Key points
- A 3DThree-dimensions, length, width, and height. shape can be made from a 2DTwo-dimensions, length, and width. shape called a netA group of joined 2D shapes which fold to form a 3D shape..
- The two-dimensional shapes that form a net can be arranged in different ways for a particular 3D shape. The relationship of faces, vertexThe point where two lines meet is called the vertex. In a 3D shape this is the corner point. and edges must remain the same. There are eleven different nets that will form a cube.
- An isometric gridA pattern of lines or dots arranged at regular intervals and angles of 60°. A useful background for drawing three dimensional (3D) objects. is used as a guide for drawing a 3D shape on paper.

Video
Watch the video to learn how 3D shapes, such as a cube, can be created from nets, an arrangement of 2D shapes.
Let's talk about nets. More specifically, mathematical nets.
A net in maths is a flat 2D shape that can be cut out and folded to form the 3D shape. Put another way, a net is a plane figure composed of polygons, that by folding and joining can form a polyhedron.
A net will always be made up of the same number of connected 2D shapes as there are faces on the 3D shape, excluding folding flaps of course.
For example, this cube net becomes this die. Or this cuboid net could become this shipping container.
The net of a triangular prism will be made of three rectangles and two triangles - a bit like a tent.
And the net of these pyramids will become, well, The Pyramids!
How to draw the net of a cube and a cuboid
To draw a net of a cubeA 3D shape with six square faces. or a cuboidA 3D shape with six rectangular faces. The opposite faces are congruent., imagine the 3DThree-dimensions: length, width and height. shape is being unfolded. Each face is a rectangleA quadrilateral with opposite pairs of sides that are both equal in length and parallel. All four angles are right angles. or square.
Draw the base faceThe face that the shape rests on. , which has the same dimensions as the top face.
Draw the faces that are attached to the base face.
Draw the top face attached to an edge of the front or back, or left or right face.
The top face must not touch the base face at all (edge or vertex). The top and base faces do not touch on the 3D shape, this is also true on the net.
The net of a cube is called a hexomino. Hex is a prefix in Greek meaning 'six'. The net is made up of six congruent squares joined together along their edges. There are eleven different ways of arranging the square for a correct net of a cube.
Examples
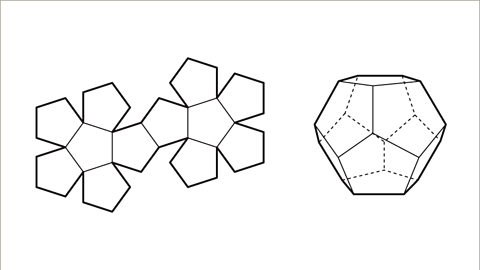
Image caption, A net is a 2D shape that folds to make up a 3D shape. The net of a dodecahedron (a platonic solid with twelve pentagonal faces) is made up of 12 regular pentagons.
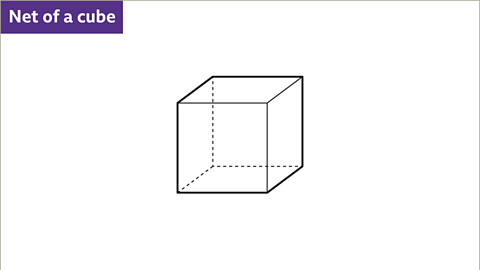
Image caption, Draw the net of a cube.
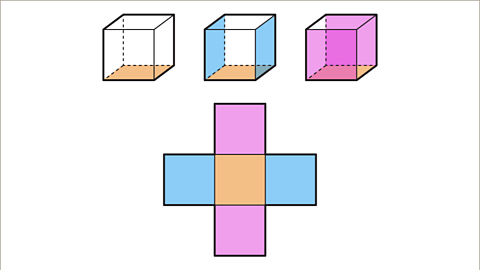
Image caption, A cube has six faces. The net of a cube is made up of six squares. First draw the square base face. Then draw the faces that are attached to the base face. These are the front and back face and the left and right faces.
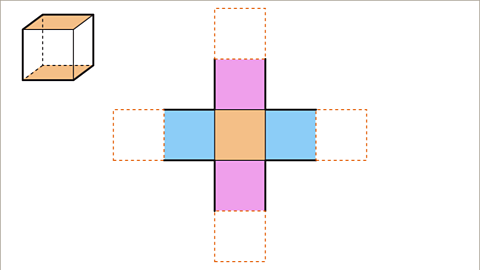
Image caption, The sixth square on the net is the top face. There are several possible positions for the top face. The top face may be attached to an edge of the front or back or left or right face. The top face of the cube does not touch the base face. On the net the top face must not touch an edge or a vertex of the base face.
