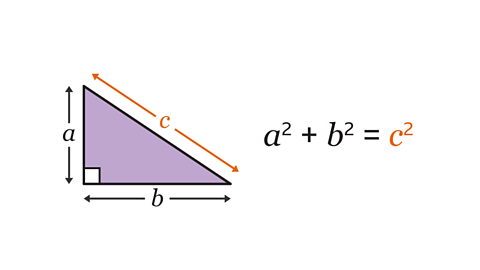Key points
Trigonometry explores the relationship between sides and angles in right-angled triangles.
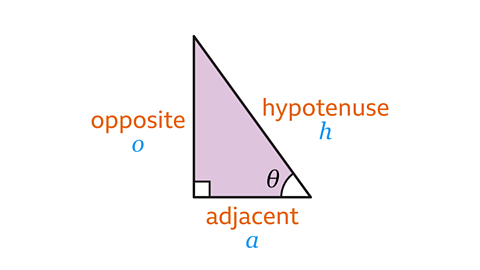
The sides of a right-angled triangle are labelled with:
- Hypotenuse (\(h\)) – the longest side, which is opposite the right angle.
- Opposite (\(o\)) – the side opposite to the given angle.
- Adjacent (\(a\)) – the side next to the given angle.
The Greek letter Ɵ (theta) is often used as a symbol for an unknown (given) angle.
similar shapesOne shape is an enlargement of another. The angles in each shape are the same, and the side lengths are in the same proportion. triangles are enlargementA transformation that changes the size of a shape, keeping the lengths in the same proportions. of each other. The angles in similar triangles are the same. The sides of similar triangles are in the same proportionA comparison between numbers so that when one number increases, the other does at the same rate..
Trigonometric ratios show how long one side of the triangle is compared to another. The 3 important ratios are known as the sine (sin), cosine (cos) and tangent (tan) of the angle:
sinƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{hypotenuse} \)
cosƟ = \( \frac{adjacent}{hypotenuse} \)
tanƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{adjacent} \)

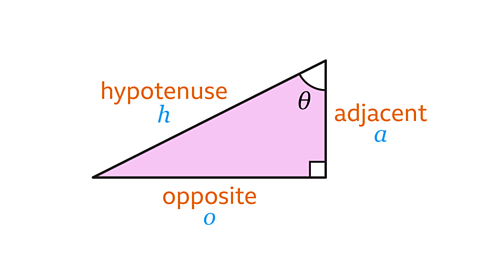
Labelling sides of a right-angled triangle for trigonometry
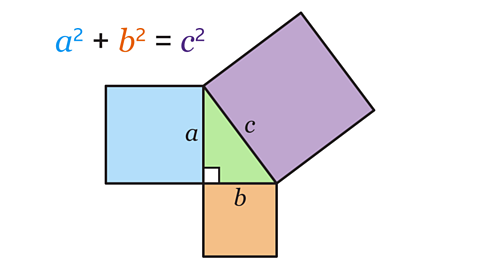
When a question about right-angled triangles involves all three sides and no angles, Pythagoras’ theoremPythagoras’ theorem states the relationship between sides in a right-angled triangle. It states that 𝒂² + 𝒃² = 𝒄², where 𝒄 is the hypotenuse (longest side), and 𝒂 and 𝒃 are the other two sides. is used to calculate the value of a missing side.
When the question involves two sides and an angle in a right-angled triangle, trigonometryThe study of sides and angles in triangles. is used.
The sides are labelled depending on where the angle is.
The sides are called the hypotenuseThe longest side of a right-angled triangle, which is always opposite the right angle. When labelling a length as the hypotenuse, it can be shortened to 𝒉. (\(h\)), the oppositeThe side of a right-angled triangle that is opposite the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the opposite, it can be shortened to 𝒐. (\(o\)) side, and the adjacentThe side of a right-angled triangle between the right-angle and the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the adjacent, it can be shortened to 𝒂. (\(a\)) side.
The Greek letter theta, which has the symbol Ɵ, is often used to show an unknown angle.
