What is the circulatory system?
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system is a network of organs and blood vessels that work together to circulate blood around the body.
The circulatory system is made up of three main components:
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood

Watch: The circulatory system
Look! The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body.
The heart is a pump, and the blood goes round, and round, and round all the time.
And why does it do that?
Why can't it just have a rest?
Well, the blood has to be kept moving around all the time because it's the body's delivery system.
Every possible part of the body has to be supplied with oxygen and food and water, and the veins and arteries are like roads going all the way through your body with the blood cells like delivery vans.
The body is all the time shouting out:
“Over here! Delivery needed! I need oxygen! I need nutrients!”
That means that the vans are very busy indeed, all the time.
So it's a good job we've got the circulatory system to transport nutrients, water and oxygen to the entire body.
Right come on heart, back to work. Quick!
Fascinating facts
If we could join all the blood vessels in a human body together end-to-end, they would wrap around the world twice!
The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps approximately 9,092 litres of blood per day.
Every second, your body produces millions of red blood cells to replace those that wear out.
People have different blood types. There are four main blood types: A, B, AB and O.
It takes about 20-30 seconds for blood to circulate completely throughout the body.
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in our circulatory system.
Veins contain valves which prevent the backflow of blood.
There is evidence that the ancient Egyptians were studying the human circulatory system as early as the 16th century BC.

How does the circulatory system work?
The human heart is a very strong muscle that pumps blood around the body. It is made of four chambers, two upper chambers and two lower chambers.
Blood enters the upper chambers which are called atria. These squeeze and push the blood into the lower chambers called ventricles which then squeeze and push the blood out of the heart.
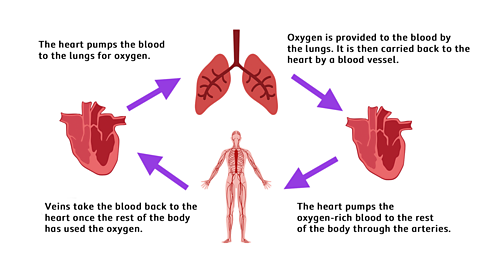
- The right side of the heart first pumps blood to the lungs. Here, the blood picks up oxygen from the air that has been breathed in.
- The blood (now carrying oxygen) then travels back to the left side of the heart.
- The heart gives the blood a second push. This time, it's sent to all the other parts of your body, including the brain, arms, legs and stomach. The blood delivers oxygen to them all.
- The blood travels back to the right side of the heart, and it all begins again.
- The tubes that carry blood away from your heart are called arteries. The tubes that carry blood back to your heart are called veins.

The heart
Your heart is a very strong muscular organ which repeatedly contracts (becomes smaller) and relaxes to pump blood around your body.
It has four chambers:
- the right atrium
- the right ventricle
- the left atrium
- the left ventricle
A heart beat varies from person to person, for an average person it beats 60 to 100 times a minute. You can feel this when you take your pulse.
This is the journey that blood takes:
Watch: How the heart pumps blood
Check out the muscular heart and its extraordinary pumps.
Narrator: Well here we are ladies and gentlemen, in the heart, the powerhouse of the circulatory system, the hardest working muscle in the entire human body!
He’s looking very strong today… and here comes the blood cell… I think we’re ready…
AND HE’S OFF!
Look at that extraordinary pumping power!
He’s off into the lungs. Incredible! He has picked up oxygen, and he’s coming back! He’s coming back!
We’re ready for another pump, I think this is the big one, here it comes!
Oh my goodness LOOK AT THAT! What an unbelievable pump! Our friend the blood cell is out of sight!
He’s been sent swooshing around the entire body along with trillions of others!
This heart just never stops, he's pumping away 24/7. Just absolutely incredible, quite extraordinary…
Did you know?
The term cardiovascular comes from two latin words; the prefix cardio- which means heart and the word vascular which relates to tubular blood vessels.
Many other common medical words begin with the prefix cardio-, such as a cardiometer which measures the health of a person's heart, cardiology which is the scientific study of the heart, and cardiogram which is a scan used by doctors to look at a heart.
What are blood vessels?
Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body. There are three main types of blood vessels.
- Arteries
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and to the body's cells. - Veins
Veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body's cells and into the heart. - Capillaries
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries to veins. They allow oxygen, nutrients and waste products to pass between the blood and the body's cells.