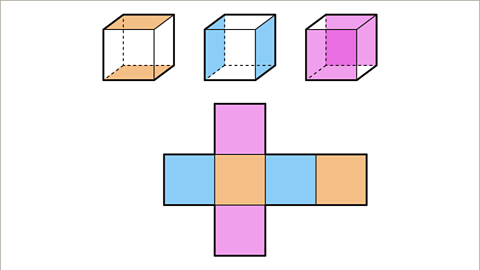
Image caption, This net is in the shape of a cross. The opposite faces of the cube are not next to each other on the net.
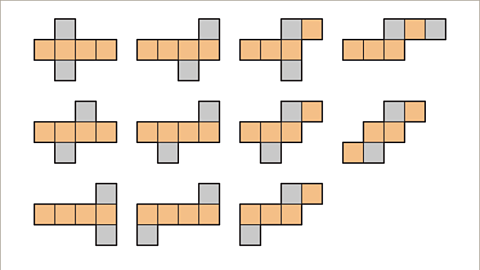
Image caption, There are eleven possible nets that will form a cube.
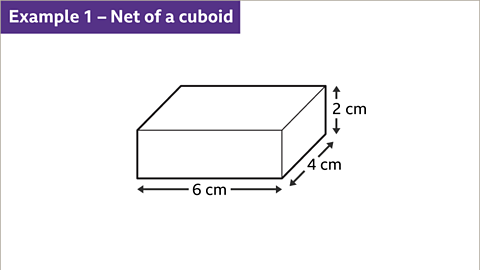
Image caption, Draw the net of a 6 cm by 2 cm by 4 cm cuboid.
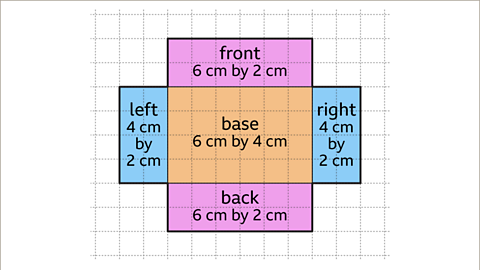
Image caption, First draw a rectangle for the base face. The base measures 6 cm by 4 cm. Then draw the faces that are attached to the base face. The left and right faces measure 4 cm by 2 cm. The front and back faces measure 6 cm by 2 cm.
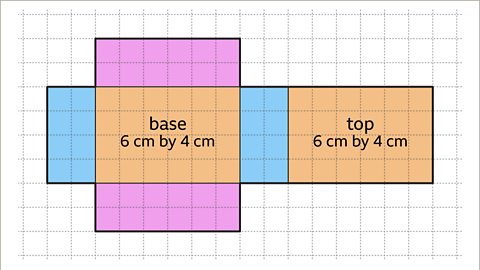
Image caption, The final rectangle on the net is the top face. There are several possible positions for the top face. The top face may be attached to an edge of the front or back or left or right face. The top face must not touch an edge or a vertex of the base face. The top face is congruent to the base face, it measures 6 cm by 4 cm. The net is complete.
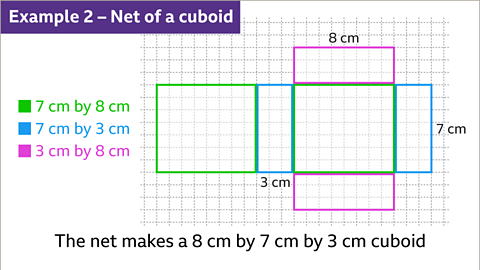
Image caption, The three rectangles used to make the cuboid net give the dimensions of the cuboid. The rectangles are 7 cm by 8 cm, 7 cm by 3 cm and 3 cm by 8 cm. The dimensions of the cuboid for this net are 7 cm, 8 cm and 3 cm. The length, width and height can be any combination of these measurements.
1 of 10
How to draw the nets of a prism and a pyramid
To draw the net of a triangular prismA 3D shape with a constant polygon cross-section.:
- The net is made up of three rectangles and two triangles.
