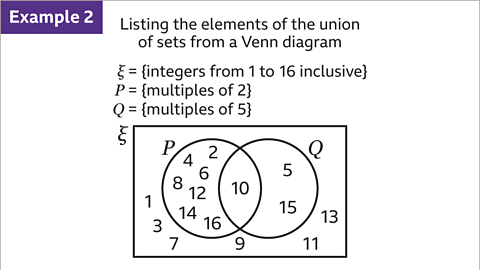
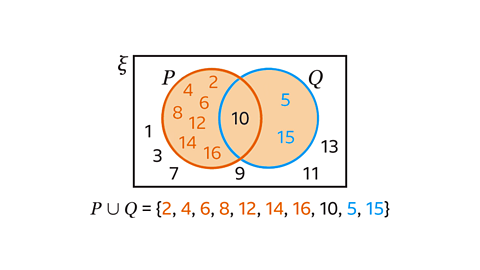
Image caption, The Venn diagram is drawn for positive integers (whole numbers) from 1 to 16 inclusive. 𝑷 = {multiples of 2} and 𝑸 = {multiples of 5}. List the elements of 𝑷ᴜ𝑸, the union of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸.
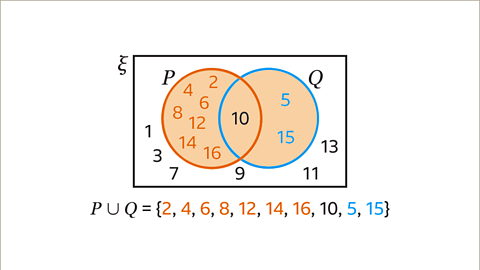
Image caption, 𝑷ᴜ𝑸 is the union of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. The sets are combined. The shaded region shows 𝑷ᴜ𝑸. This region contains the elements only in set 𝑷, the elements in both set 𝑷 and set 𝑸 and the elements only in set 𝑸. These are integers (whole numbers) that are multiples of 2 or multiples of both 2 and 5 or multiples of 5. 𝑷ᴜ𝑸 = {2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 10, 5, 15}.
1 of 6
Question
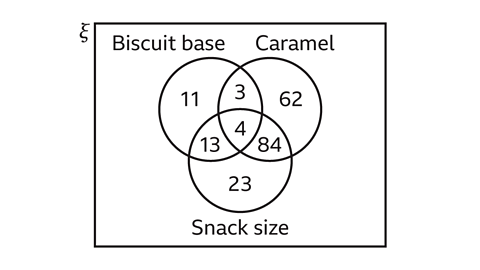
The Venn diagram shows the number of people in a large office who bring home-baked treats into the office to share.
How many people do this?
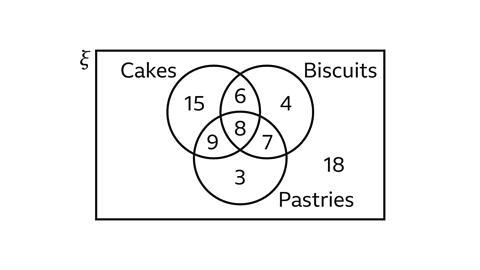
The people who bring home-baked treats into the office are in the union of the three sets.
This is the number of people who have provided one or more of cakes, biscuits and pastries.
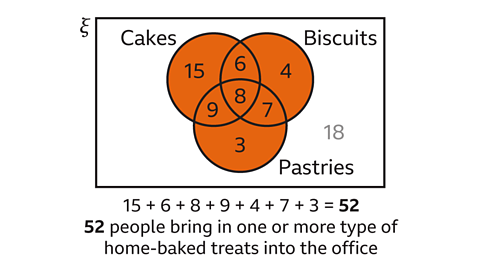
The total number of people in the union of the sets is found by adding up the numbers in the shaded region, shown in the image below:
15 + 6 + 8 + 9 + 4 + 7 + 3 = 52
There are 52 people who bring one or more of the home-baked treats into the office.
There are 18 people who (so far) have not brought in any of these home-baked treats.
Finding the lowest common multiple using the union of sets
- To use a Venn diagram to find the lowest common multiple (LCM) of two numbers:
- Write each number as a product of prime factorsThe factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12. The prime factors of 12 are 2 and 3. 12 may be expressed as a product of its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3 without using indicesIndices are powers eg, 3 to the power of 2, written 3² .
- Draw a circle for each number. The circles will overlap.
- Place the common factorA whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers. Eg, 2, 5 and 10 are common factors of 30 and 20 in the intersection (of sets) (∩)On a Venn diagram, the region where sets overlap. 𝑷∩𝑸 is the intersection of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∩𝑸 = {elements in 𝑷 that are also in 𝑸}. of the circles and place the remaining prime factors for each number in its own circle.
- Multiply the numbers in the union (of sets) (∪)On a Venn diagram, the region of two or more sets when they are combined. 𝑷∪𝑸 is the union of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∪𝑸 = {elements just in 𝑷, in both 𝑷 and 𝑸, just in 𝑸}. of the sets. The product of all these numbers is the LCM.