Examples
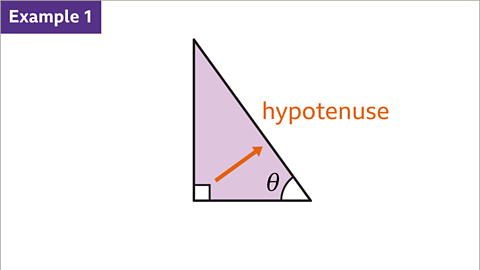
Image caption, When using trigonometry in right-angled triangles, each side is labelled based on a given angle, Ɵ. The hypotenuse (𝒉) is the longest side of the triangle, which is always opposite the right angle.
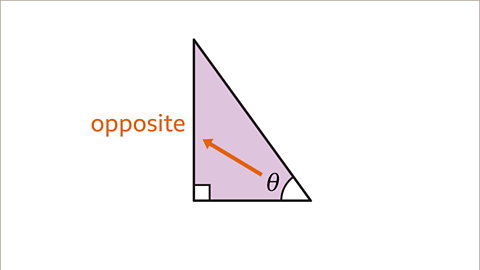
Image caption, The opposite side (𝒐) is the side opposite the given angle.
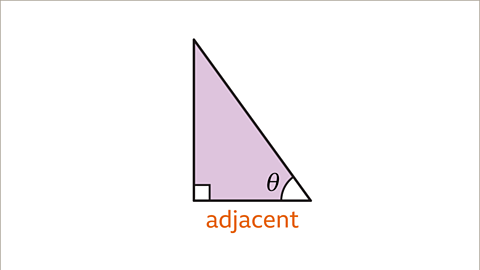
Image caption, The adjacent side (𝒂) is the side next to the given angle. It is between the given angle and the right angle.
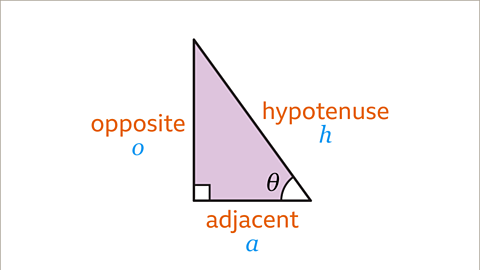
Image caption, A fully labelled triangle.
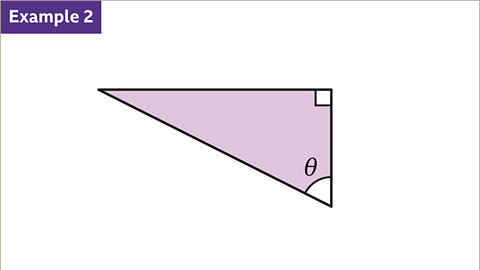
Image caption, Label the right-angled triangle with the hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent side.
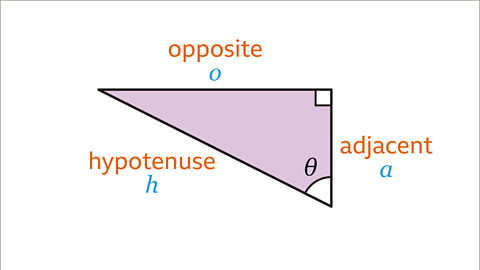
Image caption, The hypotenuse is the longest side and is always opposite the right angle. The opposite side is the side opposite the given angle. The adjacent side is the side next to the given angle. It is between the given angle and the right angle.
1 of 6
Question
Label the right-angled triangle with the hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent sides.

The hypotenuse is the longest side and is always opposite the right angle.
The opposite side is the side opposite the given angle.
The adjacent side is the side next to the angle. It is between the given angle and the right angle.
The three trigonometric ratios
Triangles that have the same three angles are enlargementA transformation that changes the size of a shape, keeping the lengths in the same proportions. of each other and are known as similar triangles.
For two right-angled triangles, if an angle (other than the right angle) is the same, the third angle will also be the same. This is true because angles in a triangle add up to 180°.
Therefore, right-angled triangles that include the same angle are similar shapesOne shape is an enlargement of another. The angles in each shape are the same, and the side lengths are in the same proportion..
