Gravitational fields
All objects with massThe amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g). produce a gravitational field. The more mass an object has, the greater its gravitational field will be. Mass is a measure of the quantity of matter in an object at rest relative to the observer.
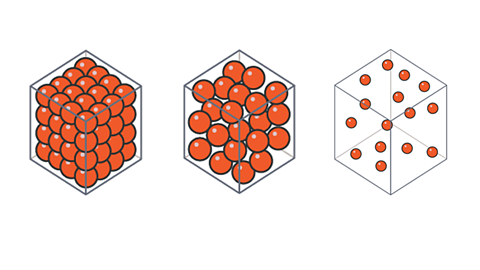
Planet size and gravitational field strength
Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity - it has the unit newtons (N) and acts towards the centre of a gravitational field. So weight is a gravitational force on an object that has mass.
Weight is a non-contact forceForce exerted between two objects, even when they are not touching, such as the force of gravity. because gravity exerts its force through a field. An object does not need to be touching the Earth to have a weight.
The weight of an object may be thought of as acting at a single point called its centre of mass. Depending on the object's shape, its centre of mass can be inside or outside it.
Video: Gravity on the Moon
Space, the Moon landing and different planets are used to discuss gravity
Gravitational field strength (g) is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg). The Earth's gravitational field strength is 9.8 N/kg. This means that for each kg of mass, an object will experience 9.8 N of force.
Where there is a weaker gravitational field, the weight of an object is smaller. For example, the gravitational field strength of the Moon is 1.6 N/kg. This means that for each kg of mass, an object will experience 1.6 N of force. Therefore, an astronaut will weigh less on the Moon than they do on the Earth.
Podcast: Gravity
In this episode, James and Ellie explore gravity, gravitational field strength, weight and how to use an equation to calculate them.
ELLIE: Hello and welcome to the BBC Bitesize Physics podcast.
JAMES: The series designed to help you tackle your GCSE in physics and combined science. I'm James Stewart, I'm a climate science expert and TV presenter.
ELLIE: And I'm Ellie Hurer, a bioscience PhD researcher.
ELLIE: We're covering lots of different aspects of forces in this series, so make sure to listen to the rest of the episodes too.
JAMES: Yeah, and they're really good. Okay, let's get started because today, I thought so, because today we're talking all about the force that keeps our feet on the ground, gravity.
ELLIE: While we often think about space and astronauts when we talk about gravity, gravity actually acts all around us every single day. Because the definition of gravity is a force of attraction between two objects.
JAMES: The gravitational field is the area around an object where another object will feel a force of gravitational attraction from it.
Gravitational field strength is measured in newtons per kilogram, written out as ‘n’ forward slash ‘kg’.
ELLIE: And the size of the gravitational field strength affects the force of gravity acting on an object in that gravitational field. The other thing that affects the size of gravity is the object's mass. The bigger the mass, the greater the force of gravity.
JAMES: So one key thing to know that a lot of people misunderstand is that weight and mass are actually two different things.
ELLIE: Yeah, so when we say, oh, this loaf of bread weighs 400 grams, we're actually saying that the mass of the loaf of bread is 400 grams.
JAMES: Because mass is about the amount of matter, whereas weight is a force and is the heaviness due to gravity.
ELLIE: Exactly. So let me tell you about the equation you need to calculate the force of weight of an object.
JAMES: Yeah, I'm gonna get my pen and paper out for this one, so if you're listening, please feel free to do the same thing and write along as we go through this.
ELLIE: So, weight equals mass multiplied by the gravitational field strength.
JAMES: Weight is measured in newtons. Mass is measured in kilograms and gravitational field strength is measured in newtons per kilogram.
ELLIE: So to calculate the weight of an object in newtons, you multiply its mass in kilograms by the strength of the gravitational field in newtons per kilogram.
JAMES: That was a lot. Don't panic. Let's just hear that again.
ELLIE: So weight equals mass multiplied by the gravitational field strength.
JAMES: Weight is measured in newtons, mass is measured in kilograms, and gravitational field strength is measured in newtons per kilogram.
ELLIE: So, to calculate the weight of an object in Newtons, you multiply its mass in kilograms by the strength of the gravitational field in Newtons per kilogram.
JAMES: Right, let's try out some examples then. And if you don't have your pen and paper just yet, now would be the perfect time to grab them and you can write down these calculations with us as we go along.
