Key points about percentage change, interest and exponential change

- Percentage change can be either successive percentage changeWhen an amount is increased or decreased by one percentage, then increased or decreased by another. or repeated percentage changeWhen the same percentage calculation is applied more than once on an amount. .
- interestA cost that is paid for borrowing money, or additional money earned on savings. It is often calculated ‘per annum’ (per year). is a cost that is paid for borrowing money, or additional money earned on savings. The two types of interest are simple and compound interest.
- Higher - exponential growthWhen a quantity increases by a consistent percentage of the original, over time, meaning that the amount it increases by gets larger each time. It produces a j-shaped graph. and exponential decayWhen a quantity decreases by a consistent percentage of the original, over time, meaning that the amount it decreases by gets smaller each time. can be represented by the equation 𝑦 = 𝑎 × 𝑘\(^𝑥 \), where 𝑦 is the new value, 𝑎 is the starting value and 𝑘 is the growth or decay factor.
Make sure you can calculate a percentage increase and decrease using decimal multiplierA decimal that multiplies an amount. The decimal has usually been converted from a percentage. For example, in the calculation 80 × 0∙2, the multiplier is 0∙2..
Check your understanding
Video - Calculating percentages
Watch this video to learn some useful ways to help you with calculating percentages: the number swap hack and the decimal multiplier hack.
Calculating percentages is something you should be confident about.
Here's a couple of hacks to make them easier and faster to solve.
Firstly, when asked to find the percentage of a number, here's a handy trick for you.
Swap the numbers around.
So, what's 14% of 50?
It's tricky, right?
But if you swap the numbers to work out 50% of 14, this will give you the same answer.
50% of 14 is 7, and 14% of 50 is also 7.
Pretty cool right?
It's all because 𝑥% of 𝑦 gives you the exact same answer as 𝑦% of 𝑥.
And this method will work with any percentage conversion.
12% of 75?
Swap it round to 75% of 12 and now you need to find 3 quarters of 12, which is 9, and 9 is also 12% of 75.
Okay here's another hack that's very useful when increasing or decreasing the value by a percentage.
It's called the decimal multiplier hack.
Every percentage has an equivalent decimal value.
If your favourite shop sends you an email offering you a 20% discount, you can use this hack to work out the new price of an item you want.
To decrease something by 20%, you multiply by the decimal equivalent of 80% because 80% is 20% less than the original amount, 100%.
80% as a decimal is 80 divided by 100, which equals 0·8.
Let's say that £40 top you've got your eye on, is reduced by 20%.
You have to multiply 40 by 80% as a decimal, which is 0·8.
40 times 0·8 equals £32.
And to increase by a percentage is similar.
For example, train tickets often go up in price during peak travel times.
If you wanted to increase a value by 30%, you need to multiply by the decimal equivalent of 130%, as this is 30% more than the original amount - 100%.
130% as a decimal is 130 divided by 100, which equals 1·3.
So, if we want to increase 80 by 30%, you have to multiply 80 by 1·3, which equals 104.
Successive percentage change
Successive percentage change is when an amount is increased or decreased by one percentage, then increased or decreased by another.
The most efficient way to work with more than one percentage change is to use decimal multiplierA decimal that multiplies an amount. The decimal has usually been converted from a percentage. For example, in the calculation 80 × 0∙2, the multiplier is 0∙2. for each stage.
To increase an amount by 35%, the decimal multiplier is 1·35.
- This is because 100% + 35% = 135%.
- 135 ÷ 100 = 1·35
To decrease an amount by 35%, the decimal multiplier is 0·65.
- This is because 100% – 35% = 65%.
- 65 ÷ 100 = 0·65
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- There are 850 visitors to a museum on Monday.
On Tuesday, the number of visitors increases by 20%.
On Wednesday, the number of visitors increases again, but by 5%.
How many visitors were there on Wednesday?
1071
- Increase 850 by 20%.
There are 850 × 1·2 = 1020 visitors on Tuesday. - Increase 1020 by 5%.
There are 1020 × 1·05 = 1071 visitors on Wednesday.
