Key points
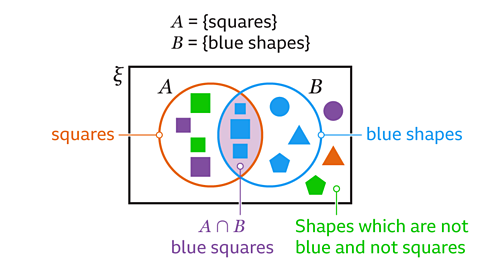
An elementA piece of information or a letter, or a number, in a set. Also described as a member of the set. of a setA collection of information or letters or numbers. The members of the set can be listed inside curly brackets, { }. A set may be described in words inside curly brackets { }. On a Venn diagram a set is shown as a circle. is a member of that set.
An element that is contained in two different sets is a member of both of those sets and is in the intersection (of sets) (∩)On a Venn diagram, the region where sets overlap. 𝑷∩𝑸 is the intersection of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∩𝑸 = {elements in 𝑷 that are also in 𝑸}.
The intersection contains any elements that are common to all of the sets being considered.
The highest common factor (HCF) The largest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. Eg, 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20. Highest common factor is written as HCF. of two or more numbers can be found using the intersection of sets in a Venn diagramA diagram used to sort data..

Understanding and using the intersection of sets
The intersection of two or more sets is the overlap between the sets.
The symbol ∩ is used to show that sets intersectWhere lines cross or overlap..
\(A\)∩\(B\) is the intersection of set \(A\) and set \(B\) and contains the set of elements which are in both set \(A\) and set \(B\).
\(A\)∩\(B\)∩\(C\) is the intersection between set \(A\), set \(B\) and set \(C\) and contains the set of elements which are in set \(A\), set \(B\) and set \(C\).
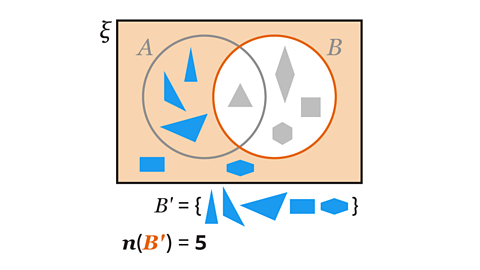
The symbol \('\) is written after the lettered name of the set to give the complement of the set. \(Q'\) is the complement of set \(Q\).
Examples
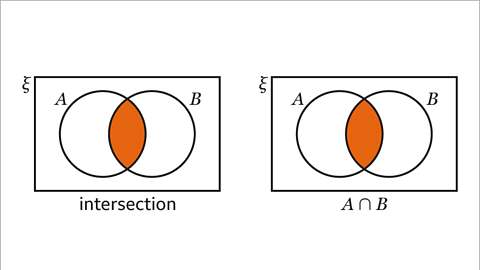
Image caption, The intersection of a set is the overlap between the sets. 𝑨∩𝑩 is the intersection of set 𝑨 and set 𝑩.

Image caption, Draw the Venn diagram. ξ = {whole numbers from 1 to 12 inclusive}, 𝑨 = {even numbers}, and 𝑩 = {multiples of three}. List the elements (members) of 𝑨∩𝑩 and describe the intersection.

Image caption, List the elements of each set.
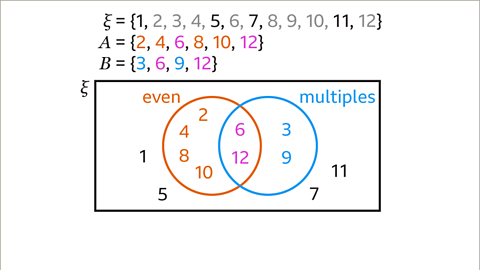
Image caption, Place the elements that are in both sets (6 and 12) in the intersection. Complete set 𝑨 with 2, 4, 8 and 10. Complete set 𝑩 with 3 and 9. Complete the universal set with 1, 5, 7 and 11
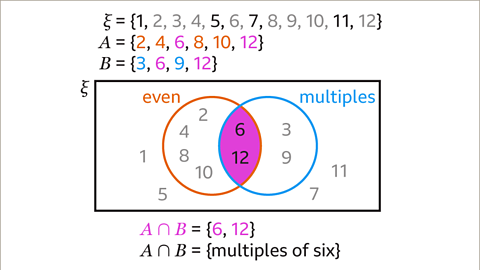
Image caption, 𝑨∩𝑩 = {6, 12}. The intersection of the set of even numbers and the set of multiples of 3 gives the set of multiples of 6. 𝑨∩𝑩 = {multiples of 6}.