- For a cross-sectionThe face that results from slicing through a solid shape. that is an equilateral triangle, the rectangles are congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical..
- For a cross-section that is an isosceles triangleTwo sides are equal in length. Two angles are the same size., two of the rectangles are congruent.
- For a cross-section that is a scalene triangleEach side is a different length. Each angle is a different size., the rectangles are all different.
- The rectangles are drawn next to each other, joined along the dimension that is the length of the prism.
- A triangle is drawn at each end of one of the rectangles, making sure that when folded the edge lengths match exactly.
To draw the net of a prism with a regular polygonA 2D shape with three or more edges and vertices. cross-section:
- The net is made up of congruent rectangles and two polygon ends.
- The number of rectangles is equal to the number of sides of the polygon. One dimension of a rectangle is the length of the prism, the other is the side-length of the polygon cross-section.
- The rectangles are drawn next to each other, joined along the dimension that is the length of the prism.
- The polygon is drawn at each end of one of the rectangles.
To draw the net of a pyramidA 3D shape with a polygon-shaped base and a pointed apex. Named by the shape of its base, such as square-based or hexagon-based.:
- The net is made up of the base polygon and congruent isosceles triangles attached to each side of the base.
- The measurements given are the side-length of the polygon and the height of each triangle. The height of the triangle is the slant heightOn a pyramid the height of an isosceles triangle face, the distance from the apex to the midpoint of the base. of the pyramid.
- Draw the base shape.
- On each side of the base draw an isosceles triangle.
Examples
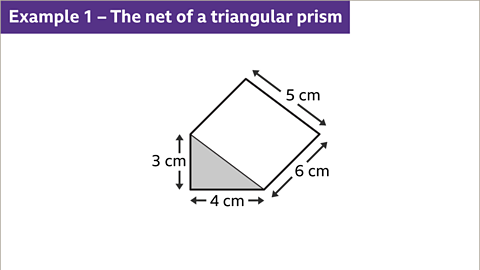
Image caption, Draw the net of a triangular prism.
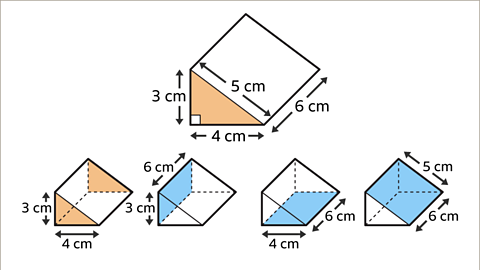
Image caption, The cross-section of the prism is a right-angled triangle with side-lengths 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm. The prism is 6 cm long. The net is made up of two right-angled triangles and three rectangles. The dimensions of the rectangles are 3 cm by 6 cm, 4 cm by 6 cm, and 5 cm by 6 cm.
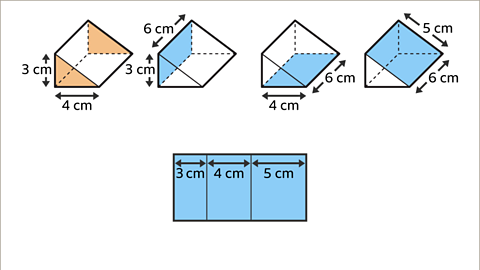
Image caption, Draw the three rectangles next to each other joined along the dimension that is the length of the prism (6 cm).
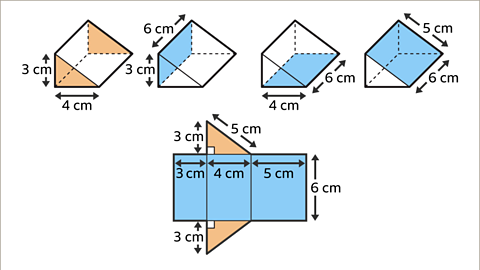
Image caption, Draw a right-angled triangle at opposite ends of a rectangle. The net is complete.
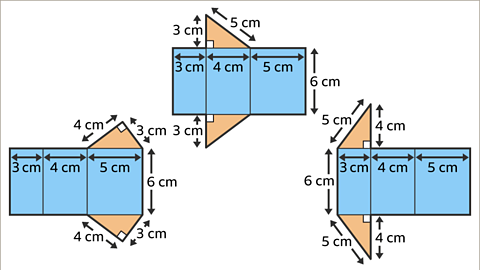
Image caption, The net may be drawn in more than one way.