This could be done in one calculation:
850 × 1·2 × 1·05 = 1071
Remember: A 20% increase followed by a 5% increase is not a 25% increase overall.
The combined decimal multiplier is:
1·2 × 1·05 = 1·26
So, there is actually a 26% overall increase.
- Ellie’s salary starts at £46,000.
At the end of the first year, her wage decreases by 5%.
At the end of the second year, her wage increases by 10%.
What is her salary at the end of the second year?
£48,070
- At the end of the first year, her wage is:
£46,000 × 0·95 = £43,700 - At the end of the second year, her wage is:
£43,700 × 1·1 = £48,070
This could be done in one calculation:
£46,000 × 0·95 × 1·1 = £48,070
Remember: a 5% decrease followed by a 10% increase is not a 5% increase overall.
The combined decimal multiplier is:
0·95 × 1·1 = 1·045
So, there is actually a 4·5% overall increase.
Repeated percentage calculations
When a percentage calculation is applied more than once, it can often be more efficient to work out the final result using decimal multiplierA decimal that multiplies an amount. The decimal has usually been converted from a percentage. For example, in the calculation 80 × 0∙2, the multiplier is 0∙2. and index (plural indices)Positioned above and to the right of a number. It is an abbreviation of repeated multiplication, eg 7³ means 7 × 7 × 7. An index may be positive, negative, zero or fractional. Indices are also referred to as powers or exponents..
Instead of multiplying by the decimal over and over again, the decimal multiplier can be power (raised to)A number that is multiplied by itself one or more times is raised to a power. 𝑛⁴ is ‘𝑛 to the power of 4’ and means 𝑛 × 𝑛 × 𝑛 × 𝑛. The power is the value of the index or exponent..
For example, to increase an amount by 27% three times, the following methods give the same result:
- Multiply by 1·27 × 1·27 × 1·27.
- Multiply by 1·27³.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
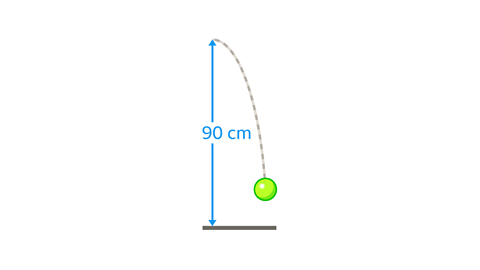
- A ball bounces to 80% of its original height every time it bounces.
If it is bounced from a height of 90 cm, after how many bounces does it stop reaching a height of 40 cm?
4 bounces
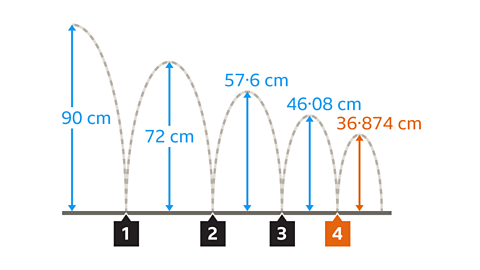
To find 80% of the height, use the decimal multiplier 0·8.
- After 1st bounce: 90 × 0·8 = 72 cm.
- After 2nd bounce: 90 × 0·8² = 57·6 cm.
- After 3rd bounce: 90 × 0·8³ = 46·08 cm.
- After 4th bounce: 90 × 0·8⁴ = 36·864 cm, which is under 40 cm.
This could also be found by multiplying by 0·8 repeatedly.
- The value of a ring is £8000.
It depreciationA decrease in value. If the value of something depreciates by 5%, it decreases by 5%. by 15% each year.
How much is the ring worth after 3 years?
£4913
Depreciates means to decrease in value.
To decrease by 15%, use the decimal multiplier 0·85.
- After 1 year, the ring is worth
£8000 × 0·85 = £6800 - After 2 years, the ring is worth
£6800 × 0·85 = £5780 - After 3 years, the ring is worth
£5780 × 0·85 = £4913
The most efficient way to reach the answer is:
£8000 × 0·85³ = £4913
- A salary increases by 4% every year.