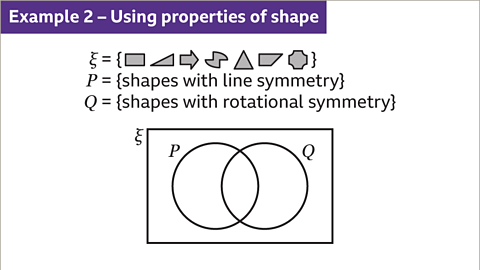
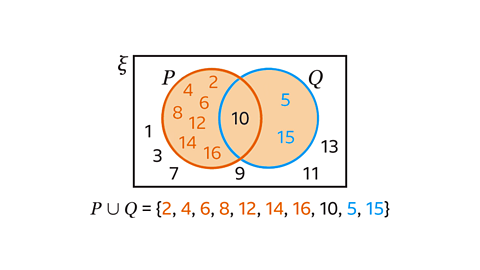
Image caption, Complete the Venn diagram and describe the elements in 𝑷∩𝑸.
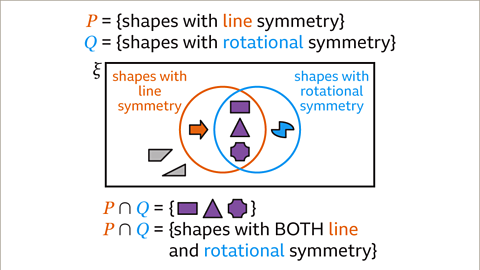
Image caption, The Venn diagram shows 𝑷, the set of shapes with line symmetry, and 𝑸, the set of shapes with rotational symmetry. 𝑷∩𝑸 is the set of shapes that have both line symmetry and rotational symmetry.
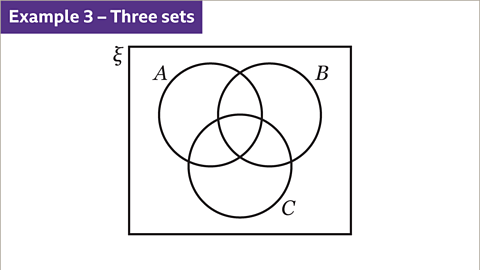
Image caption, Identify the regions 𝑨∩𝑪 and 𝑨∩𝑩∩𝑪 on the Venn diagram.
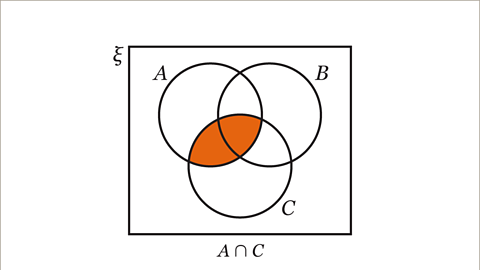
Image caption, 𝑨∩𝑪 is the intersection of set 𝑨 and set 𝑪, ie the overlap of the circles for set 𝑨 and set 𝑪.
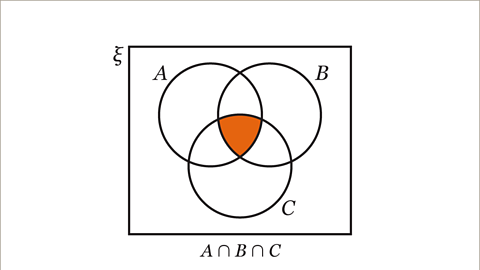
Image caption, 𝑨∩𝑩∩𝑪 is the intersection of set 𝑨, set 𝑩 and set 𝑪, i.e. the overlap of the circles for set 𝑨, set 𝑩 and set 𝑪.
1 of 10
Question
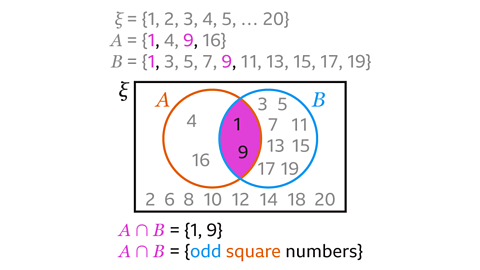
List the elements in 𝑨∩𝑩 and describe the intersection.
The elements in 𝑨∩𝑩 are numbers that are both odd and square.
These are the numbers 1 and 9
𝑨∩𝑩 = {1, 9}.
Use a Venn diagram to find the HCF of two or more numbers
- To use a Venn diagram to find the HCF (highest common factor) of two or more numbers:
- Write each number as a product of prime factorsThe factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12. The prime factors of 12 are 2 and 3. 12 may be expressed as a product of its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3 without using indicesIndices are powers eg, 3 to the power of 2, written 3² .
- Draw a circle for each number. The circles will overlap.
- Place the factors that are common to both (or all) numbers in the intersection (of sets) (∩)On a Venn diagram, the region where sets overlap. 𝑷∩𝑸 is the intersection of set 𝑷 and set 𝑸. 𝑷∩𝑸 = {elements in 𝑷 that are also in 𝑸}. of the circles and place the remaining prime factors for each number in its own circle.
