Key points
All quadrilateralA 2D shape with 4 edges and 4 vertices. are polygonA closed 2D shape bounded by straight lines. with four edgeSide of a polygon or a 3D shape.. They are classified by the comparative lengths and position of their edges.
The angles in a quadrilateral always sum to 360°.
The properties of a quadrilateral include additional facts relating to their diagonalsA line joining two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of a polygon. and their line of symmetryAn imaginary line which splits a shape equally in two, where both sides are a reflection of each other..
A specific property may apply to more than one quadrilateral.

Properties of squares, rhombuses, and rectangles
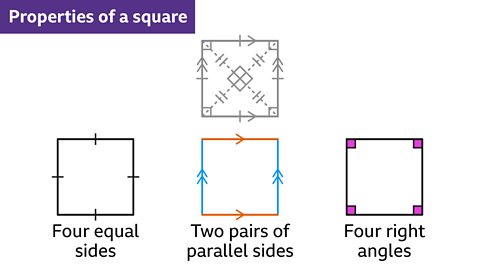
To classify a quadrilateralA 2D shape with 4 edges and 4 vertices. as a squareA regular quadrilateral. All four sides are equal in length and all four angles are right angles. a rhombusA quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. All sides are equal. Opposite angles are equal. or a rectangleA quadrilateral with opposite pairs of sides that are both equal in length and parallel. All four angles are right angles., check for the following properties.
A square has:
- Four sides equal in length.
- Two pairs of parallel sides.
- Four right angles.
- diagonalsA line joining two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of a polygon. that are equal in length.
- Diagonals that bisectTo divide into two equal sections, cut in half. each other and are perpendicularPerpendicular lines are at 90° (right angles) to each other. .
- Four line of symmetryAn imaginary line which splits a shape equally in two, where both sides are a reflection of each other..
- rotational symmetryA 2D shape has rotational symmetry about a point if it looks the same after a rotation through an angle greater than 0° and less than 360° about that point. of order (eg '4')Used to describe rotational symmetry. A shape, such as a square, has order 4 rotational symmetry, for example, because it will fit into its outline four times in a complete turn.
A rhombus has:
- Four sides equal in length.
- Two pairs of parallel sides.
- Two pairs of equal opposite angles.
- Diagonals that bisect each other and are perpendicular.
- Two lines of symmetry.
- Rotational symmetry of order 2
A rectangle has:
- Two pairs of opposite sides that are equal in length.
- Two pairs of parallel sides.
- Four right angles.
- Diagonals that are equal in length.
- Diagonals that bisect each other.
- Two lines of symmetry.
- Rotational symmetry of order 2
Examples
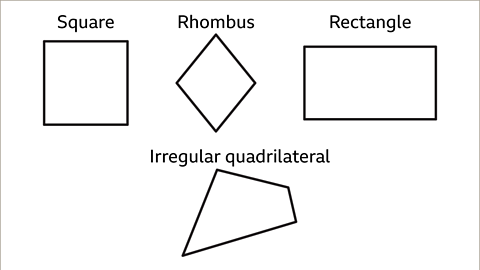
Image caption, All quadrilaterals have four sides and four angles. The lengths and position of the edges help to identify the quadrilateral. A quadrilateral that is not a specific type is called an irregular quadrilateral.
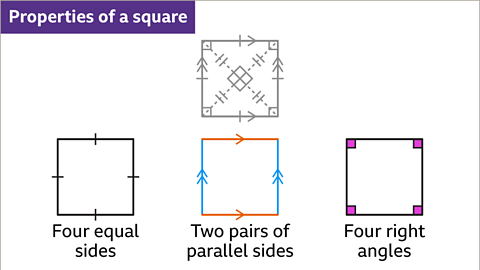
Image caption, A square has four sides that are equal in length. Equal lengths are shown on the diagram by hash marks annotated on each side. The opposite sides are parallel, meaning the square has two pairs of parallel sides. The parallel sides are annotated with matching arrowhead(s) in the same direction. The angles are all right angles. The right angles are marked on the diagram as a small square at each vertex.