Image caption, Sketch the net of a hexagonal prism.
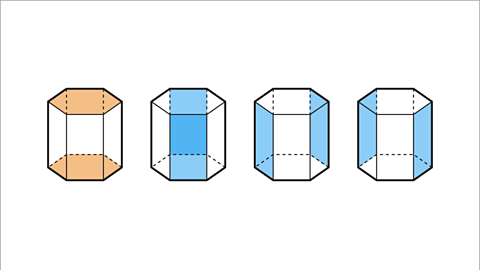
Image caption, There are no measurements on the 3D shape. The sketch will show the shapes used to form the net of the hexagonal prism. The cross-section of the prism is a regular hexagon. The net is made up of two hexagons and six rectangles.
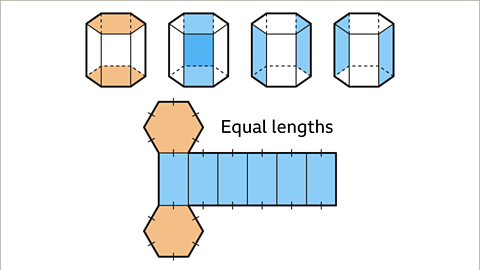
Image caption, Draw the six rectangles next to each other joined along the dimension that is the length of the prism (5 cm) and draw a hexagon at opposite ends of one of the rectangles. The net is complete.
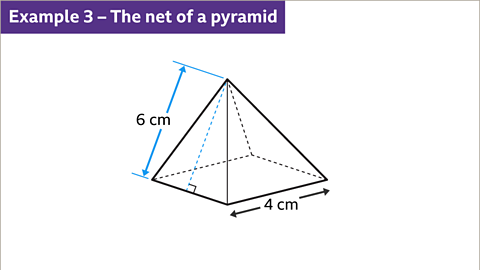
Image caption, Draw the net of a square-based pyramid. The square has sides-lengths of 4 cm, the slant height of the pyramid is 6 cm.
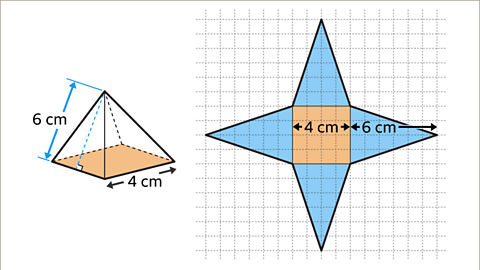
Image caption, The net is made up of a square and four congruent isosceles triangles. Draw the square 4 cm by 4 cm base and attach the four congruent isosceles triangles with base 4 cm and height 6 cm on each side of the square. The net is complete.
1 of 10
Question
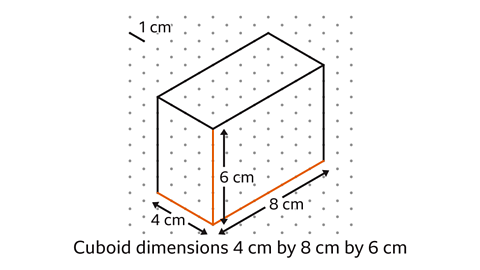
A cuboid is drawn on isometric paper. What are the dimensions of the cuboid?
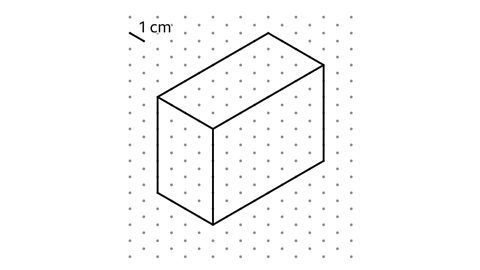
Each oblique line down from left to right is 4 cm long.
Each oblique line up from left to right is 8 cm long.
Each vertical line is 6 cm long.
The dimensions of the cuboid are 4 cm, 8 cm and 6 cm.
How to draw a 2D representation of a 3D shape
A 3D shape may be drawn on plain paper as a sketch or on an isometric gridA pattern of lines or dots arranged at regular intervals and angles of 60°. A useful background for drawing three dimensional (3D) objects..
To draw any 3D shape with a constant cross-sectionThe face that results from slicing through a solid shape. on plain paper:
- Use faint lines when drawing, so that they can be made heavier or lighter as needed when complete.