- Multiply the numbers in the intersection. The product of these numbers is the HCF.
Examples
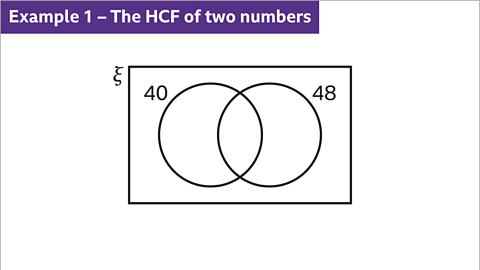
Image caption, Find the highest common factor (HCF) of 40 and 48
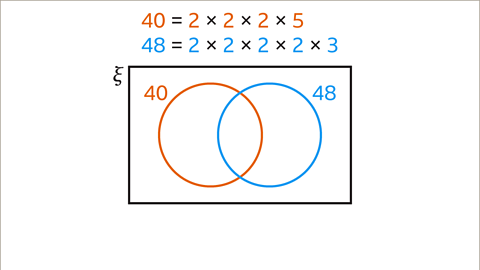
Image caption, Write each number as a product of prime factors. 40 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5. 48 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3. Then, draw the Venn diagram. Draw one circle for 40 and another for 48
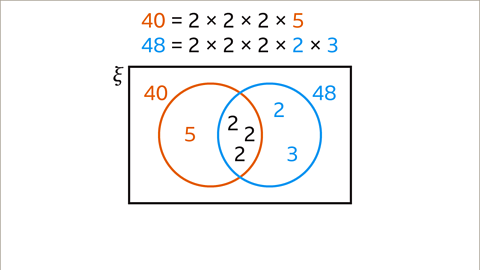
Image caption, The common prime factors of 40 and 48 are three 2s. Place these in the intersection of the Venn diagram. The remainder of the prime factors are placed in the circle for each number. 5 is placed inside the circle containing the prime factors of 40. 2 and 3 are placed inside the circle containing the prime factors of 48. Each circle contains all the prime factors that multiply to give each number.
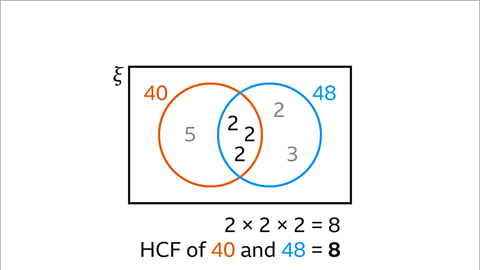
Image caption, The intersection contains three 2s; these are the common factors because they are factors of both 40 and 48. The highest common factor (HCF) of 40 and 48 is calculated by multiplying the common prime factors. 2 × 2 × 2 = 8. The HCF of 40 and 48 is 8
1 of 4
Question
Given the product of prime factors of 36 and 54, use the Venn diagram to work out the highest common factor of 36 and 54.
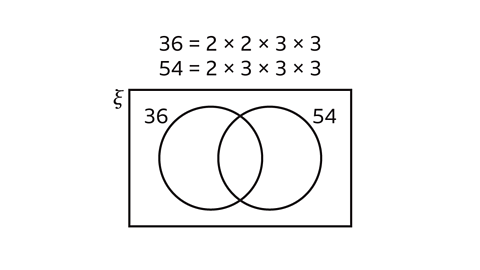
The circle for 36 contains the prime factors of 36. The circle for 54 contains the prime factors of 54
The intersection contains all the prime factors that are common to both 36 and 54
The HCF of 36 and 54 is the product of the common prime factors.
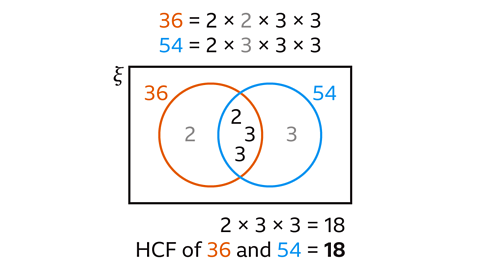
2 × 3 × 3 = 18
The HCF of 36 and 54 is 18
Practise understanding and using the intersection of two sets
Quiz
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Sets and Venn diagrams
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 5
- count4 of 5
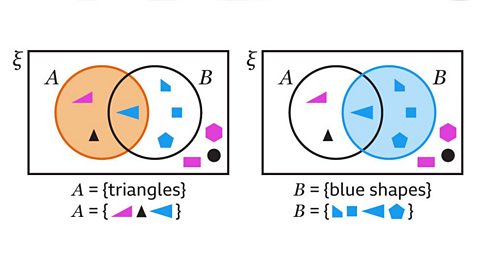
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5