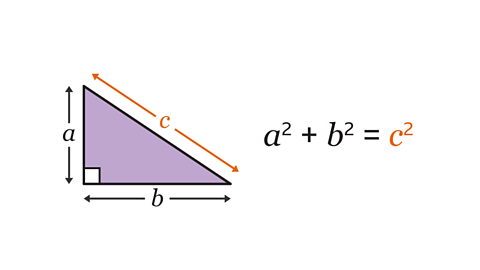Key points
trigonometryThe study of sides and angles in triangles. can be used to find a missing side in a right-angled triangle when another side and an angle are known.
An understanding of the three trigonometric ratios and how to change the subject of a formula is essential.
The Greek letter, Ɵ (theta) is often used as a symbol for an unknown angle.
For any right-angled triangle with angle Ɵ, the three trigonometric ratioA ratio written as a fraction that calculates how long one side of a right-angled triangle is compared to another, based on a given angle, Ɵ. The three main ratios are sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse; cosƟ = adjacent/hypotenuse; and tanƟ = opposite/adjacent. are:
sinƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{hypotenuse} \)cosƟ = \( \frac{adjacent}{hypotenuse} \)tanƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{adjacent} \)
- To find a missing side, the angle and sides are substituteIn algebra substitute means to replace a letter (or variable) with a number. into one of the trigonometric equations above. The equation used must contain the two sides that are involved in the question.
- The equation is rearrange (a formula)Change the subject of a formula. The formula for the area of a circle (A = πr²) can be rearranged to change the subject, in this case to make the subject the radius r =√(A/π) to make the missing side the subject (of a formula)The formula for the area of a circle is A = πr² The area A is the subject of the formula. The subject can be changed if the formula is rearranged.. The missing side can then be calculated.

How to calculate the length of a side 𝒙
For a right-angled triangle, follow these steps to calculate the length of a side, \(x\), when another side and an angle Ɵ is given:
Label the two sides that contain information in the diagram with hypotenuseThe longest side of a right-angled triangle, which is always opposite the right angle. When labelling a length as the hypotenuse, it can be shortened to 𝒉. \(h\), oppositeThe side of a right-angled triangle that is opposite the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the opposite, it can be shortened to 𝒐. \(o\) or adjacentThe side of a right-angled triangle between the right-angle and the angle mentioned. When labelling a length as the adjacent, it can be shortened to 𝒂. \(a\).
Choose the trigonometric ratio that contains the two sides that have been labelled.
The three trigonometric ratioA ratio written as a fraction that calculates how long one side of a right-angled triangle is compared to another, based on a given angle, Ɵ. The three main ratios are sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse; cosƟ = adjacent/hypotenuse; and tanƟ = opposite/adjacent. are:
sinƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{hypotenuse} \)
cosƟ = \( \frac{adjacent}{hypotenuse} \)
tanƟ = \( \frac{opposite}{adjacent} \)
- Substitute the values of the sides and angle into the trigonometric equation.
- To make \(x\) the subject, rearrange the equation by doing the inverse operationThe opposite of a mathematical process. Eg, the inverse of × 5 is ÷ 5. The inverse operation undoes the original process..
- Type the expressionA mathematical sentence expressed either numerically or symbolically made up of one or more terms. for \(x\) into a calculator to find the length of the side.
Formula triangles can be used to help with rearranging the equation, but it is important that the algebraic method for rearranging is understood.
Note that scientific calculators need to be used for trigonometry and should be in degrees mode. Make sure there is a small D at the top of the calculator screen, and if not, go into the calculator settings to change the angle unit to 'degrees' (or 'deg.').
Examples
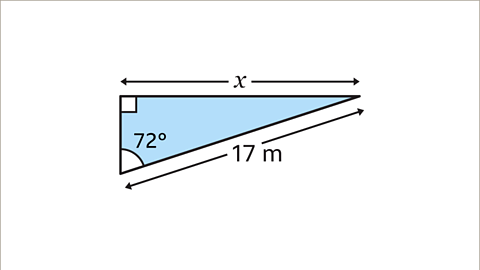
Image caption, Find the value of 𝒙 to 1 decimal place (1 dp).