- Draw the shape of the cross-section.
- Draw the same shape higher and to the right of the original shape.
- Join the corresponding vertices.
- For a solid 3D shape, rub out the edges that would be hidden from view.
- For a skeleton 3D shape, make the hidden edges dotted lines.
To draw a cuboidA 3D shape with six rectangular faces. The opposite faces are congruent. on an isometric grid:
- First make sure the paper is the right way round. The correct orientation is when the longest line is vertical.
- Pick a dot, draw a vertical line for the height of the cuboid and draw oblique lineA line that is slanted, neither horizontal nor vertical. to the left and up, and to the right and up for the dimensions of the base of the cuboid.
- Draw vertical lines at the ends of the oblique lines.
- Draw the top face of the cuboid with two pairs of parallel lines.
Examples
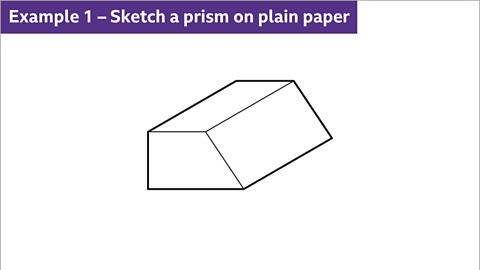
Image caption, Sketch a prism on plain paper.
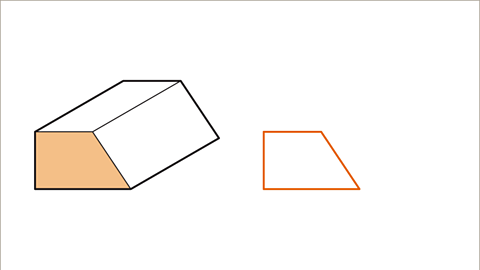
Image caption, Draw the shape of the cross-section. The shape of the cross-section is a trapezium. Use faint lines when drawing so that they can be made heavier or lighter as needed when complete.
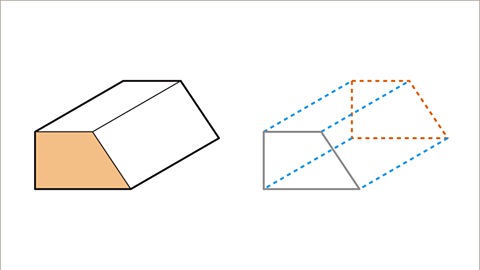
Image caption, Draw the same trapezium higher and to the right of the original shape and then join the corresponding vertices.
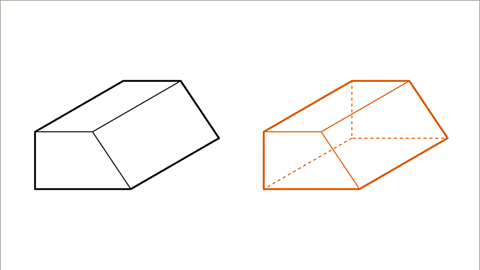
Image caption, For a solid 3D shape, rub out the edges that would be hidden from view. For a skeleton 3D shape make the hidden edges dotted lines.
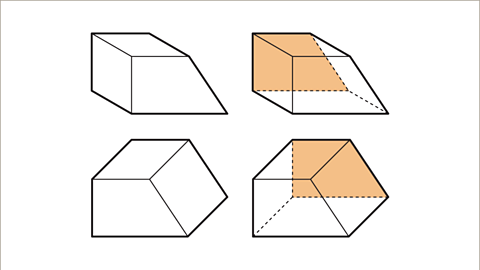
Image caption, Drawing the second trapezium in different positions gives a different result.
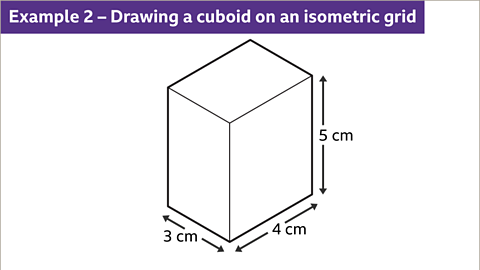
Image caption, Draw a 3 cm by 4 cm by 5 cm cuboid on isometric paper.
