Key points
- A map scaleThe ratio of the length of a feature on a map to the same length in real life. is a ratio of the distance on a map to the actual distance on the ground.
- The scaleTo enlarge or reduce a number, quantity or measurement by a given amount (called a scale factor). of a map shows how much you need to enlarge the map to get the actual size. For example, a scale of 1 : 25,000 means each 1 cm on the map represents 25,000 cm. This is the same as 250 m.
- The scale 1: 25,000 on the map could also be given as 4 cm to 1 km.
- Maps are made at different scales for different purposes. Eg, a 1 : 25,000 scale map is useful for walking as it shows greater detail. However, a map with a 1 : 250,000 scale shows a greater area, but in far less detail. This would be a useful map for planning a car journey.

Understanding map scales
map scaleThe ratio of the length of a feature on a map to the same length in real life. are often written as a ratio, eg 1 : 250,000. They can also be written using measurements, eg 2 cm to 5 km.
To understand a map scale, find the real distance represented by each (1 cm or 1 inch) on a map. This will differ depending on the type of scaleTo enlarge or reduce a number, quantity or measurement by a given amount (called a scale factor).. Some map scales use centimetres (cm) and others may use inches. This process is referred to as interpreting the scaleWorking out the real distance that each unit (1 cm or 1 inch) on the map represents.. This is an essential skill for any map-based problem solving.
For a measurement-based scale, where more than one unit is given:
- Divide both parts of the scale by the number of units. Eg, for a scale of 5 cm to 6 km, divide both parts of the scale by 5
- The scale will now give the real distance represented by 1 unit on the map.
For a ratio scale:
- Write both parts of the ratioA part-to-part comparison. with equal units, eg centimetres (cm).
- Divide the greater number by 100 to convert to metres (m).
- Divide the greater number by 1000 to convert to kilometres (km).
- The scale will now give the real distance represented by 1 unit on the map.
Examples

Image caption, What does 1 cm represent when the map scale is 5 cm to 2 km?
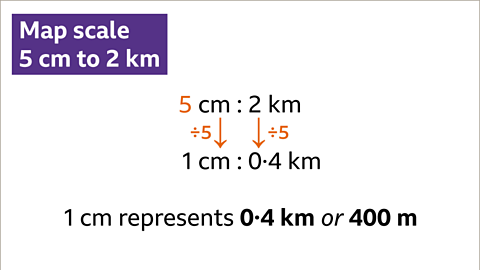
Image caption, The scale states that 5 cm represents 2 km. Both parts of the scale (5 cm and 2 km) must be divided by 5. 5 cm ÷ 5 = 1 cm. 2 km ÷ 5 = 0∙4 km. The scale now states that 1 cm represents 0∙4 km. This is the same as 1 cm on the map representing 400 m.
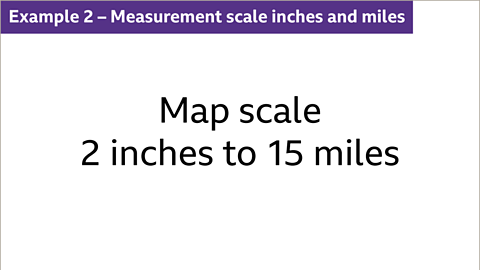
Image caption, What does 1 inch represent when the map scale is 2 inches to 15 miles?