Example
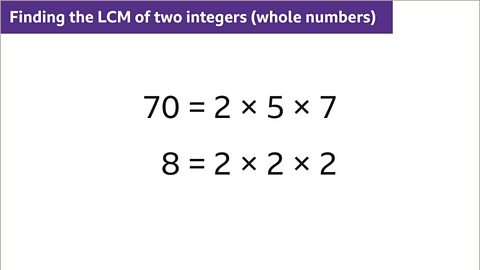
Image caption, Given that 70 = 2 × 5 × 7 and 8 = 2 × 2 × 2, use a Venn diagram to find the lowest common multiple (LCM) of 70 and 8
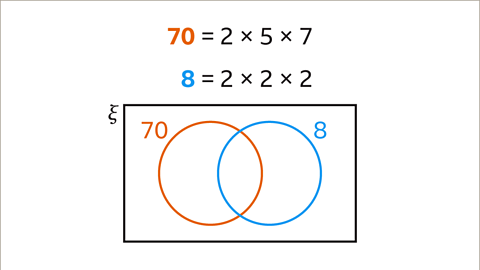
Image caption, Draw two overlapping circles, one for 70 and one for 8
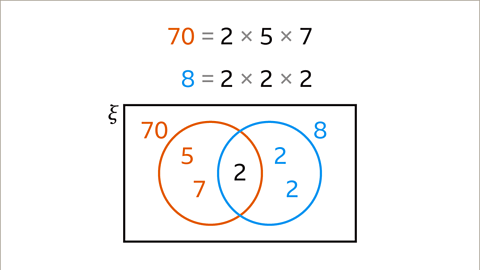
Image caption, Place any common factor(s) in the intersection. The only common prime factor for 70 and 8 is 2. The remaining prime factors of 70 are 5 and 7. These are placed inside the 70 circle, but not in the intersection. The remaining prime factors of 8 are 2 and 2. These are placed inside the circle for 8 but not in the intersection.
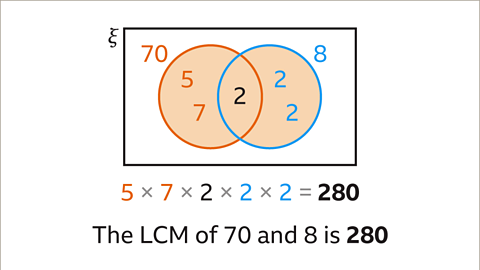
Image caption, The product of all the prime factors in the union of the sets of prime factors gives the lowest common multiple (LCM). 5 × 7 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 280. The LCM of 70 and 8 is 280
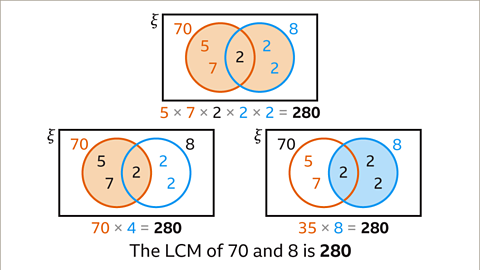
Image caption, The calculation for the lowest common multiple (LCM), 5 × 7 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 280, may also be written using one of the original numbers, 70 or 8. 70 × 4 = 280 and 35 × 8 = 280. In this case 70 × 4 is simpler. The lowest common multiple (LCM) of 70 and 8 is 280 every time.
1 of 5
Question
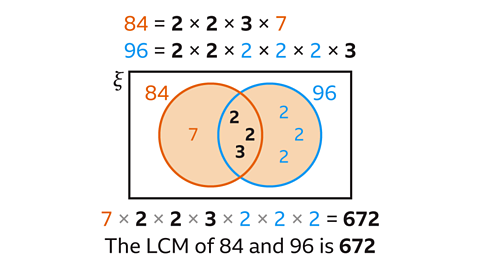
Use a Venn diagram to calculate the lowest common multiple (LCM) of 84 and 96
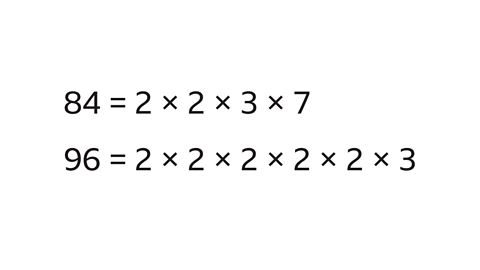
The common prime factors of 84 and 96 are 2, 2 and 3. These are placed in the intersection of the circles.
The remaining prime factor for 84 is 7. This is placed inside the circle for 84 but not in the overlap with 96.
The remaining prime factors of 96 are two 2s. These are placed inside the circle for 96 but not in the overlap with 84.
The lowest common multiple (LCM) of 84 and 96 is the product of the prime factors in the union of the circles.
7 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 672
The LCM of 84 and 96 is therefore 672
Practise the union of two sets
Practise using the union of two sets, with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Quiz
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Sets and Venn diagrams
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 5
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5
- count2 of 5