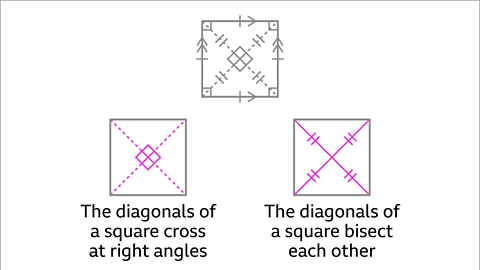
Image caption, The diagonals of a square are equal in length. The diagonals are perpendicular, they cross at right angles. The diagonals of a square bisect each other, that means they cut each other in half.
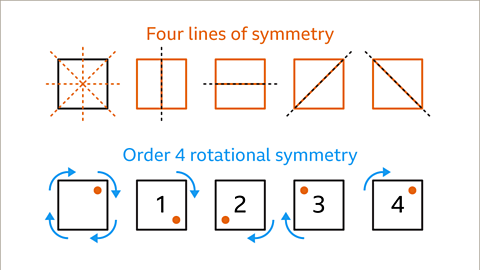
Image caption, A square has four lines of symmetry. There are four ways the square can be cut into a pair of mirrored halves. Two lines of symmetry go through the midpoints of the opposite parallel sides and two go along the diagonals of the square. There are four ways in which the square can be cut into reflecting halves. A square has order 4 rotational symmetry, it will fit into its outline four times in a complete turn.
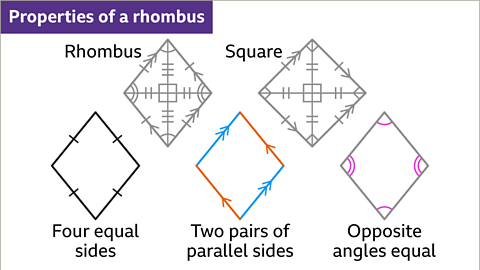
Image caption, A rhombus has four sides equal in length. The opposite sides are parallel, meaning the rhombus has two pairs of parallel sides. Opposite angles are equal. When the angles are 90° the rhombus becomes a square.

Image caption, The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular, they cross at right angles. When the diagonals of a rhombus are equal the rhombus becomes a square. The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other.
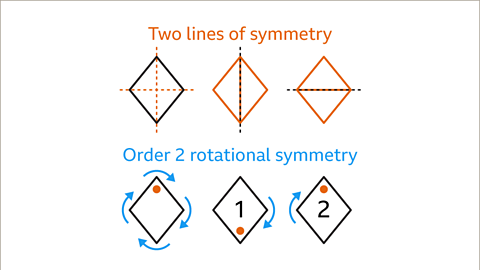
Image caption, A rhombus has two lines of symmetry. There are two ways the rhombus can be cut into a pair of mirrored halves. The lines of symmetry follow the diagonals of the rhombus. A rhombus has rotational symmetry of order 2. It will fit into its outline twice in a full turn.
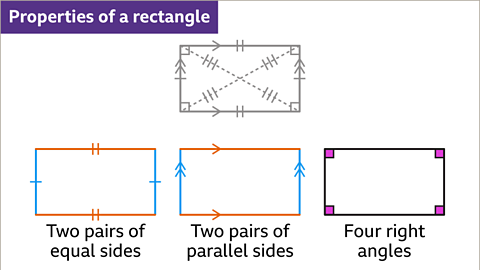
Image caption, A rectangle has two pairs of equal parallel sides. When the sides are all equal the rectangle is a square. When the sides are not equal in length the rectangle is an oblong. The angles in a rectangle are all 90°.
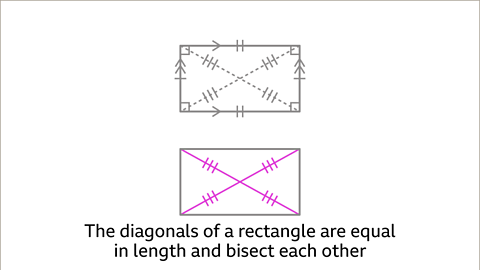
Image caption, The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length. They bisect each other.