Watch and learn about the magnificent blood vessels in your body.
Inside you, there is an amazing network of blood vessels, the tubes that carry blood all around your body.
Every part of the body needs oxygen, food and water.
The blood vessels are a bit like roads going around a city with deliveries, while the veins take away waste.
Do you know how many roads there are in just one person?
Well, if we could take them all apart and lay each section out in a straight line, it would go all the way around the world…twice!
Of course, you could only drive on it in a very very very small car.
Did you know?
If you need an easy way to remember what veins and arteries do, then try this!
The word artery starts with the letter ‘a’ and so does the word ‘away’ and arteries carry blood away from the heart.
The word vein has the word ‘in’inside of it and veins carry blood back into the heart.
What is blood?
Blood is a liquid tissue that circulates throughout the body. It is made up of:
- Red blood cells
Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body's cells. - White blood cells
White blood cells help the body to fight infection. - Platelets
Platelets are cells which help blood to clot and stop bleeding. - Plasma
Plasma is a liquid that carries nutrients, water and sugar around the body.
There are different types of blood cells with different jobs.
Narrator: Blood gets around our bodies through a system of blood vessels.
To picture the blood vessels, imagine a busy network of roads.
And those roads are always full of little vans which are busy making deliveries and rubbish trucks picking up rubbish and police cars looking out for intruders.
Police: We have a suspect heading full speed towards the stomach. Require immediate backup!
Narrator: Your blood has different cells with different jobs.
Some cells do repairs if you get a cut.
Red blood cells deliver oxygen and take away rubbish.
And your white blood cells are like police looking for germs.
There's a lot going on inside you!

Did you know?
Our blood is red because it contains a red coloured protein called haemoglobin that carries oxygen.
Molluscs don't have haemoglobin, so their blood so is blue coloured!

What is a pulse?
Your pulse is a measure of how fast your heart is beating.
It is the number of beats your heart makes in one minute.
Your heart beats faster or slower depending on what you are doing.
When you exercise, your heart beats faster. This is because your muscles are working harder and need more oxygen to keep going.
Your lungs also work harder, making you breathe more quickly to take in more oxygen.
When you sleep, your muscles need less oxygen so your heart rate slows down.

Important words
Important words about the circulatory system!
Arteries - They take the blood with oxygen away from the heart and spreads it around your body.
Atria - The upper chambers of the heart.
Blood - A liquid tissue that circulates throughout the body, it is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma.
Blood vessels - Tubes that carry blood around the body.
Cardiovascular system - Another name for the circulatory system, see below.
Circulatory system - A network of organs and blood vessels that work together to circulate blood around the body.
Deoxygenated blood - Blood without oxygen.
Heart - The organ that pumps blood around your body.
Organs - Parts of our body that have a function like the skin, lungs, heart, stomach et al.
Oxygenated blood - Blood with oxygen.
Platelets - Help the blood to clot and stop bleeding.
Plasma - A liquid that carries nutrients, water and sugar around the body.
Pulse - A measure of how fast your heart is beating.
Red blood cells - They carry oxygen to the body's cells.
Veins - A type of blood vessel that takes deoxygenated blood to your heart.
Ventricles - The lower chambers of the heart.
White blood cells - They defend the body and help to fight infection.
Haemoglobin - A red coloured protein that carries oxygen.
Activities
Activity 1 – Fill in the gaps
Activity 2 – Circulatory system quiz
Activity 3 – Label the heart
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Animals including humans
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 11

- count11 of 11

- count1 of 11

- count2 of 11

