What are the key learning points about nuclear fusion?
What are the steps involved in the nuclear fusionThe joining together of two smaller atomic nuclei to produce a larger nucleus. Radiation is released when this happens. Nuclear fusion happens in stars like our sun, and in hydrogen bombs. process?
Where does fusion occur naturally?
How close are scientists to achieving fusion on Earth?
The advantages and disadvantages of fusion for producing electricity.
What happens during nuclear fusion?

Image caption, 1. Fusion reactions occur naturally in stars like our sun, where hydrogen nuclei fuse together under high temperatures and pressure to form helium nuclei. Energy is released as electromagnetic radiation such as light, infra-red radiation and ultra violet radiation, which then travels through space.
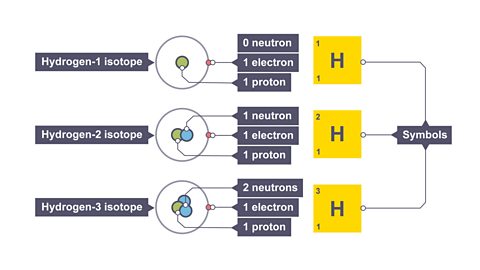
Image caption, 2. There are three main isotopes of hydrogen used in fusion reactions: hydrogen – 1; hydrogen – 2 (Deutreium); hydrogen – 3 (Tritium). To get hydrogen to fuse – extremely high temperatures are required. The electrons “boil off” the atom, leaving the positive nuclei behind.
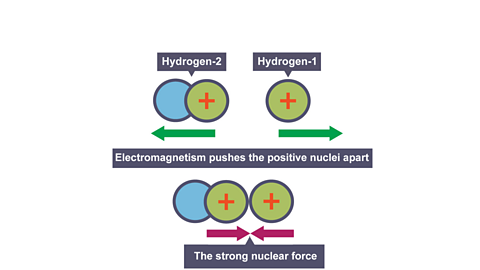
Image caption, 3. The nuclei of hydrogen are positively charged; therefore, they want to repel due to the force of electromagnetism (like charges repel). However, if the nuclei are moving fast enough to collide, another force of nature, (the strong nuclear force), beats electromagnetism and the nuclei fuse together. To get the nuclei moving fast enough to fuse requires temperature around 150,000,000 °C
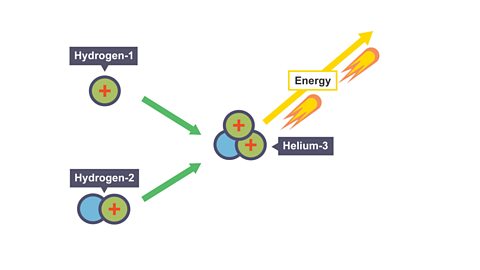
Image caption, 4. The helium-3 nucleus formed has less mass than the combined mass of hydrogen-1 and hydrogen- 2. This missing mass is released as energy.
1 of 4
As with nuclear fissionThe splitting of a large nucleus to produce two smaller ones. Two or three neutrons are also released in the process. The energy from the neutrons powers a nuclear reactor. there are many political, social, environmental and ethicalRegarding questions of right or wrong and how one should behave. issues relating to using the energy released by nuclear fusion to generate electricity.
What are the arguments for and against nuclear fusion?
For nuclear fusion:
Nuclear fusion could solve the world’s energy needs because hydrogen and deuterium are widely available as the constituents of seawater and so are relatively cheap and nearly inexhaustible.
Fusion does not emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gasThe gases responsible for global warming - carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). into the atmosphere.
There is no radioactive waste with a fusion reaction, and the major by-product is helium, an inert (unreactive), non-toxic gas.
Fusing nuclei together in a controlled way releases four million times more energy per kg than a chemical reaction such as burning coal, oil or gas - this keeps transportation and mining costs low and reduces the associated hazards.
Nuclear fusion releases four times more energy per kg than a nuclear fission reaction.
Against nuclear fusion:
The technological difficulties of fusion reactors are difficult to overcome.
Temperatures approaching the temperature of the Sun (approximately 150,000,000 °C) are required for fusion to occur on Earth, and reaching this very high temperature and containing the reaction at it for a sufficiently long time is very difficult.
There are many difficulties to overcome before nuclear fusion provides electricity on a commercial scale and it may be another 50 years before that happens.
Nuclear fusion reactors will be expensive to build because of the technology required.
The system used to contain the nuclear fusion reaction will be expensive to operate because of the very high temperatures needed for the nuclei to fuse.
What is the ITER project?
Research into using energy released from nuclear fusion to generate electricity on a commercial basis requires international co-operation between governments and scientists because of the huge costs involved and the level, range and quantity of expertise required.
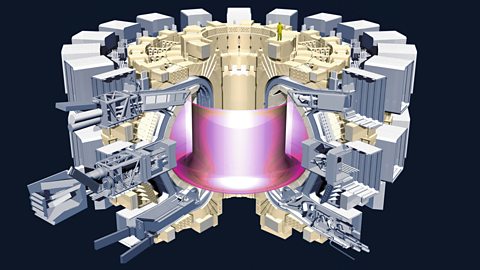
In Europe much of this work is being carried out at the ITER project (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor), the main facility of which is based in southern France.
The ITER project aims to use hydrogen fusion, controlled by large superconducting magnets, to produce massive heat energy which would drive turbines that would generate electricity – in a similar way to conventional coal, oil and gas fired power stations.
This would produce power using hydrogen from seawater, a relatively cheap and nearly inexhaustible source of energy.
The process would be free from greenhouse gases, and potentially at low cost, if the technology can be made to work on a large enough scale.
Nuclear fusion in the ITER reactor
Scientists believe that fusion can be achieved on Earth using the two heavy radioactive isotopeAn isotope of an atom of an element that releases ionising radiation. Also called a radioisotope.of hydrogen, hydrogen-2 (deuterium) and hydrogen-3 (tritium).
This is commonly referred to as the D-T reaction.
When a nucleus of hydrogen-2 (deuterium) collides with a nucleus of hydrogen-3 (or tritium) a nucleus of helium-4 is created and a neutron is released.
\(_{1}^{2}\textrm{H} + _{1}^{3}\textrm{H} \rightarrow_{2}^{4}\textrm{He} + _{0}^{1}\textrm{n} +\textrm{energy}\)
Energy is released as electromagnetic radiation.
Nuclear fusion occurs when two nuclei fuse to form a new nucleus, a neutron and energy is released.
The nuclei of deuterium and tritium are fired into a plasma where extreme temperatures overcome their repulsion and forces them together.
Per kg of fuel, nuclear fusion releases four times more energy than nuclear fission.
How much do you know about nuclear fusion?
More on Unit 1: Atomic and nuclear physics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 6
- count2 of 6

- count3 of 6

- count4 of 6