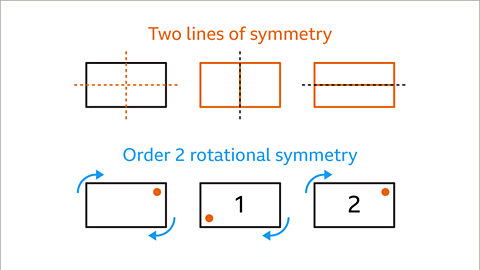
Image caption, A rectangle has two lines of symmetry. There are two ways the rectangle can be cut into a pair of mirrored halves. The lines of symmetry pass through the midpoints of the opposite parallel sides. A rectangle has rotational symmetry of order 2. It fits into its outline twice in a full turn.
1 of 10
Question
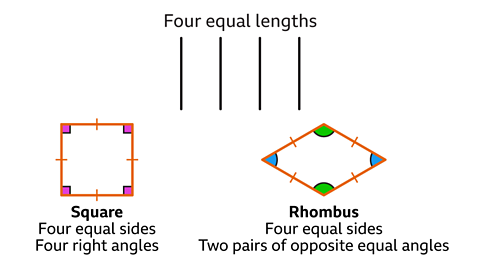
Name a polygon with four sides that are all equal in length.
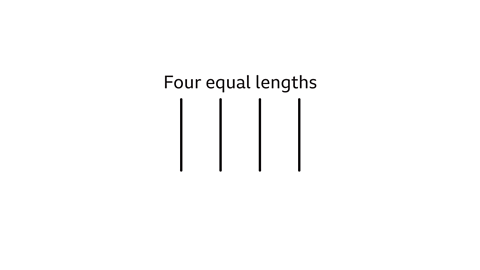
A polygon with four sides is a quadrilateral.
Four equal lengths can form two different quadrilaterals.
The quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles is a square.
The quadrilateral with four equal sides and two pairs of opposite equal angles is a rhombus.
Properties of parallelograms, kites and trapeziums
To classify a quadrilateralA 2D shape with 4 edges and 4 vertices. as a parallelogramA quadrilateral with opposite pairs of sides that are both equal in length and parallel. Opposite angles are equal., trapeziumA quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. or a kiteA quadrilateral with adjacent pairs of sides that are equal in length. One pair of opposite angles are equal. , check for the following properties.
A parallelogram has:
- Two pairs of opposite sides that are equal in length.
- Two pairs of parallel sides
- Two pairs of equal opposite angles
- diagonalsA line joining two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of a polygon. that bisectTo divide into two equal sections, cut in half. each other.
- No reflection symmetry
- rotational symmetryA 2D shape has rotational symmetry about a point if it looks the same after a rotation through an angle greater than 0° and less than 360° about that point. of order (eg '4')Used to describe rotational symmetry. A shape, such as a square, has order 4 rotational symmetry, for example, because it will fit into its outline four times in a complete turn. 2
A kite has:
- Two pairs of adjacentTwo angles or sides that lie next to each other. sides that are equal in length.
- One pair of opposite equal angles.
- Diagonals that are unequal in length.
- One diagonal is bisected by the other.
- One line of symmetry.
- Rotational symmetry of order 1
A trapezium has:
- One pair of unequal parallel sides.
- Diagonals that are not equal in length.
- No reflection symmetry
- No rotational symmetry.
An isosceles trapezium has:
- One pair of unequal parallel sides.
- Two non-parallel equal sides.
- Two pairs of adjacent equal angles.
- Diagonals that are equal in length.
- One line of symmetry.
- No rotational symmetry.
Examples

Image caption, Parallelograms, kites and trapeziums have four sides and four angles. The lengths and position of the edges help to identify the quadrilateral.