For similar right-angled triangles, the hypotenuseThe longest side of a right-angled triangle, which is always opposite the right angle. When labelling a length as the hypotenuse, it can be shortened to 𝒉., oppositeThe side of a right-angled triangle that is opposite the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the opposite, it can be shortened to 𝒐. and adjacentThe side of a right-angled triangle between the right-angle and the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the adjacent, it can be shortened to 𝒂. sides stay in the same . For example, the adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse will give the same answer no matter how much the triangle is enlarged.
The hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent side can be divided in three important ways.
The answer to these division calculations depends on a given angle, Ɵ.
The three divisions are written as fractions. They are called the three trigonometric trigonometric ratioA ratio written as a fraction that calculates how long one side of a right-angled triangle is compared to another, based on a given angle, Ɵ. The three main ratios are sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse; cosƟ = adjacent/hypotenuse; and tanƟ = opposite/adjacent. because they show how long one side is compared with another.
The trigonometric ratios are known as the sine (sin), cosine (cos) and tangent (tan) of the angle.
sinƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{hypotenuse} \)
cosƟ = \( \frac{adjacent}{hypotenuse} \)
tanƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{adjacent} \)
Examples
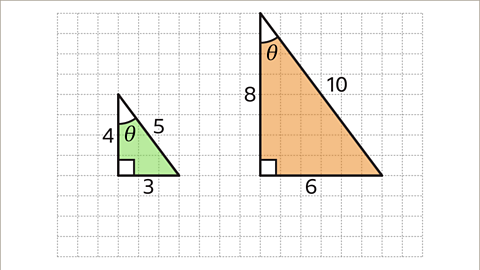
Image caption, The right-angled triangle on the left has sides 3, 4, and 5 units long. The right-angled triangle on the right has sides 6, 8, and 10 units long. The triangles are mathematically similar because one is an enlargement of the other. The lengths of the right triangle are double those on the left triangle
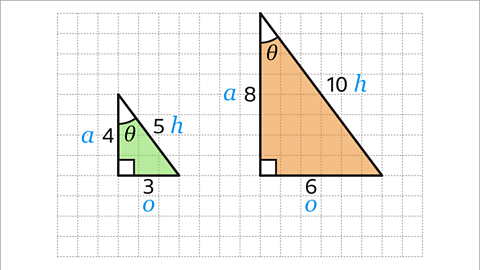
Image caption, The sides have been labelled as the hypotenuse (𝒉), opposite (𝒐), and adjacent (𝒂) based on the angle Ɵ.
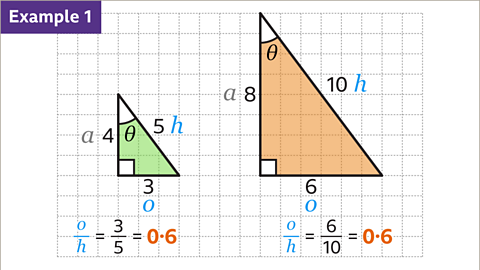
Image caption, The opposite side divided by the hypotenuse for each triangle is 3/5 and 6/10. These two fractions are equivalent and both equal 0·6. No matter how much the triangle is enlarged, the opposite divided by the hypotenuse will always be 0·6. This is because the angle stays the same and the sides stay in the same proportion.
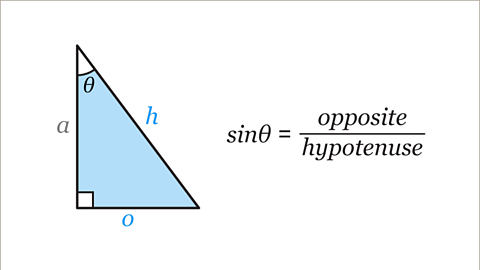
Image caption, The answer to the opposite side divided by the hypotenuse depends on how big the angle is. The opposite side divided by the hypotenuse is called the sine of the angle, and is abbreviated to sin. For a given angle Ɵ, sinƟ = opposite ÷ hypotenuse. This is written as a fraction.
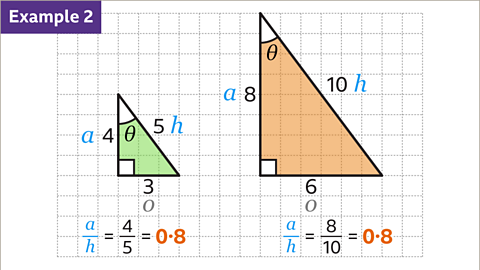
Image caption, The adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse for each triangle is 4/5 or 8/10. These two fractions are equivalent and both equal 0·8. No matter how much the triangle is enlarged, the adjacent divided by the hypotenuse will always be 0·8. This is because the angle stays the same and the sides stay in the same proportion.