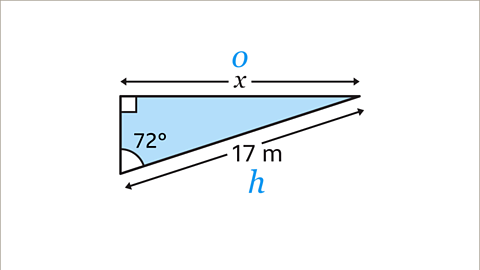
Image caption, Label the hypotenuse (𝒉) and opposite (𝒐) side. The hypotenuse (𝒉) is the longest side and is opposite the right angle. The opposite side (𝒐) is the side opposite the given angle. There is no need to label the adjacent side because it is not the side that is being calculated.
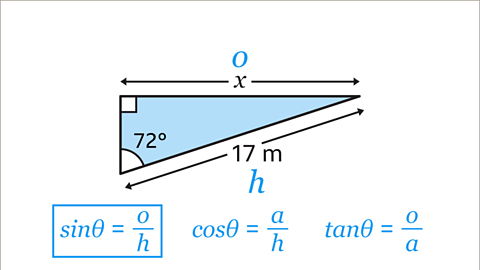
Image caption, Choose which of the three trigonometric ratios to use. The equation has to contain 𝒐 and 𝒉 because these are the sides with information in the diagram. The only equation that contains both 𝒐 and 𝒉 is the sine ratio.

Image caption, Write down the trigonometric equation. sinƟ = 𝒐 / 𝒉. Substitute the values of Ɵ, 𝒐 and 𝒉 into the equation. Ɵ is the angle 72ᵒ, 𝒐 should be substituted with 𝒙, and 𝒉 is 17. Always put brackets around the angle. This gives sin(72) = 𝒙 / 17
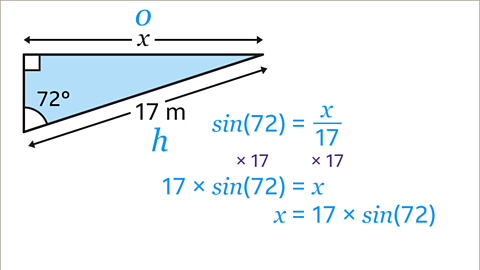
Image caption, The equation needs to be rearranged to make 𝒙 the subject. In the original equation, 𝒙 is being divided by 17, so to make 𝒙 on its own, multiply both sides of the equation by 17. This gives 17 x sin(72) = 𝒙. The equation can be written the opposite way so that it begins with 𝒙 = …. This gives 𝒙 = 17 x sin(72).
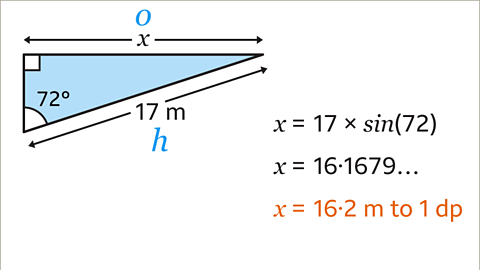
Image caption, Type 17 × sin(72) into a scientific calculator. Usually, the calculator will automatically open a bracket after pressing the sin, cos, or tan button. Remember to close the bracket after typing in the angle. The answer is = 16.1679… Rounded to 1 dp, 𝒙 = 16.2 m.
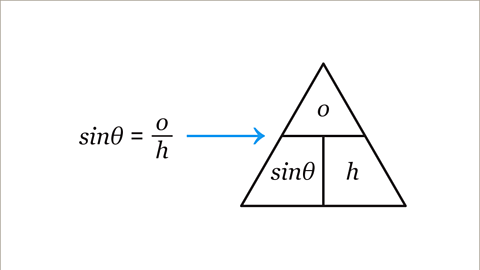
Image caption, Another way to work out an equation for 𝒙 is to use a formula triangle for the equation sinƟ = 𝒐/𝒉. Write each term (part) of the equation into the correct space in a formula triangle. 𝒐 is the numerator (top) of the fraction in the equation, so 𝒐 goes on the top of the formula triangle.
