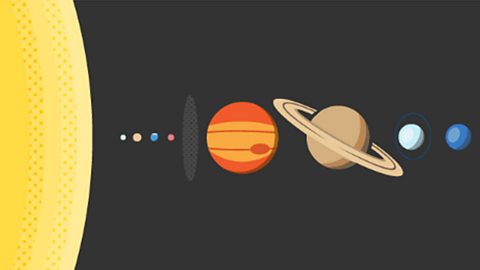
What are the key learning points about stars?
Formation of a solar systemA group of planets and other objects in space that revolve around a star. Earth is the third planet in orbit around the Sun in the Solar System..
Lifecycles of stars.
How was the Sun formed?
The Solar System was formed around 4.6 billion years ago from a giant cloud called a nebulaA cloud of gas and dust in outer space. If massive enough, these can collapse under gravity to form a protostar., mainly made up of hydrogen gas and dust.
The nebula collapsed under its own gravity and, as it did, temperature and pressure increased.
It became denser and rotated more rapidly, spiralling inwards.
The hot core in the centre is called a protostarThe early stage in the formation of a star, before nuclear fusion occurs..
The collapsing and joining together of gas and dust under gravity is called accretion.
Eventually gravity compressed the hydrogen so much that the temperature reached about 15 million °C.
At this temperature and pressure nuclear fusionThe joining together of two smaller atomic nuclei to produce a larger nucleus. Radiation is released when this happens. Nuclear fusion happens in stars like our sun, and in hydrogen bombs. began and our Sun was born.
It is therefore called a main sequenceA stable stage in the life cycle of a star. Nuclear fusion occurs, fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. There is a balance between the outwards thermal expansion and the force of gravity pulling inwards. star.
WATCH: How the Earth was formed
Brian Cox explains how the Earth was formed
In fusion reactions:
Hydrogen nucleiNuclei is the plural of nucleus. The nucleus is the central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons, and has most of the mass of the atom.fuse together to form helium nuclei.
Energy is released and radiates outwards.
A star, like the Sun, in its main sequenceA stable stage in the life cycle of a star. Nuclear fusion occurs, fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. There is a balance between the outwards thermal expansion and the force of gravity pulling inwards.period, is stable.
There are two equal and opposite forces acting on the star:
The inward force of gravity.
The outward force due to the thermal expansion from the nuclear reactions.
These forces are balanced, therefore the star remains the same size for most of its life.
The Sun is expected to be a main sequence star for billions of years.
What is the life cycle of stars? (Higher tier only)
The life cycle for a particular star depends on its size.
The diagram shows the life cycles of stars that are:
About the same size as the Sun.
Much greater than the Sun in size.
All stars begin life in the same way.
A cloud of dust and gas, also known as a nebula, becomes a protostarThe early stage in the formation of a star, before nuclear fusion occurs., which goes on to become a main sequenceA stable stage in the life cycle of a star. Nuclear fusion occurs, fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. There is a balance between the outwards thermal expansion and the force of gravity pulling inwards. star.
Following this, stars develop in different ways depending on their size.
Stars that are a similar size to the Sun follow the left hand path shown in the diagram above:
\({protostar}\rightarrow{main~sequence~star}\rightarrow{red~giant}\rightarrow{white~dwarf}\rightarrow{black~dwarf}\)
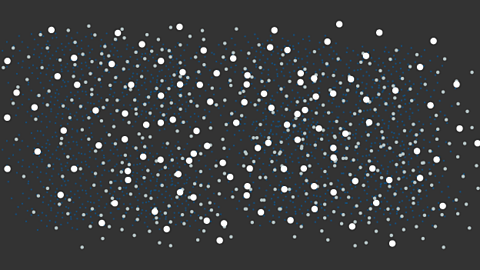
Image caption, A nebula
A star forms from massive clouds of dust and gas in space, also known as a nebula. Nebulae are mostly composed of hydrogen.
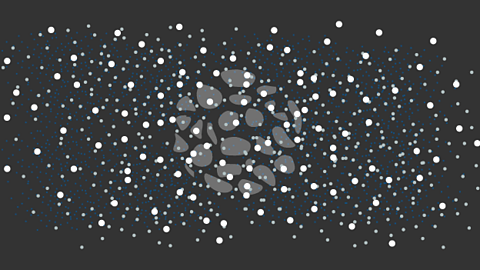
Image caption, A nebula
Gravity begins to pull the dust and gas together.

Image caption, Protostar
As the mass falls together it gets hot. A star is formed when it is hot enough for the hydrogen nuclei to fuse together to make helium. The fusion process releases energy, which keeps the core of the star hot.