Image caption, The scale states that 2 inches represents 15 miles. Both parts of the scale (2 inches and 5 miles) must be divided by 2. 2 inches ÷ 2 = 1 inch. 15 miles ÷ 2 = 7∙5 miles. The scale now states that 1 inch represents 7∙5 miles.
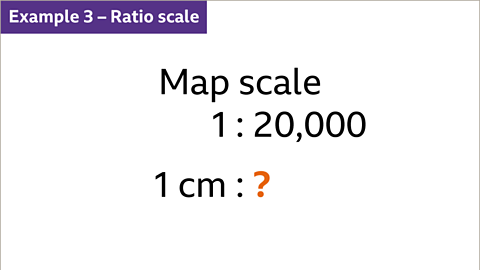
Image caption, Find what 1 cm represents on a scale of 1 : 20,000
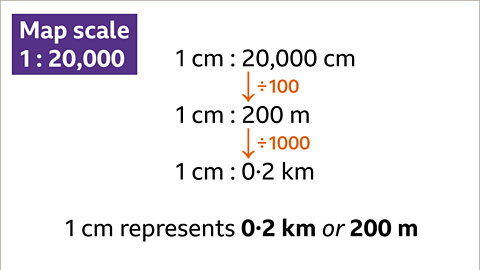
Image caption, Write both parts of the ratio as cm lengths. 1 cm represents 20,000 cm. Divide the greater number by 100 to convert to metres. Divide the greater number by 1000 to convert to kilometres. 1 cm represents 0∙2 km. This is the same as 1 cm representing 200 m.
1 of 6
Question
For a map scale of 1 : 2,500,000 what distance does 1 cm on the map represent?
Write both parts of the ratio as centimetre lengths. 1 cm represents 2,500,000 cm.
Divide the greater number by 100 to convert to metres. 1 cm represents 25,000 m.
Divide the greater number by 1000 to convert to km.
1 cm represents 25 km.

How to write a ratio scale for a map from a measurement-based scale
- In order to write the ratio, both measurements need to have the same units. Write both parts of the ratio with the same units (using the smaller units, usually cm).
- To convert km to metres, multiply by 1000
- To convert metres to cm, multiply by 100
- simplify (a ratio)To reduce a ratio to its simplest form, also known as its lowest terms. A ratio written in simplest form is written using whole numbers. by dividing both parts of the ratio by their highest common factor (HCF) The largest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. Eg, 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20. Highest common factor is written as HCF. (HCF).
Example

Image caption, Write the scale 5 cm to 2 km as a ratio.

Image caption, Write both parts of the scale with the same units, using the smaller units (cm). Convert km to cm by multiplying by 1000 then multiplying by 100. 2 km is the same as 200,000 cm. The scale is 5 cm to 200,000 cm. The ratio is 5 : 200,000. This ratio can be simplified.

Image caption, Simplify the ratio 5 : 200,000 by dividing by the highest common factor (HCF) of 5 and 200,000. This is 5. The ratio simplifies to 1 : 40,000
1 of 3
Question
Write the scale 4 cm to 5 km as a ratio.
Write both parts of the scale in the same smaller units (cm). Convert km to cm by multiplying by 1000 then multiplying by 100. 5 km is the same as 500,000 cm.
The scale is 4 cm to 500,000 cm. The ratio is 4 : 500,000. This ratio can be simplified.
Simplify the ratio 4 : 500,000 by dividing by the highest common factor (HCF) of 4 and 500,000. This is 5. The ratio simplifies to 1 : 125,000

How to use a measurements-based map scale to find a real distance
To find the real distance using a map scale, first measure the distance on the map. For distances that are not in a straight line (eg, a journey on a map), use a piece of string that can be measured against a ruler. For distances that are a straight line, use a ruler.
The method used then depends on the way the scale is written.
For a measurement-based scale where one or more units (cm or inch) represent a given distance, eg 2 cm to 5 km, or 1 inch to 16 miles:
Interpret the scale, if necessary. Find the real distance represented by each unit (cm or inch) on the map.
Multiply the measured distance by the distance each unit on the map represents.
For a measurement-based scale where more than one unit (cm or inch) represents 1 km (or 1 mile), eg 4 cm to 1 km, or 2 inches to 1 mile:
- Divide the measured distance by the number of units on the map (cm or inch) that represent 1 km (or 1 mile).
Examples
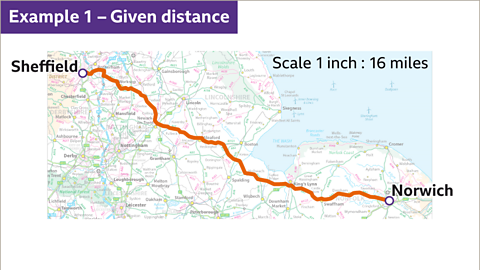
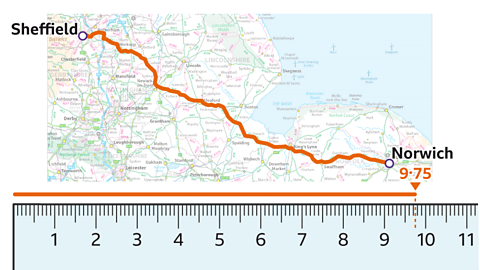
Image caption, The journey from Sheffield to Norwich is shown on the map. The map scale is 1 inch to 16 miles.
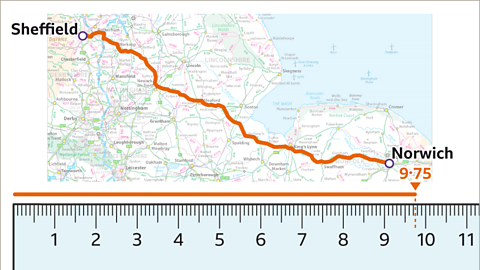
Image caption, The car journey from Sheffield to Norwich is not a straight line, so it is measured with some string against a ruler. The string is about 9∙75 inches long.

