What is the autumn equinox and when does it happen?

- Published
Wherever you are on the planet the equinox occurs at the same moment and this year that will be on Monday 22 September at 19:19 BST.
It's when the Earth's axis lies perpendicular to the Sun, making day and night nearly equal in length. It happens twice a year - in September and March.
In the northern hemisphere it marks the start of autumn and south of the equator, where the seasons are reversed, it marks the first day of spring.
For meteorologists though, autumn begins on 1 September, covering the months of September, October and November.
Spectacular autumn leaves expected after warm UK summer
- Published19 September 2025
Five celestial events to look out for this autumn
- Published15 September 2025
What is the equinox?
The Earth spins on its axis, tilted at 23.5 degrees and as it orbits around the Sun it is tilted towards or away from it, which gives us our seasons.
On the day of the equinox the tilt of Earth's axis is at a right angle to the Sun, giving us nearly equal amounts of day and night all over the world. On this date the Sun is directly over the equator.
Normally the autumn equinox falls on either 22 or 23 of September. Very rarely it can fall on 24 September. This last happened in 1931, but if you missed it good luck experiencing the next one - it's due in 2303!
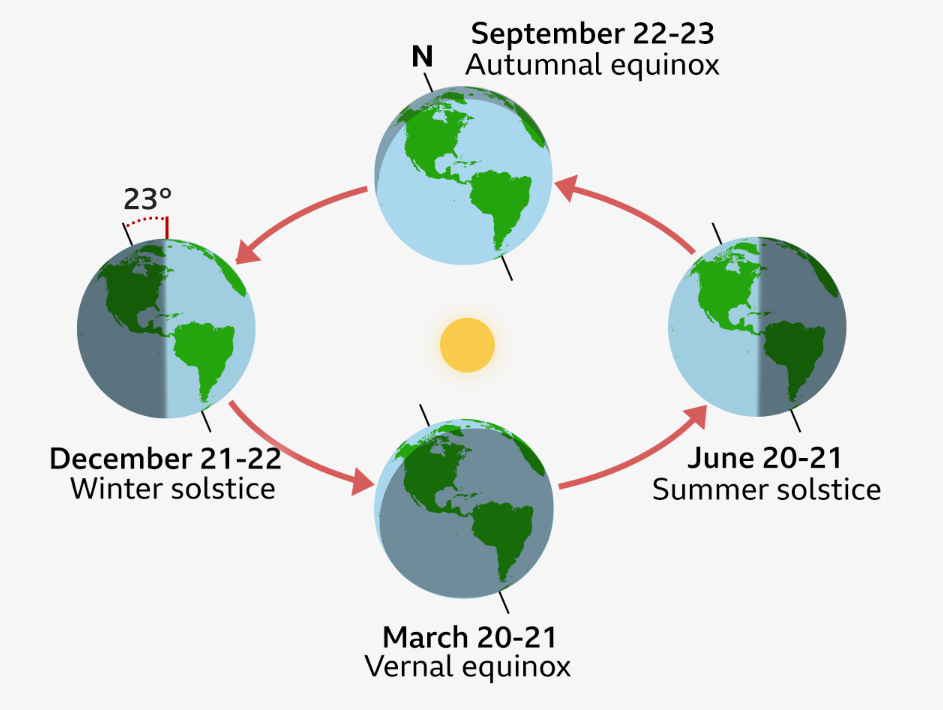
At the equinox the Earth's axis (shown by a black line) is neither tilted towards or away from the Sun but perpendicular to it
What does equinox mean?
The word "equinox" is derived from Latin and literally translates to "equal night".
On the equinox, day and night are roughly 12 hours long - although not exactly.