Image caption, Main sequence star
During this stable phase in the life of a star, the force of gravity holding the star together is balanced by higher pressure due to the high temperatures. The Sun is at this stable phase in its life.

Image caption, Red giant
When all the hydrogen has been used up in the fusion process, larger nuclei begin to form and the star may expand to become a red giant.

Image caption, White dwarf
When all the nuclear reactions are over, a small star like the Sun may begin to contract under the pull of gravity. In this instance, the star becomes a white dwarf which fades and changes colour as it cools.
1 of 6
What is a supernova? (Higher tier only)
More massive stars than the Sun have a very different life cycle and follow the right hand path in the diagram above:
\({Nebula}\rightarrow{protostar}\rightarrow{main~sequence~star}\rightarrow{red~super~giant}\rightarrow\)\({supernova}\rightarrow{neutron~star,~or~a~black~hole~(depending~on~size)}\)
After the main sequenceA stable stage in the life cycle of a star. Nuclear fusion occurs, fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. There is a balance between the outwards thermal expansion and the force of gravity pulling inwards. period, they expand and become red super giants.
This is followed by an explosion in which the outer layers of the star are ejected.
This is called a supernova.
The star will shine as supernova for a relatively short period of time with the brightness of 10 billion suns.
After the supernova the remaining core of the star may collapse further.
Some become neutron starA massive and very compact star. A high mass star, which is not quite massive enough to form a black hole, becomes a neutron star at the end of its life cycle. while very massive ones become black holeA region of space where gravity is so strong that not even light can escape. Black holes are the final stage of the lifecycle of the largest stars..
An exploding supernova throws hot gas into space.
What are neutron stars and black holes?
Depending on the mass at the start of its life, a supernova will leave behind either a neutron star or a black hole.
A black hole is made when the centre of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses.
All the matterSub-atomic particles and anything made from them, such as atoms and molecules, are matter. Energy and forces are not matter. of the star becomes squeezed into a tiny volume of space and the force of gravity increases greatly.
There is such a strong gravitational fieldThe region of space surrounding a body in which another body experiences a force of gravitational attraction. in a black hole that nothing can escape from it, including electromagnetic radiation such as light.
Since no light can escape, it appears black, and hence the name black hole.
Key fact
There is such a strong gravitational field in a black hole that nothing can escape from it, including electromagnetic radiation such as light.
What is a fusion reaction? (Higher tier only)
In a main sequenceA stable stage in the life cycle of a star. Nuclear fusion occurs, fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. There is a balance between the outwards thermal expansion and the force of gravity pulling inwards. star, hydrogen nucleiNuclei is the plural of nucleus. The nucleus is the central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons, and has most of the mass of the atom. fuse together to form helium nuclei.
This happens in several steps, but one way to simplify the overall change is:
\(_{1}^{2}\textrm{H} +~ _{1}^{3}\textrm{H} \rightarrow _{2}^{4}\textrm{He} +~ _{0}^{1}\textrm{n}\)
Two hydrogen nuclei fuse to produce a helium nucleus and a neutronUncharged subatomic particle, with a mass of 1 relative to a proton. The relative charge of a neutron is 0..
What role did a supernova play in the formation of the Solar System?
Scientists believe that at the start of the Universe, 13.8 billion years ago, only hydrogen gas was present.
All the naturally occurring elements apart from hydrogen have been formed by nuclear fusionThe joining together of two smaller atomic nuclei to produce a larger nucleus. Radiation is released when this happens. Nuclear fusion happens in stars like our sun, and in hydrogen bombs. in stars.
For example, beryllium and carbon nuclei can be produced from helium nuclei:
During the majority of the lifetime of a star, hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nucleiNuclei is the plural of nucleus. The nucleus is the central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons, and has most of the mass of the atom.
As the star runs out of hydrogen, other fusion reactions take place forming the nuclei of other elements.
Elements heavier than iron are formed in the supernovaThe large explosion at the end of a large star’s life, which distributes much of the elements formed in the star across space. explosions of high mass stars.
When the supernova explodes, all the elements produced are thrown out into the Universe.
The heavy elements found on Earth, such as gold, came from material thrown out in previous supernova explosions.
The presence of gold and other heavier elements such as uranium in the Earth is evidence that the Solar System was formed from the remains of a supernova.
WATCH: Brian Cox on the death of stars
Professor Brian Cox demonstrates how the chemical elements are made in the death throes of a dying star
Key fact
All the naturally occurring elements apart from hydrogen are formed by nuclear fusion in stars.
How much do you know about stars?
More on Unit 2: Space physics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4

- count1 of 4