With a starting salary of £24,000, how much will the salary be after 5 years?
Give your answer to the nearest pound.
£29,200
The decimal multiplier is 1·04.
£2400 × 1·04 × 1·04 × 1·04 × 1·04 × 1·04
= £24000 × 1·04⁵
= £29,199·67
This is £29,200 to the nearest pound.
Simple and compound interest
interestA cost that is paid for borrowing money, or additional money earned on savings. It is often calculated ‘per annum’ (per year). is money that is paid or charged regularly when money has been invested (saved) or borrowed.
A bank pays its customers interest on their savings at a certain percentage rate. Banks charge interest to anyone who borrows money using a credit card or loanMoney that is borrowed with an agreement to pay it back..
Interest on loans is often added monthly.
The rate of interest is mostly calculated per annum, which means ‘per year’.
Simple interest is calculated by working out a percentage of the borrowed or invested money using the interest rateThe percentage used to calculate the amount of interest on a loan or savings. . The interest stays the same every time it is added.
Compound interestaccumulatesBuilds up and grows over time., which means that every time interest is added, it is calculated based on the latest amount.
Calculating compound interest involves repeated percentage changeWhen the same percentage calculation is applied more than once on an amount. because the amount grows by the interest rate each time. Using a decimal multiplierA decimal that multiplies an amount. The decimal has usually been converted from a percentage. For example, in the calculation 80 × 0∙2, the multiplier is 0∙2.power (raised to)A number that is multiplied by itself one or more times is raised to a power. 𝑛⁴ is ‘𝑛 to the power of 4’ and means 𝑛 × 𝑛 × 𝑛 × 𝑛. The power is the value of the index or exponent. allows for a more efficient way to find the total amount.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions

- Sam wants to invest £4000.
Which account should they choose in order to have the most money after 5 years?
Account A: 3% simple interest per annum
Account B: 2·6% compound interest per annum
They should choose account A.
Account A:
- Find the simple interest by using the multiplier 0·03:
£4000 × 0·03 = £120 per year. - Find the total interest over 5 years:
£120 × 5 = £600 - Add the total interest to the original investment:
£4000 + £600 = £4600
Account B:
- Work out the decimal multiplier to increase by 2·6%:
100% + 2·6% = 102·6% = 1·026 - Multiply £4000 by the decimal multiplier five times. Raise 1·026 to the power 5 to do this most efficiently:
£4000 × 1·026⁵ = £4547.75
The figure for account A is higher.
- £7000 is invested in a savings account that pays 2·5% compound interest per annum.
How much is in the account after 3 years?
Use the decimal multiplier method on a calculator to work this out.
£7538.23
The decimal multiplier to increase by 2·5% is:
100% + 2·5% = 102·5% = 1·025
Increase the investment by 2·5% each year:
£7000 × 1·025 × 1·025 × 1·025
= £7000 × 1·025³
= £7538.23 (to the nearest penny)
- The total amount of a loan after 3 years is £4287.65.
The loan has a compound interest rate of 7% per annum.
What was the initial loan amount?
£3500
This is a reverse percentage problem.
Let 𝑥 be the initial loan amount at the start.
Set up an equation to show the total amount after 3 years.
𝑥 × 1·07³ = 4287·65Solve the equation by dividing both sides by 1·07³.
𝑥 = 4287·65 ÷ 1·07³ = £3500
For extra practice look at this guide on reverse percentages.
Quiz – Repeated percentage change, simple and compound interest
Practise what you've learned about repeated percentage change and interest with this quiz.
Compound interest – interactive activity
This interactive activity will help you understand how to work out the value of a compound interest calculation based on the initial amount, percentage change and number of repetitions.
Higher – Exponential growth and decay
exponential growthWhen a quantity increases by a consistent percentage of the original, over time, meaning that the amount it increases by gets larger each time. It produces a j-shaped graph. occurs when a value keeps increasing by the same scale factor.
compound interestCompound interest is interest that accumulates. Every time interest is added, it is calculated based on the latest amount and so the amount added increases each time. is an example of exponential growth.