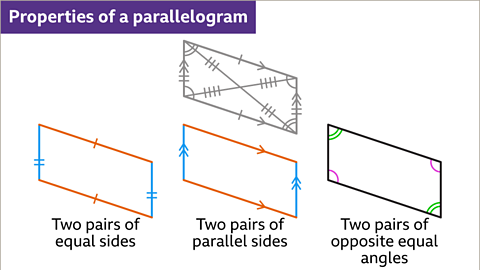
Image caption, A parallelogram has two pairs of equal and parallel sides. When the lengths are equal the parallelogram is a rhombus. A parallelogram has two pairs of equal angles. The opposite angles in a parallelogram are equal. When the angles are 90° the parallelogram is a rectangle. When the sides are all equal and the angles are all 90° the parallelogram is a square.
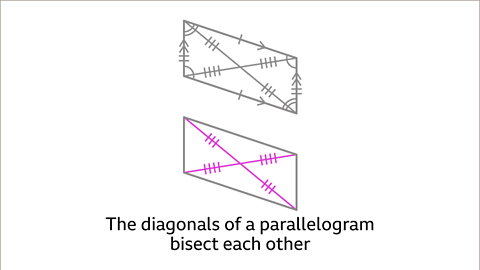
Image caption, The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. When the diagonals are equal in length the parallelogram is a rectangle.
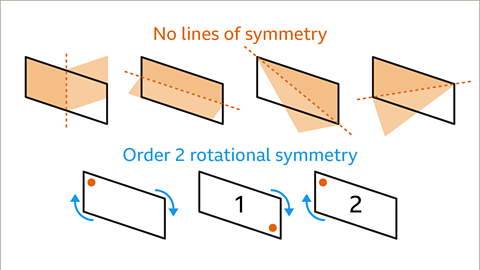
Image caption, A parallelogram has no line symmetry. It is not possible to cut a parallelogram into two mirrored halves. A parallelogram has order 2 rotational symmetry and fits into its outline twice in a full turn.
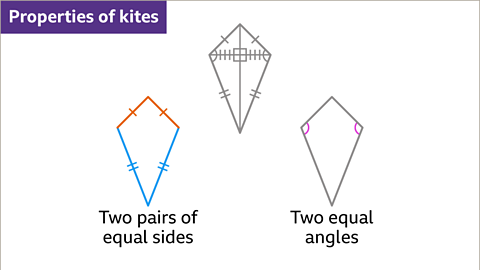
Image caption, A kite has two pairs of equal adjacent sides. The equal sides are next to each other. When the sides are equal in length the kite is a rhombus. A kite has two equal angles.
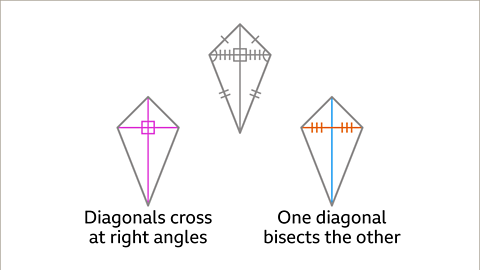
Image caption, The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, they cross at right angles. One of the diagonals is bisected by the other.
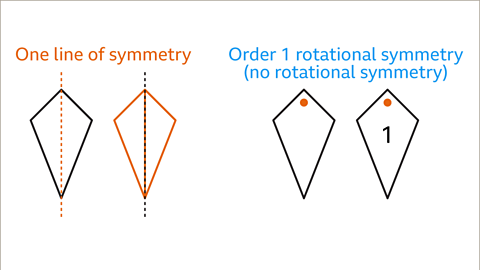
Image caption, A kite has one line of symmetry. There is one way that a kite can be cut into a pair of mirrored halves. A kite has rotational symmetry of order 1, it only fits into its outline in one position. This means that a kite does not have rotational symmetry.
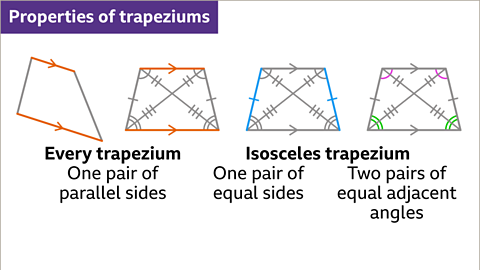
Image caption, Every trapezium has one pair of unequal parallel sides. An isosceles trapezium also has two equal sides and two pairs of equal adjacent angles.