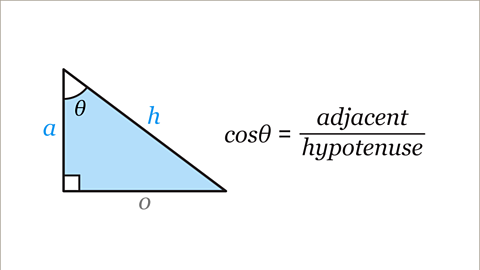
Image caption, The answer to the adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse depends on how big the angle is. The adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse is called the cosine of the angle, and is abbreviated to cos. For a given angle Ɵ, cosƟ = adjacent ÷ hypotenuse. This is written as a fraction.
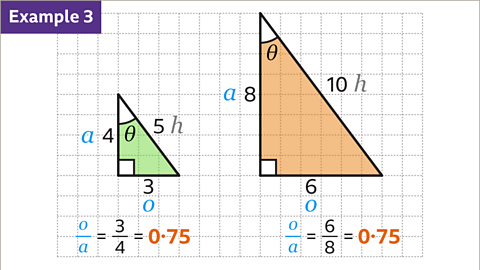
Image caption, The opposite divided by the adjacent for each triangle is 3/4 or 6/8. These two fractions are equivalent and both equal 0·75. No matter how much the triangle is enlarged, the opposite divided by the adjacent will always be 0·75. This is because the angle stays the same and the sides stay in the same proportion.
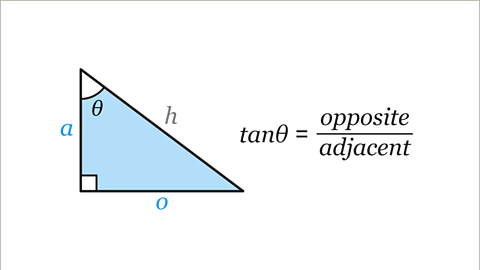
Image caption, The answer to the opposite side divided by the adjacent depends on how big the angle is. The opposite side divided by the adjacent side is called the tangent of the angle and is abbreviated to tan. For a given angle Ɵ, tanƟ = opposite ÷ adjacent. This is written as a fraction.

Image caption, These three equations are true for all right-angled triangles. They are known as the three trigonometric ratios because they show how large one side is compared to the other based on an angle Ɵ.
1 of 9
Question
Calculate the value of sinƟ, cosƟ and tanƟ for the right-angled triangle.
Give your answer as a fraction.
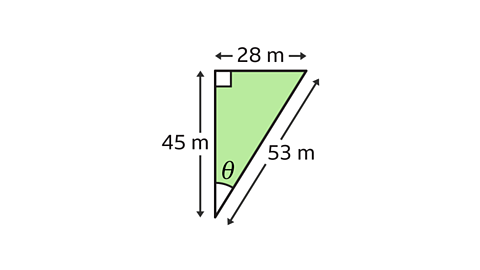
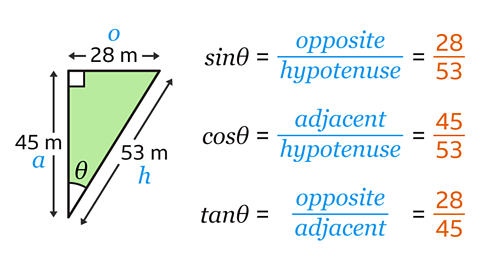
Label the sides hypotenuse (\(h\)), opposite (\(o\)) and adjacent (\(a\)).
Write the trigonometric ratios and substitute the correct values into the equations.
sinƟ = \( \frac{28}{53} \)
cosƟ = \( \frac{45}{53} \)
tanƟ = \( \frac{28}{45} \)
Practise trigonometric ratios in right-angled triangles
Practise trigonometric ratios in similar right angled triangles with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Quiz
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Pythagoras and trigonometry
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5
- count2 of 5