Image caption, The scale is 1 inch to 16 miles. One unit (1 inch) represents a given distance (16 miles). Multiply the measured distance (9∙75) by the distance each unit on the map (1 inch) represents (16 miles). 9∙75 × 16 = 156. The journey from Sheffield to Norwich is approximately 156 miles.
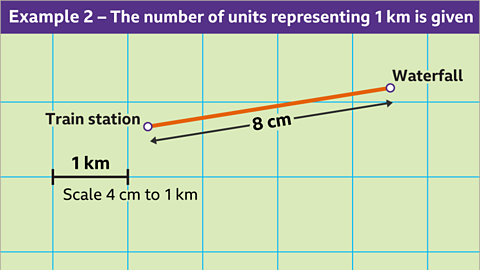
Image caption, A cycle route from the train station to a waterfall measures 8 cm on the map. How long is this cycle route in km?

Image caption, The scale is 4 cm to 1 km. Divide the measured distance (8) by the number of cm on the map that represent 1 km (4) to find the actual distance in km. 8 ÷ 4 = 2. The distance between the train station and the waterfall is 2 km.
1 of 5
Question
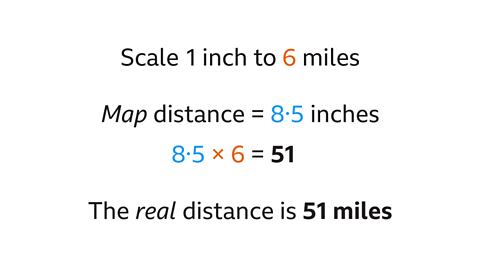
A map has a scale of 1 inch to 6 miles.
What is the real distance, in miles, represented by 8∙5 inches on the map?
The scale is 1 inch to 6 miles.
One unit (1 inch) represents a given distance (6 miles).
- Multiply the measured distance (8∙5 inches) by the distance each inch on the map represents (6 miles).
- 8∙5 × 6 = 51. The real distance is 51 miles.
How to use a ratio-based map scale to find a real distance
To find the real distance using a ratio map scale (eg 1 : 250,000), first measure the distance on the map. Use a ruler for straight lines, or for distances not in a straight line (eg, a journey on a map), use a piece of string that can be measured against a ruler.
There are two possible methods.
Either multiply by the scale to find the real distance in cm:
- Find the real distance by multiplying the measured distance by the scale.
- Convert the distance (in cm) to metres by dividing by 100
- Convert the distance (in metres) to km by dividing by 1000
Or interpret the scale:
- interpreting the scaleWorking out the real distance that each unit (1 cm or 1 inch) on the map represents. by finding the real distance represented by each cm on the map.
- Multiply the measured distance by the distance each unit on the map represents.
Both calculations will give the same answer.
Examples

Image caption, A map scale is 1 : 400,000. The distance between two places on the map is 5∙7 cm. What is the real distance between these two places?

Image caption, The map scale 1 : 400,000 means that the distance in real life is 400,000 times the distance on the map. The distance on the map multiplied by 400,000 gives the real distance in centimetres. 1 cm on the map is 400,000 cm in real life.