Image caption, The diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are equal in length. This is not true for other trapeziums.
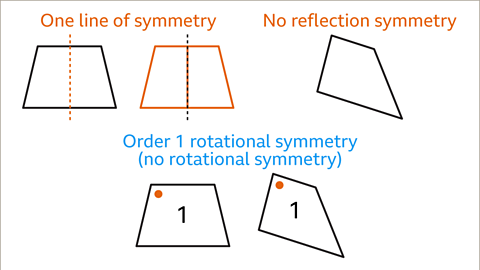
Image caption, An isosceles trapezium has one line of symmetry. There is one way to cut the shape into a pair of mirrored halves. Trapeziums do not have line symmetry or rotational symmetry.
1 of 10
Questions
Question 1: Which quadrilaterals have exactly one line of symmetry?
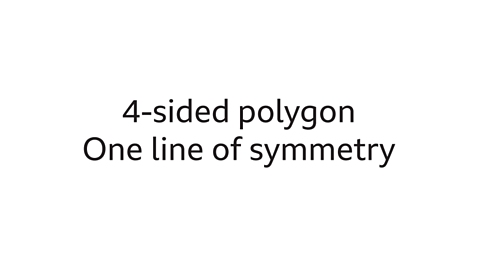
The quadrilaterals with exactly one line of symmetry are a kite and an isosceles trapezium.
The line of symmetry cuts the shape into two mirrored halves.
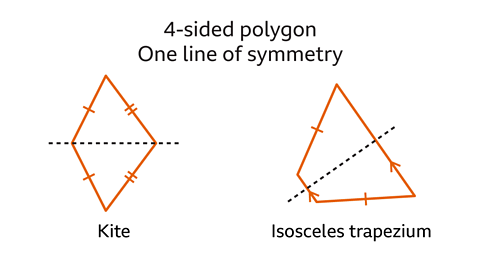
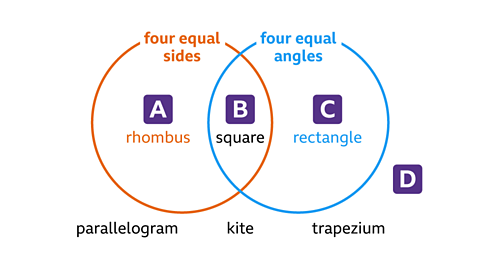
Question 2: On a copy of the Venn diagram, place the quadrilaterals square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, kite and trapezium in the correct regions.
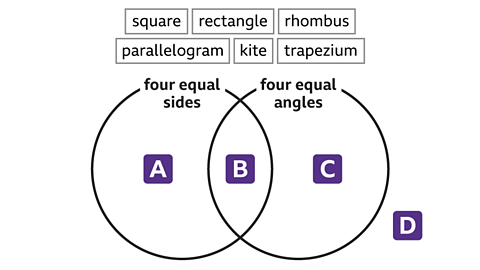
Region A contains the rhombus, it has four equal sides and does not have four equal angles.
Region B contains the square, it has four equal sides and four equal angles.
Region C contains the rectangle, it has four equal angles and does not have four equal sides.
Region D contains the parallelogram, the kite and the trapezium. These quadrilaterals do not have four equal sides, they do not have four equal angles.
Identifying quadrilaterals by their properties
To identify a quadrilateral by a property, keep the following in mind.
- Consider known facts:
- equal side lengths
- parallel sides
- equal angles
- diagonal properties
- reflection symmetry
- rotational symmetry
Remember: a property may apply to more than one quadrilateral.
Examples
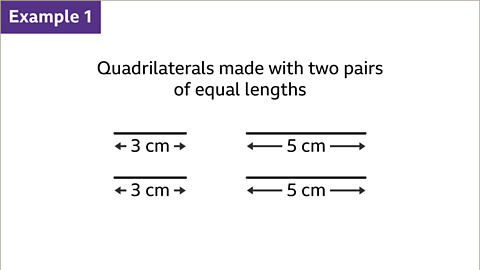
Image caption, What quadrilaterals can be created from two lines that are 3 cm long and two lines that are 5 cm long?