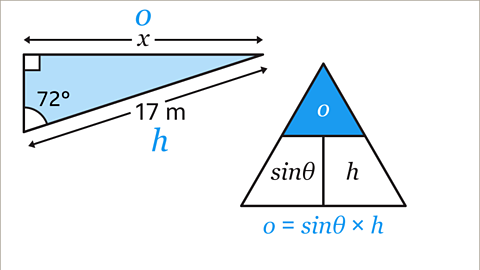
Image caption, Cover up the term in the formula triangle that is being calculated. In the original question, it is 𝒐 that is being calculated, so cover up 𝒐. The remaining expressions in the formula triangle are next to each other, which means they should be multiplied together. The equation for 𝒐 is 𝒐 = sinƟ × 𝒉.
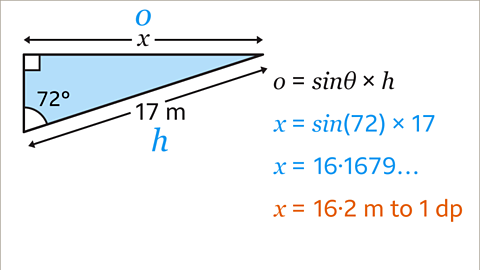
Image caption, Substitute the values of 𝒐, Ɵ, and 𝒉 into the equation. o should be substituted with 𝒙. Ɵ is the angle 72ᵒ, and 𝒉 is 17. This gives the equation 𝒙 = sin(72) × 17 as in the previous method. Type this into a calculator to give the answer 𝒙 = 16.2 m rounded to 1 dp.
1 of 9
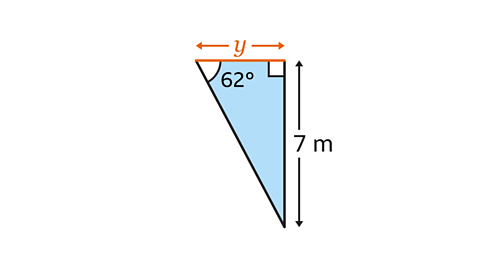
How to calculate the length of a side 𝒚
Here is an example of how to calculate the length of a side, \(y\), when another side and an angle Ɵ is given in a right-angled triangle.
Examples
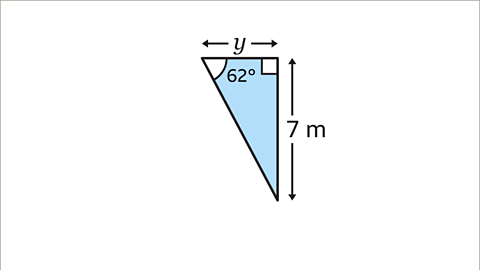
Image caption, Find the value of 𝒚 to 2 decimal points (2 dp).
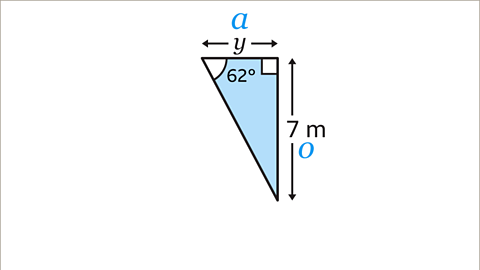
Image caption, Label the opposite (𝒐) and adjacent (a) side. The opposite side (𝒐) is opposite the given angle. The adjacent side (𝒂) is the side between the right angle and the given angle. There is no need to label the hypotenuse because there is no information about its length, and it is not the side that is being calculated.