Image caption, To find the real distance, multiply the distance on the map (5∙7 cm) by the scale (400,000). 5∙7 × 400,000 = 2,280,000. The real distance is 2,280,000 cm. This needs to be converted into kilometres (km).

Image caption, Convert the distance (in cm) to metres by dividing by 100. 2,280,000 cm ÷ 100 = 22,800 m. Convert the distance (in metres) to km by dividing by 1000. 22,800 m ÷ 1000 = 22∙8 km. 5∙7 cm on the map represents 22∙8 km in real life.

Image caption, A map scale is 1 : 400,000. The distance between two places on the map is 5∙7 cm. What is the real distance between these two places?

Image caption, Interpret the scale. Write both parts of the ratio as cm lengths. 1 cm represents 400,000 cm. Divide the greater number (400,000) by 100 to convert to metres. Divide the greater number (4000) by 1000 to convert to kilometres. 1 cm represents 4 km. This can also be written as 1 cm to 4 km. The scale can now be used to find the real distance that 5∙7 cm represents on the map.
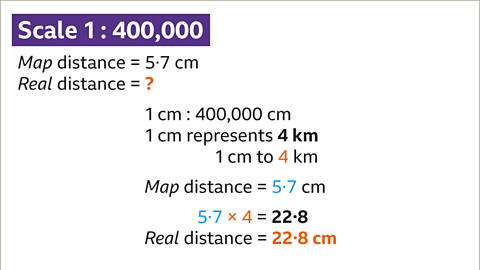
Image caption, The scale is 1 cm to 4 km. One unit (1 cm) represents a given distance (4 km). Multiply the measured distance (5∙7 cm) by the distance each cm on the map represents (4 km). 5∙7 × 4 = 22∙8. The real distance is 22∙8 km.
1 of 7
Question
A map has a scale of 1 : 800,000
What is the real distance in kilometres represented by 3∙2 cm on the map?
To find the real distance using a ratio map scale, there are two possible methods.
Either multiply by the scale to find the real distance in cm first and convert to km:
- The scale 1 : 800,000 means that the real distance is 800,000 times the distance on the map.
- Multiply the distance on the map (3∙2 cm) by 800,000
3∙2 × 800,000 = 2,560,000
The real distance is 2,560,000 cm. - Convert the distance (2,560,000 cm) to metres (m) by dividing by 100. Convert the distance (25,600 m) to kilometres (km) by dividing by 1000
3∙2 cm on the map represents 25∙6 km in real life.
Or interpret the scale:
- Write both parts of the ratio as cm lengths. 1 cm represents 800,000 cm.
- Divide the greater number (800,000) by 100 to convert to metres. Divide the greater number (8000) by 1000 to convert to kilometres. 1 cm represents 8 km.
- Multiply the measured distance (3∙2 cm) by the distance each cm on the map represents (8 km). 3∙2 × 8 = 25∙6
3∙2 cm on the map represents 25∙6 km in real life.
Using a map scale to find the distance for a given real distance
To find the distance on the map that represents the given real distance:
- Interpret the scale by finding the real distance represented by each cm on the map.
- For the given real distance, divide by the distance on the map that each cm represents.
Examples
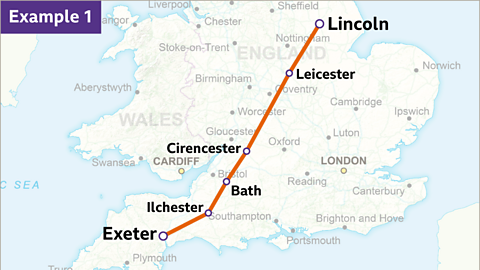
Image caption, A group plans a charity walk from Lincoln to Exeter. They are setting off from Lincoln and plan to walk about 16 km each day. The map they are using has a scale of 1 : 50,000. How far is 16 km on their map?