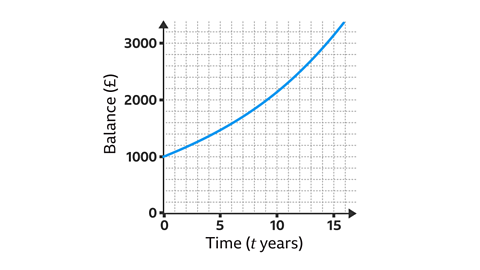
If £1000 is invested into an account offering 8% compound interest each year, the balance would be:
1000 × 1·08\(^𝑡 \) after 𝑡 years.
This graph shows the balance over time. The starting value is £1000, and the decimal multiplier of 1·08 shows the growth of 8% each year:
Exponential equations are of the form 𝑦 = 𝑎 × 𝑘\(^𝑥 \) where 𝑦 is the new value, 𝑎 is the starting value and 𝑘 is the decimal multiplier that describes the growth or decay.
If 𝑘 > 1, the equation shows exponential growth, eg interestA cost that is paid for borrowing money, or additional money earned on savings. It is often calculated ‘per annum’ (per year). or population growth.
If 0 < 𝑘 < 1, the equation shows exponential decayWhen a quantity decreases by a consistent percentage of the original, over time, meaning that the amount it decreases by gets smaller each time. , eg depreciationA decrease in value. If the value of something depreciates by 5%, it decreases by 5%. or radioactive decay.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions

- The value, 𝑉, of a new motorbike after 𝑡 years is shown on the graph, and given by:
𝑉 = 15,000 × 0·92\(^𝑡 \)
What is the original value of the motorbike, and by what percentage does it depreciate each year?
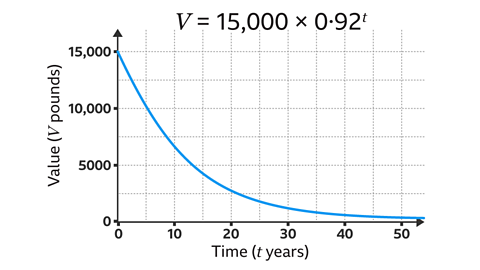
The original value is £15,000 and the value depreciates by 8% each year.
- To find the starting value, find the value of
𝑉 when 𝑡 = 0:
𝑉 = 15,000 × 0·92⁰
= 15,000 × 1
= 15,000
This is the 𝑦-intercept on the graph.
- The multiplier of 0·92 shows that each value is 92% of the previous year.
This means the motorbike’s value is depreciating (decreasing) by 8% each year.
- A population of rare butterflies is decreasing exponentially at a rate of 20% each year.
The population is currently 240,000.
After how many years will there be fewer than 100,000 butterflies?
4 years
Multiply 240,000 by the decimal multiplier 0·8 raised to different powers until the answer drops below 100,000.
- After 3 years, the population would be:
240,000 × 0·8³ = 122,880 - After 4 years, the population would be:
240,000 × 0·8⁴ = 98,304
This is below 100,000.
- A population of rabbits increases exponentially. There were originally 400 rabbits. After 2 years there were 441 rabbits.
How many rabbits will there be after 6 years?
536
Set up an equation to find the growth rate, 𝑘.
400 × 𝑘² = 441Divide both sides by 400 to give 𝑘².
𝑘² = 441 ÷ 400
𝑘² = 1·1025Square root both sides to find 𝑘.
𝑘 = √(1·1025) = 1·05Write an equation for the number of rabbits, 𝑁.
𝑁 = 400 × 1·05\(^𝑡 \)
After 6 years, 𝑡 is 6.
- Substitute the value of 6 in place of 𝑡.
𝑁 = 400 × 1·05⁶ = 536 to the nearest integer.
Higher – Quiz – Interest and exponential change
Practise what you've learned about interest and exponential change with this quiz for Higher tier.
Now you've revised repeated percentage change, interest and exponential change, why not look at this guide on laws of indices?
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Ratio, proportion and rates of change
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 8

- count8 of 8