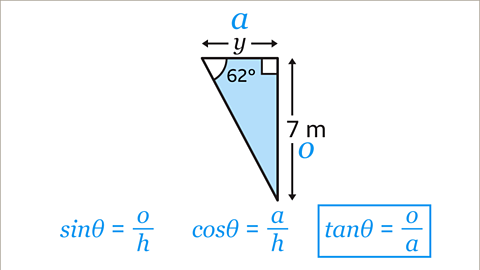
Image caption, Choose which trigonometric ratio to use. The equation has to contain 𝒐 and 𝒂 because these are the sides with information in the diagram. The only equation that contains both 𝒐 and 𝒂 is the tangent ratio.
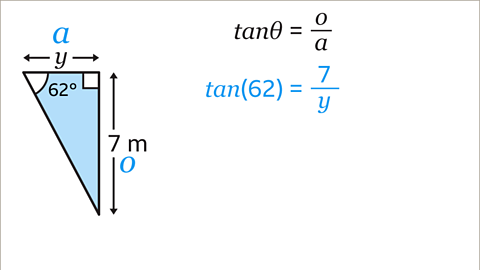
Image caption, Write down the trigonometric equation. tanƟ = 𝒐 / 𝒂. Substitute the values of Ɵ, 𝒐 and 𝒂 into the equation. Ɵ is the angle 62ᵒ, 𝒐 is 7, and 𝒂 should be substituted with 𝒚. Always put brackets around the angle.
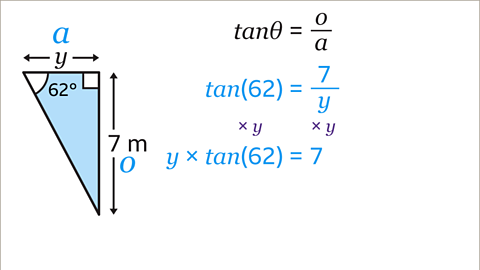
Image caption, The equation needs to be rearranged to make 𝒚 the subject. In this case, there will be two steps to rearranging. In the original equation, 7 is being divided by 𝒚. Do the inverse operation and multiply both sides by 𝒚. This gives 𝒚 × tan(62) = 7

Image caption, 𝒚 is now being multiplied by tan(62). To make 𝒚 on its own, do the inverse operation and divide both sides by tan(62). This gives 𝒚 = 7/tan(62).
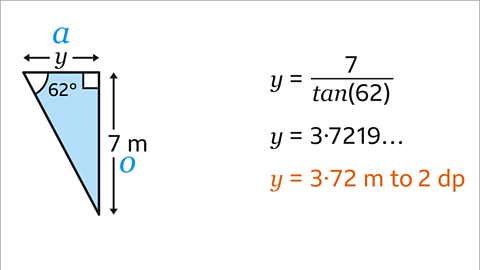
Image caption, Type 7/tan(62) into a scientific calculator using the fraction button to put 7 on the numerator (top) and tan(62) on the denominator (bottom). Usually, the calculator will automatically open a bracket after pressing the sin, cos, or tan button. Remember to close the bracket after typing in the angle. The answer is 𝒚 = 3.7219… Rounded to 2 decimal places, 𝒚 = 3.72 m.
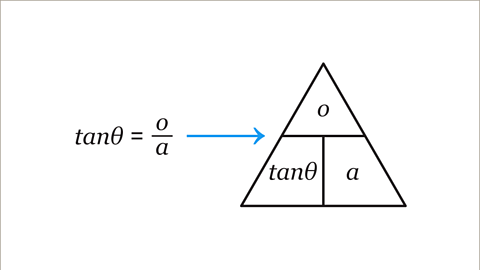
Image caption, Another way to work out an equation for 𝒚 is to use a formula triangle for the equation tanƟ = 𝒐/𝒂. Write each term (part) of the equation into the correct space in a formula triangle. 𝒐 is the numerator (top) of the fraction in the equation, so 𝒐 goes on the top of the formula triangle.