Image caption, Interpret the scale. Write both parts of the ratio as cm lengths. 1 cm represents 50,000 cm. Divide by 100 to convert to metres. Divide by 1000 to convert to kilometres. 1 cm on the map represents 0∙5 km in real life.
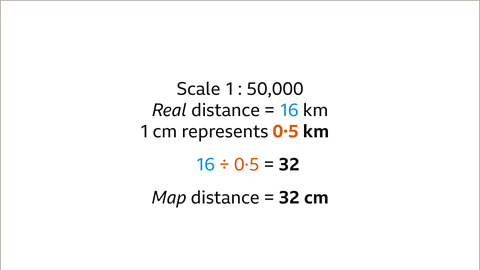
Image caption, Each 1 cm on the map represents 0∙5 km in real life. To find the distance on the map, divide the real distance (16) by the number of km that each cm on the map represents (0∙5). 16 ÷ 0∙5 = 32. The distance on their map for 16 km is 32 cm.
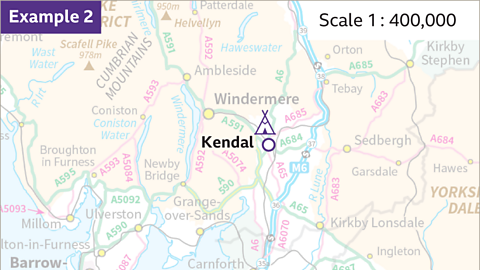
Image caption, A family is staying at a campsite near Kendal. They plan to walk each day within 20 km of the campsite. They want to mark the map with the area they are planning to explore. The map scale is 1 : 400,000. A radius is a straight line from the centre of a circle to the circumference of a circle. Find the radius of the circle to be drawn on the map.

Image caption, Interpret the map scale. 1 cm to 400,000 cm is the same as 1 cm to 4 km. Each 1 cm on the map represents 4 km in real life. The map distance (in cm) multiplied by 4 gives the real distance (in km).
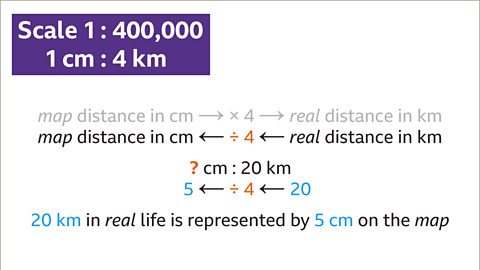
Image caption, Each 1 cm on the map represents 4 km in real life. The real distance in km (20) divided by the number of km each cm represents (4) gives the map distance (in cm). 20 ÷ 4 = 5. 20 km in real life is represented by a length of 5 cm on the map.
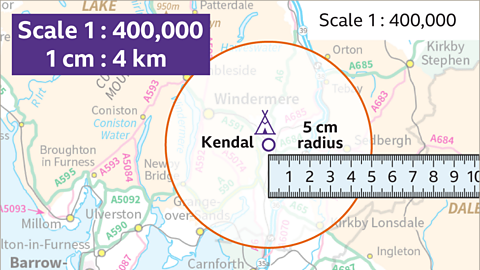
Image caption, 20 km in real life is represented by 5 cm on the map. A circle with a radius of 5 cm will be drawn on the map to show the area they will explore.
1 of 7
Question
A map has a scale of 1 : 20,000
What distance on the map represents a real distance of 3 km?
- Interpret the scale. Write both parts of the ratio as cm lengths. 1 cm represents 200,000 cm.
- Divide the greater number (20,000) by 100 to convert to metres.
- Divide the greater number (200) by 1000 to convert to kilometres. 1 cm represents 0∙2 km.
- Divide the real distance (3 km) by the distance each cm on the map represents (0∙2 km). 3 ÷ 0∙2 = 15
The real distance of 3 km is represented on the map by 15 cm.

Practise map scales
Practise map scales in this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to complete these questions.
Quiz
Real-world maths

Some drivers may prefer to use a paper map to plan their journeys and to be able to find alternative routes when there is traffic. Although many drivers use satellite navigation and travel apps, a paper map does not lose its signal or misdirect you.
Mountain rescue teams use their map skills both in training and in real life and death situations. Planning and coordinating the team and directing a rescue helicopter to the site of an incident is essential to a successful outcome. The team will use map scales to work out the distance they need to travel and how far they may need to carry an injured person to safety.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Ratio
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5
- count2 of 5
- count3 of 5
- count4 of 5
