What are the key points about the dangers and uses of radiation?
To identify and understand the dangers of exposure to radioactivityThe process where certain material decay and emit one of 3 different types of radiation (alpha, beta or gamma). sources.
To state ways to reduce the risk when using radioactive sources.
To identify the correct radioactive source for different applications.
What are the effects of radiation on the human body?
Radioactive materials are hazardous.
Radioactive emissions cause dangerous ionisationProcess by which electrons can be added or removed from an atom to create an ion. by removing from atoms.
When this happens with in living cells, the genetic material of a cell (the DNAThe part of the cells of living things that carries information about how they look and function. Everyone’s DNA is different, except identical twins who share the same DNA.) is damaged.
This can lead to cancerA disease caused by normal cells changing so that they grow and divide in an uncontrolled way. The uncontrolled growth causes a lump called a tumour to form. .
Radiation can also deposit large amounts of energy into the body, which can damage or destroy cells completely.
Key points
Alphanuclear radiationParticles or waves given out by the nucleus of an unstable atom. Alpha particles, beta particles and gamma waves are the three most common types of nuclear radiation. is not as dangerous if the radioactive source is outside the body, because it cannot pass through the skin and is unlikely to reach cells inside the body.
Alpha radiation will damage cells if the radioactive source has been breathed in as a gas or dust or if it is swallowed.
beta radiationA type of ionising radiation consisting of a single electron. and gamma radiationA type of ionising radiation that is also part of the EM spectrum. It has no mass. radiation can penetrate the skin and cause damage to cells inside the body.
How can the risks of radiation be managed?
The risk associated with radioactive materials depends on the amount of exposure.
Being exposed to highly radioactive materials or being exposed to radioactive materials for long periods of time or on a regular basis increases the dose received which, in turn, increases the risk.
Given that radioactive materials are hazardous, certain precautions need to be taken to reduce the risk when using radioactive sources.
These precautions fall under three main headings:
Time: being exposed to the source for as short a time as possible.
Distance: keeping the source as far away from the body as possible by using tongs.
Shielding: wearing protective clothing to prevent the body becoming contaminated should radioactive radioactive isotopeAn isotope of an atom of an element that releases ionising radiation. Also called a radioisotope. leak out and also to protect against absorbing radiation e.g. using a lead apron, face masks, etc.
Radioactive materials should be kept in lead-lined containers when not in use.
What is background radiation?
Background radiation is the radiation detected when there are no known radioactive sources present.
Background radiation released by soil, rocks and cosmic rays is always in the environment.
Most of it comes from natural sources but some also comes from artificial sources.
Radioactive sources are found all around us and in our bodies.
Most radioactive background activity comes from natural sources such as:
Soils and rocks containing uranium which is radioactive. These may be used for building materials. When uranium decays radon, a radioactive gas, is released.
Cosmic rays - radiation reaching the Earth from outer space.
Human behaviour adds slightly to the background activity that we are exposed to through medical X-rays, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants and the radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons testing.
As a result, gas, living things and plants absorb radioactive materials from the soil, which are then passed along the food chain.
For example, by eating a banana which contains radioactive potassium.
As it passes along the food chain the concentration of radioactivity will increase.
The actual amount of radiation that a person is exposed to depends on where they live, what job they do and many other things.
There is little we can do about natural background radiation, although people who live in areas with a high background radiation due to radon gas require homes to be well ventilated to remove the gas.
A radiation barrier (thick concrete based) should also be built into the foundation of the house.
How is radiation used in medicine?
Sterilisation of surgical instruments
Gamma rays are high energy electromagnetic waves which are only stopped by thick lead or concrete.
This means they can easily pass through medical equipment, such as syringes.
As gamma rays pass through the packaging and syringe, they will kill viruses and bacteria which contaminate the syringe.
As long as the equipment remains in a sealed plastic pack, it will remain free of viruses and bacteria and be safe for use with patients.
The gamma ray source used should have a long half-lifeThe half-life of a radioactive source is the time taken for its activity to fall to half of the original activity. so that the hospital does not have to replace it too frequently.