For example, on 22 September in London, the day length will be 12 hours and 11 minutes and in Shetland 12 hours and 14 minutes. So where does this extra length of day come from?
At both sunrise and sunset, light from the Sun is refracted through the Earth's atmosphere. Although we can see the Sun, in reality its position is actually below the horizon. This means we get a few extra minutes of daylight because of this light-bending trick of our atmosphere.
Additionally the equinox is measured at the centre of the Sun's disc, not at its leading or trailing edge which are used as the measure of a sunrise or sunset.
It is not until a few days after the autumn equinox that we get to the point where days and nights are 12 hours long. This is known as the equilux and will occur on 25 September.
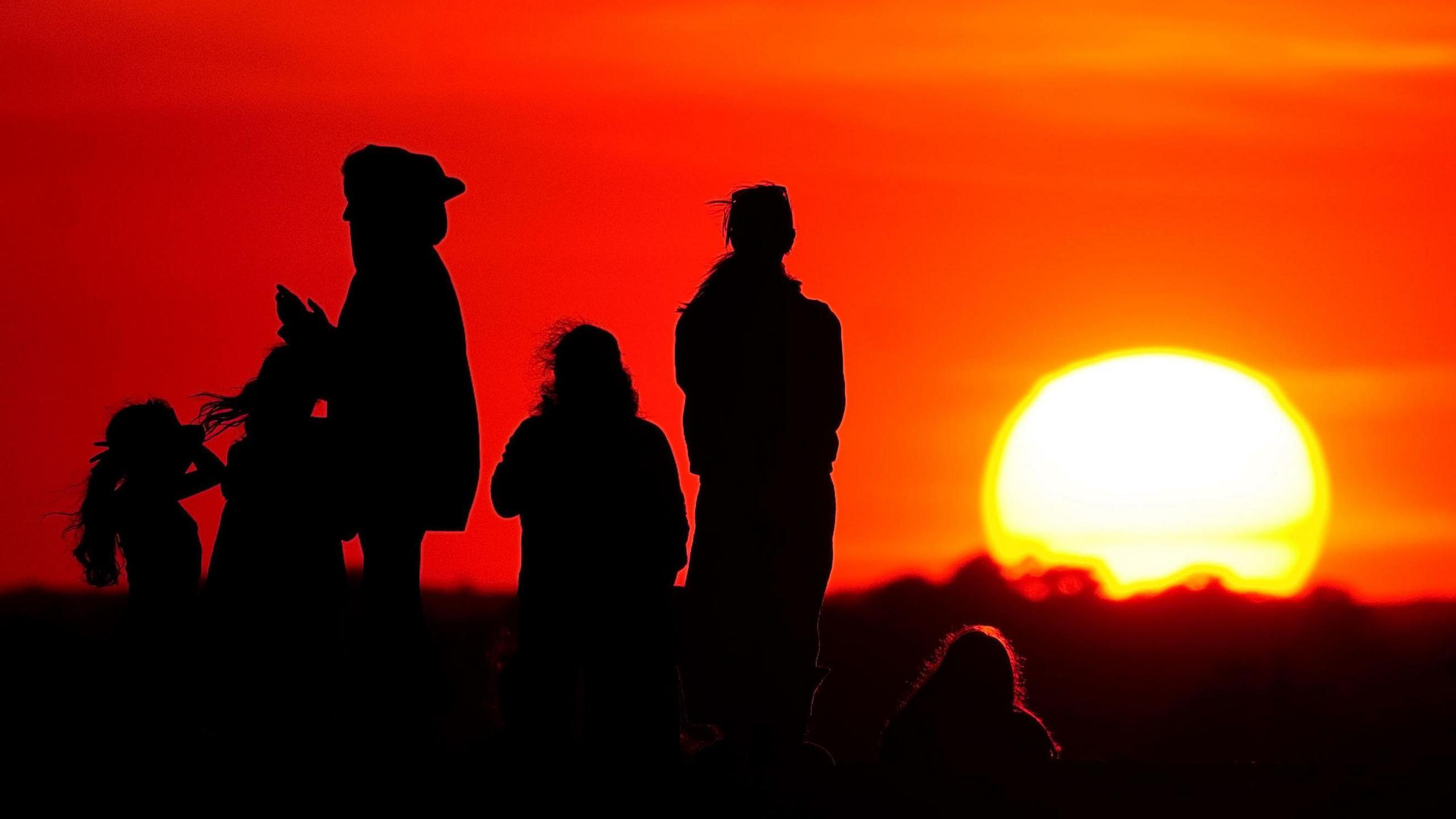

As sunlight passes through the atmosphere at sunrise or sunset, it is bent or refracted; the true position of the Sun is actually below the horizon. This process adds a few more minutes to the day
As we approach December, Earth's northern hemisphere will be tilted away from the Sun.
By 21 December the Sun will have reached its lowest point in the sky during the day, marking the winter solstice.
It is at this point that daylight hours will begin to increase once again.
When do the clocks go back?

A red squirrel forages in the autumn leaves
Another sure sign that autumn is here is when we put our clocks back and our evenings suddenly get much darker.
This happens in the UK at 02:00 BST on Sunday 26 October this year.
Clocks going back is often considered the "better" clock change as we get an extra hour in bed (or in the nightclub).
However it is not so good if you are working on a night shift, as I can tell you from experience.
Article updated on 16 September 2025 to include the time of the equinox.