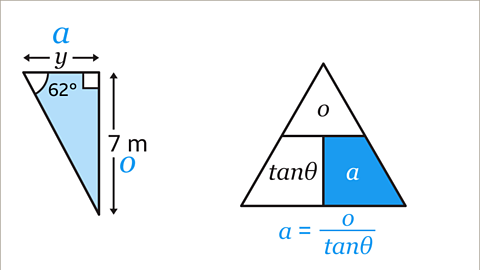
Image caption, Cover up the term in the formula triangle that is being calculated. In the original question, it is 𝒂 that is being calculated, so cover up 𝒂. The remaining expressions in the formula triangle form a fraction with 𝒐 on the top and tanƟ on the bottom. The equation for 𝒂 is 𝒂 = o/tanƟ.
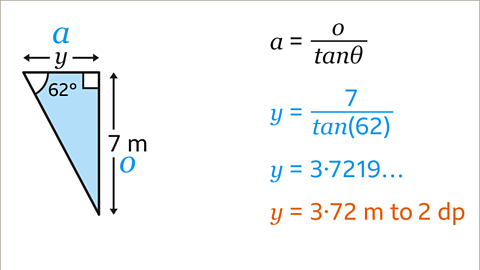
Image caption, Substitute the values of 𝒂, 𝒐 and Ɵ into the equation. 𝒂 should be substituted with 𝒚. 𝒐 is 7, and Ɵ is the angle 62ᵒ. This gives the equation 𝒚 = 7/tan(62) as in the previous method. Type this into a calculator using the fraction button to give the answer 𝒚 = 3.72 m rounded to 2 dp.
1 of 10
Question
Find the value of \(x\) to 1 decimal place (1 dp).
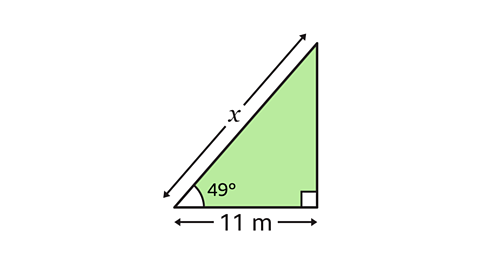
11 m should be labelled as adjacent (\(a\)) and \(x\) should be labelled as hypotenuse (\(h\)).
The only trigonometric equation that includes \(a\) and \(h\) is cosƟ = \(a\)/\(h\).
Substitute the values for Ɵ, \(a\) and \(h\) to give cos(49) = 11/\(x\).
To remove \(x\) from the denominator, multiply both sides by \(x\). This gives \(x\) × cos(49) = 11
To make \(x\) the subject, divide both sides by cos(49) to give \(x\) = 11/cos(49).
Calculate this expression and round to 1 decimal place to give the answer \(x\) = 16.8 m.
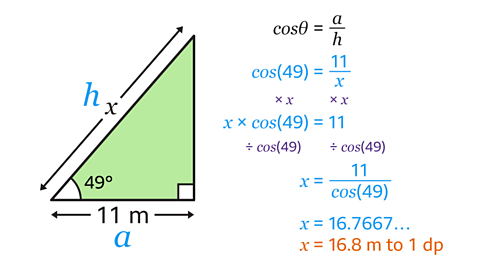
Practise calculating the length of a side in a right-angled triangle.
Quiz
Practise finding the length of a side in a right-angled triangle with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Real-life maths

trigonometryThe study of sides and angles in triangles. is essential in video game development. The code for a typical game includes the location of objects, the speed and direction a player is moving, and the angle of shots.
All of these involve sides and angles in right-angled triangles, so game programmers need to have a good understanding of trigonometric ratioA ratio written as a fraction that calculates how long one side of a right-angled triangle is compared to another, based on a given angle, Ɵ. The three main ratios are sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse; cosƟ = adjacent/hypotenuse; and tanƟ = opposite/adjacent. to write the code.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Pythagoras and trigonometry
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5
- count2 of 5