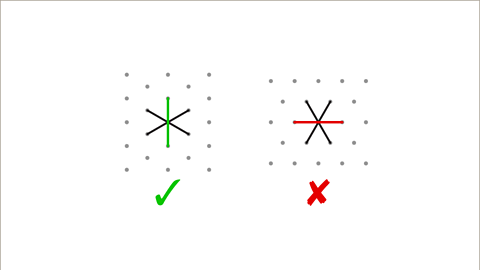
Image caption, First make sure the isometric grid is the right way round. Pick a dot and draw straight lines to the six nearest dots. The correct orientation is when the longest line is vertical. When a 3D shape is drawn on the grid, the lines will be drawn in the directions shown by the diagram used to orientate the paper. No horizontal lines are drawn. The dimensions of the cuboid are in centimetres. Treat the shortest gaps between the dots as 1 cm.
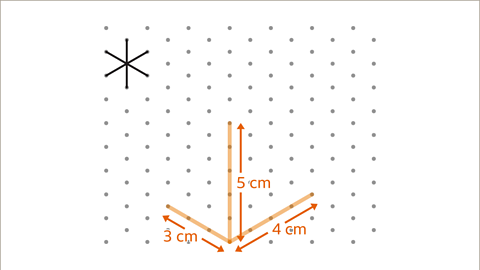
Image caption, Pick a dot and draw a vertical line to represent 5 cm for the height of the cuboid. Draw oblique lines representing 3 cm to the left and up and 4 cm to the right and up for the dimensions of the base of the cuboid.
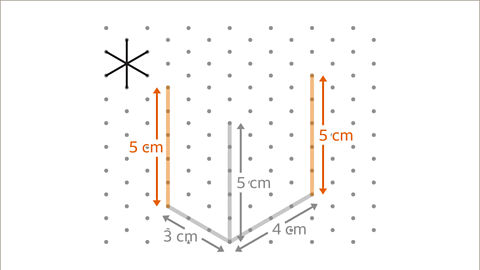
Image caption, Draw a vertical line at the end of each oblique line to show the 5 cm edges of the cuboid.
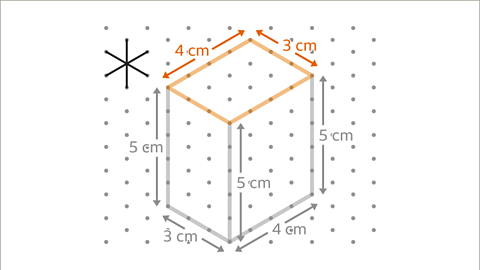
Image caption, Complete the cuboid by drawing the top face of the cuboid with two parallel 3 cm lines and two parallel 4 cm lines.
1 of 10
Question
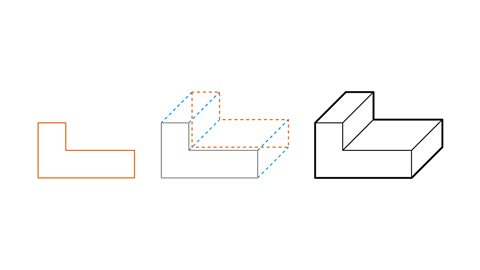
On plain paper draw a copy of this 3D shape.
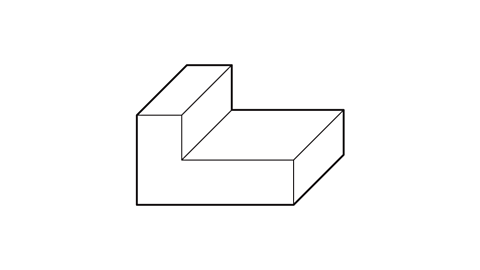
To draw the 3D shape:
Draw the front face of the 3D shape (this is an L-shape).
Draw a copy of the front face, up and to the right of the original.
Join corresponding vertices with straight lines.
Rub out the hidden line. The shape is complete.
Practise your understanding of 3D shapes and nets
Quiz
Practise applying your knowledge of 3D shapes and nets with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Real-life maths

Nets can be used in any organisation that packs goods. Flat cardboard is punched with nets that include flaps for fixing or with additional flaps for folding up into boxes.
The machinery used will punch out the net and fold it up into the box or container ready to be filled.
The design of the net is such that card waste is kept to a minimum and the fixing together of the net is straight forward. Some machines will staple the boxes, others will tape and others will fold without any other fixing.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Shapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 4
- count2 of 4
- count3 of 4
