Key points
- pulley systems make lifting heavy objects easier using ropes over wheels
- single pulleys change the direction of force but don't reduce effort
- fixed pulleys change force direction; movable pulleys reduce effort
- adding pulleys creates a mechanical advantage, making lifting easier
- velocity ratio is the distance the effort moves compared to the load
- efficiency measures how well input work converts to output work
What are pulley systems?
Pulley systems are simple machines that make lifting heavy objects easier. They consist of a rope or cable that passes over one or more wheels (pulleys).

A single pulley changes the direction of force, making pulling down easier than lifting upwards. Single pulley systems are demonstrated in cranes, lifting a bucket from a well, raising a flag or adjusting window blinds. Even though there is no actual mechanical advantage with one pulley, it is referred to as having a mechanical advantage of one. The more pulleys you use, the easier it is to lift the object.
What are the types of pulley?
There are two main types of pulleys:
- Fixed pulleys : these pulleys are attached to a fixed point, like a ceiling or wall. They change the direction of force but don't reduce the effort needed to lift the load.
- Movable pulleys: these pulleys are attached to the load being lifted. They reduce the effort needed to lift the load but don't change the direction of force.
Using pulleys in lifting systems
Pulley systems are used in various lifting systems, such as cranes, elevators, and even simple clotheslines. They are particularly useful for lifting heavy objects that would be difficult or impossible to lift manually.
Pulley calculations
How to calculate pulley mechanical advantage
One pulley doesn’t make a mechanical advantage, as the same amount of force is needed. However, if additional pulleys are added, a mechanical advantage is created. Using two pulleys together means you need half the force to lift. This is called a block and tackle and is used to lift large, difficult-shaped objects, such as furniture. Adding more pulley wheels to the block and tackle increases the load it can lift.
The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of sections of rope pulling up on the object.
Formula:
\(\text{mechanical advantage}=\frac{\text{load}}{\text{effort}}\)
Example:If a pulley system allows you to lift a 300 N load with an effort of only 100 N, the mechanical advantage is 3.
Mechanical advantage =300/100
This means the pulley system makes it three times easier to lift the load.
Question
A pulley system with two pulleys is used to lift a 240 N load. The effort required to lift the load is 120 N.
- Calculate the mechanical advantage of the pulley system.
\(\text{mechanical advantage}=\frac{\text{load}}{\text{effort}}\)
\(= \frac{240 N}{120 N}\)
\(= 2\)
How to calculate velocity rato
Velocity ratio (VR) is the ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load. In a pulley system, it is often equal to the number of ropes supporting the load.
Formula:
\(\text{velocity ratio}=\frac{\text{distance moved by effort}}{\text{distance moved by load}}\)
Example:If you pull 10 meters of rope to lift a load by 2 meters, the velocity ratio is 5.
This means the effort moves five times farther than the load.
Question
A pulley system lifts a load by 3 meters. To achieve this, the effort is applied over a distance of 15 meters.
- Calculate the velocity ratio of the pulley system.
Answer
\(\text{VR}=\frac{\text{distance moved by effort}}{\text{distance moved by load}}\)
\(= \frac{15 m}{3 m}\)
\(= 5 : 1\)
How to calculate efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of the mechanical advantage to the velocity ratio, expressed as a percentage. It indicates how effectively the pulley system converts input work into output work.
Formula:
\(\text{efficiency \% ratio}=\frac{\text{mechanical advantage}}{\text{velocity ratio}}\times 100\)
Example:
If a pulley system has a mechanical advantage of 3 and a velocity ratio of 4, its efficiency is 75%.
This means 75% of the input work is converted into useful work in lifting the load, while the remaining 25% is lost due to friction and other factors.
What other transmission systems exist?

Flat belts
Flat belts are used to transmit power between two parallel shafts. They are simple and inexpensive but can slip if the load is too high.

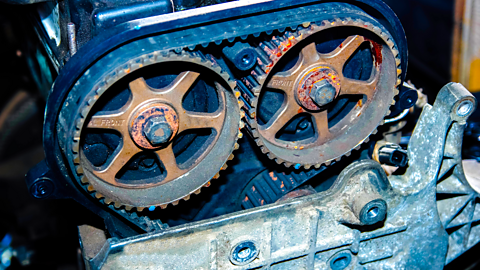
Toothed belts
Toothed belts, also known as timing belts, provide a more positive drive than flat belts. They have teeth that mesh with grooves on the pulleys, preventing slippage.


Sprockets and chains
Sprockets and chains provide the most positive drive of all. They are used in applications where high TorqueA measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis and precise timing are required, such as bicycles and motorcycles.

How to tension belts

Belts need to be tensioned correctly to prevent slippagewhen a belt doesn't turn properly around a pulley the belt slips and power is lost and ensure efficient power transmission. Flat belts can be tensioned using a sliding motor base or an adjustable idler pulley. Toothed belts are tensioned during installation and generally don't require further adjustment.

Jockey pulleys
Jockey pulleys are used with flat belts to increase the arc of contact between the belt and the pulley. This helps to prevent slippage and improve power transmission.

Test yourself
More on Mechanical and pneumatic control systems
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 7

- count5 of 7

- count6 of 7

- count7 of 7