Advantages:
Sterilisation can be done without high temperatures.
It can be used to kill bacteria on things that would melt e.g. plastic syringes.
Disadvantages:
It may not kill all bacteria on an object.
It can be very harmful - standing in the environment where objects are being treated by radiation could expose people’s cells to damage and possibly cancer.
What is radiotherapy?
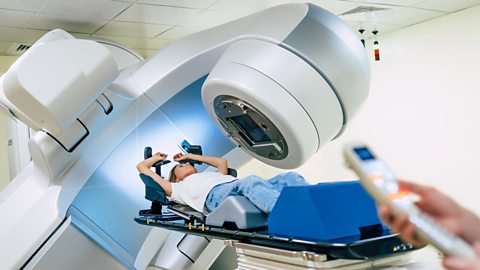
Although ionising radiationRadiation that is able to remove electrons from atoms or molecules to produce positively charged particles called ions. can cause cancer, high doses can be directed at cancerous cells to kill them.
This is called radiotherapy.
About 40 per cent of people with cancer undergo radiotherapy as part of their treatment.
It is administered in two main ways:
From outside the body using X-raysHigh frequency electromagnetic radiation, used for medical imaging. or gamma radiationA type of ionising radiation that is also part of the EM spectrum. It has no mass. from radioactive cobalt.
From inside the body by putting radioactive materials into the tumourThe lump of cells formed as a result of uncontrolled cell division. or close to it.
What is a gamma knife?
Beams of gamma rays, called a gamma knife, can be used to kill the cancerous tumour deep inside the body.
These beams are aimed at the tumour from many different directions to maximise the dose on the tumour but to minimise the dose on the surrounding soft tissue.
This technique can damage healthy tissue, so careful calculations are done to establish the best dose enough to kill the tumour, but not so much so that the healthy tissue is damaged.
The gamma ray source used should have a long half-life so that the hospital does not have to replace it too frequently.
What are radioactive tracers?
In some cases, injected radioactive sources (such as technetium-99) can be used as tracers to make soft tissues, such as blood vessels or the kidneys, show up through medical imaging processes.
An radioactive isotopeAn isotope of an atom of an element that releases ionising radiation. Also called a radioisotope. emits gamma rays that easily pass through the body to a detector outside the body, for example a ‘gamma camera’.
In this way, the radioactive isotope can be followed as it flows through a particular organ in the body.
Changes in the amount of gamma emitted from different parts would indicate how well the isotope is flowing, or if there is a blockage.
The isotope used must:
Be a source of gamma rays so that they pass out through the body to be detected by the gamma camera or GM tube.
Have very short half-lives - sources used typically have half-lives of hours so after a couple of days there will hardly be any radioactive material left in a person’s body.
Not be poisonous.
How is radiation used in industry?
To control the thickness of metal or paper
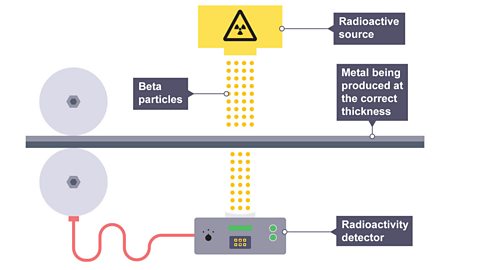
Image caption, 1. Radioactive isotopes are used in industry to control the thickness of metal or paper as it is rolled into thin sheets. An emitter is placed on one side of a sheet and a detector on the other. If the thickness of the sheet remains constant the activity will not change.
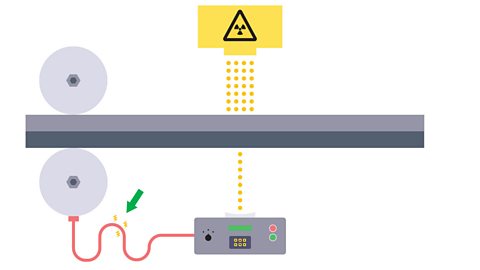
Image caption, 2. If there is a change in thickness, i.e. the metal become thicker, the detected activity will decrease.