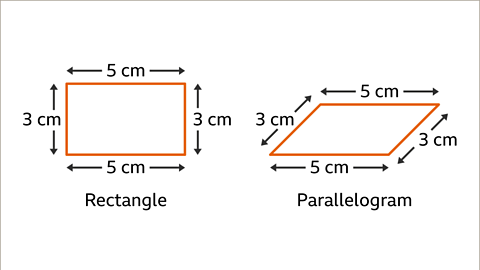
Image caption, The quadrilaterals with two pairs of opposite equal lengths are a rectangle and a parallelogram. The rectangle and the parallelogram both have opposite equal sides. The rectangle and the parallelogram both have two pairs of parallel sides. The rectangle has 90° angles, the parallelogram has two pairs of equal opposite angles. There is another quadrilateral that can be formed.
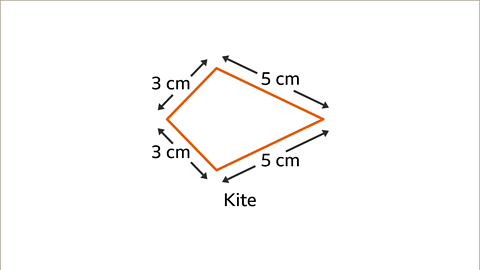
Image caption, When the two equal lines are placed next to each other, the quadrilateral is a kite. A kite has two pairs of equal adjacent sides.
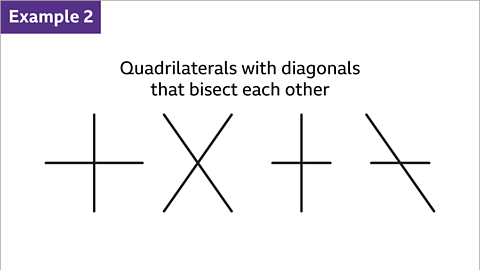
Image caption, Work out which quadrilateral has diagonals that bisect each other.
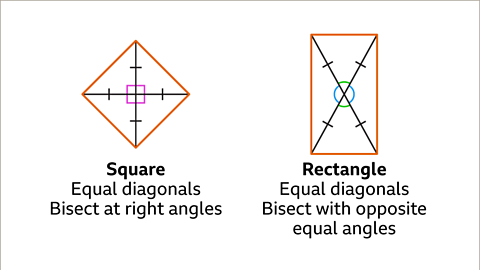
Image caption, When the diagonal lengths are equal, the quadrilateral may be a square or a rectangle. The diagonals of a square bisect each other at right angles. The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other. The angles where the diagonals cross are not right angles, the opposite angles are equal. There are other quadrilaterals whose diagonals bisect each other.
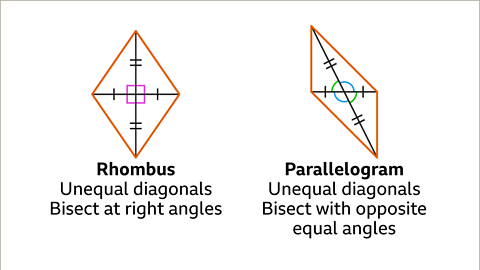
Image caption, When the diagonal lengths are unequal, the quadrilateral may be a rhombus or a parallelogram. The diagonals of a rhombus are unequal and bisect each other at right angles. The diagonals of a parallelogram are unequal and bisect each other. The angles where the diagonals cross are not right angles, the opposite angles are equal.
1 of 6
Practise finding the properties of quadrilaterals
Practise working out properties of quadrilaterals with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Quiz
Real-life maths

Properties of quadrilateralA 2D shape with 4 edges and 4 vertices. can be important in design. All quadrilaterals can tessellate. This means a single quadrilateral can be used to create a repeating pattern to cover a surface with no gaps. Geometric wallpaper and fabric designs often show tessellating patterns.
Quadrilaterals are used as the default shapes in all sorts of design software, including gaming, architecture, fashion and laser printing. A ‘basket weave’ design for use on fabric, wallpaper or even a web page is created by a series of rectangles, for example.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Shapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4

- count4 of 4
- count1 of 4