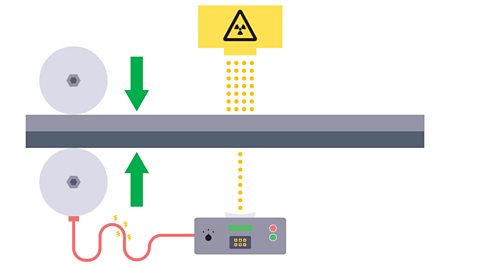
Image caption, 3. This can trigger the rollers to squeeze harder or less hard to maintain the correct thickness.
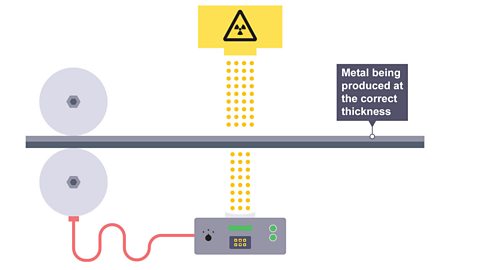
Image caption, 4. The source should have a long half-life so that the count rate remains almost constant each day and so that it does not need to be replaced too frequently.

Image caption, 5. If the sheet is thin aluminium, a beta source is used because beta radiation can penetrate a few mm of aluminium, but the amount of penetrating will vary sufficiently as thickness changes. Alpha would be unable to penetrate the sheet and reach the detector. The activity detected from a gamma source would not change if the thickness changed.

Image caption, 6. If the sheet is thick steel, a gamma source is used because gamma is the only source that can penetrate the metal. Alpha or beta would be unable to penetrate the sheet and reach the detector.
1 of 6
To check for leaks in water pipes
Water supplies can be contaminated with a gamma-emitting radioactive isotope to find leaks in pipes.
Where there is a leak, contaminated water seeps into the ground, causing a build-up of gamma emissions in that area.
The build-up of gamma emissions can be found using a Geiger-Muller tubeDevice used to detect and measure the quantity of ionising radiation in an area.
This makes it easier to decide where to dig to find the leak without having to dig along the whole length of the pipe.
The isotope used for this purpose must:
Be a gamma emitter to penetrate the ground and road surface.
Have a half-life of at least several days to allow the emissions to build up in the soil but not too long so that exposure is limited and will not be poisonous to humans as it will form part of the water supply.
How is radiation used in the home?
Smoke detectors
One type of smoke detector uses Americium-241, an alpha particleSubatomic particle comprising two protons and two neutrons (the same as a helium nucleus). source, to detect smoke.
When smoke enters between the plates, some of the alpha particles are absorbed.
An alpha source is used because alpha radiation does not penetrate very far.
It is absorbed by a few cm of air.
This means that as long as the detector is high up on a wall, or the ceiling, it is safe for humans to be in the same room.
The source should have a long half-life so that the smoke detector does not have to be replaced too frequently, and so that the count rate remains almost constant each day.
| Advantages of contamination | Disadvantages of contamination |
|---|---|
| radioactive isotopeAn isotope of an atom of an element that releases ionising radiation. Also called a radioisotope. can be used as medical and industrial tracers. | Radioactive isotopes may not go where they are wanted. |
| Use of isotopes with a short half-life means exposure can be limited. | It can be difficult to ensure that the contamination is fully removed so small amounts of radioisotope may still be left behind. |
| Imaging processes can replace some invasive surgical procedures. | Exposure to radioactive materials can potentially damage healthy cells. |
How is radiation used in agriculture?
Gamma rays are used in agriculture to kill the bacteria on food, prolonging its shelf life.
While the use of gamma radiation on food has many opponents it would be valuable in hot climates where refrigeration is not always possible.
The radioactive isotopeAn isotope of an atom of an element that releases ionising radiation. Also called a radioisotope. used in food processing plants should have a long half-life so that it is a long time before they need to be replaced.
How much do you know about the dangers and uses of radiation?
More on Unit 1: Atomic and nuclear physics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 6
- count6 of 6
- count1 of 6
- count2 of 6