ELLIE: Let's say we want to find out the force of gravity, their weight, acting on your physics teacher as they stand at the front of the classroom.
JAMES: Good image. Now first, you would need to find out their mass. Now let's say it's 80 kilograms, then you need to know the gravitational field strength of the planet they're standing on, which for the planet of Earth is 9.8 newtons per kilogram.
ELLIE: So to measure the force of weight acting on them, you would write down their mass of 80 kilograms and then multiply it by the Earth's gravitational field strength of 9.8 newtons per kilogram to get the answer 784.
JAMES: And because weight is measured in newtons, their weight would be 784 newtons downward. We always have to include those units. And because weight is a force, which is a vector quantity (more about that in episode one), we also have to say the direction it is in, which in this case is downwards.
ELLIE: In those instances, the weight of an object and its mass are directly proportional. So let's say if something had a bigger mass, its weight would be higher. And if something had a smaller mass, its weight would be lower.
JAMES: Exactly. And when we're measuring weight in terms of gravity, we don't use regular kitchen scales. We use something called a newton meter, also known as a calibrated spring balance.
ELLIE: And when we do that, we say that the weight of an object, or in this case, person, acts at a single point. The object or person's centre of mass. The force of gravity, weight, always acts from the middle of an object, straight down.
JAMES: Okay, that was a lot, but I hope that helped you understand gravity a little bit more.
ELLIE: So, let's recap the three main points.
Firstly, gravity is a force of attraction between two objects. The next point is, mass is the amount of matter in an object. However, weight is the force of gravity acting from the middle of the object straight down.
And finally, the equation to find out an object's weight is mass multiplied by gravitational field strength equals weight.
ELLIE: There's your key points about gravity. In the next episode of Bitesize Physics, we're going to dig into work done and energy transfer, and I cannot wait.
JAMES: I believe you. Thank you for listening to BBC Physics. If you found this helpful, and hopefully you did, please do go back and listen, make some notes, so you can come back here and always have this as your point to revise from.
JAMES: Thank you, bye! Bye!
Weight, mass and gravitational field strength
Measuring masses and weights
The mass of an object can be measured using a set of traditional scales. The object is placed in the larger dish. Known masses are added to the other side until the scales balance. The sum of the masses is the same as the mass of the object.
Mass is a measure of the quantity of matter in an object at rest relative to the observer. Weight is a gravitational force on an object that has mass. The weightA force that acts on mass due to gravity. Because weight is a force, it is measured in newtons (N). of an object may be thought of as acting at a single point called its centre of massThe point representing the mean position of the matter in a body.. Depending on the object's shape, its centre of mass can be inside or outside it.
Extended syllabus content: Effects of a gravitational field
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know what effect a gravitational field has on a mass. Click 'show more' for this content:
The weight of an object and its mass are directly proportional. For a given gravitational field strength, the greater the mass of the object, the greater its weight.
Weight is the effect of a gravitational field on a mass. So weight is defined as:
The force acting upon an object with mass when placed in a gravitational field.
The weight of a mass will therefore change if the gravitational field strength does.
Calculating gravitational field strengths
On Earth, the downward force of gravity on a 1 kg mass is 10 N.
This is called the gravitational field strength (g).
Gravitational field strength g = 10 N/kg
Key fact: Gravitational field strength is defined as the force per unit of mass.
The relationship between the weight of an object in N, its mass in kg and the gravitational field strength N/kg is given by the equation:
\(g = \frac{W}{m}\)
W = weight in (N)
m = mass in (kg)
g = gravitational field strength in (N/kg)
g = 10 N/kg
A mass of 1 kg has a weight of 10 N.
A mass of 6 kg has a weight of 60 N.
Calculating gravitational field strengths
On Earth an average apple has a mass of 100g or 0.1kg. Its weight is 1 N. So the gravitational field strength of Earth is calculated when the weight is divided by the mass:
\(? = \frac{1 \ \text{N}}{0.1 \ \text{kg}}\)
\(? = 10 N/Kg\)
On Mars the same apple would have a weight of 0.37 N/kg and the same mass of 0.1 kg. So the gravitational field strength of Mars is calculated when the weight is divided by the mass:
\(? = \frac{0.37 \ \text{N}}{0.1 \ \text{kg}}\)
\(? = 3.7 N/Kg\)
The gravitational field strength in N/kg is the same as the acceleration of a freely falling object within this field measured in metres per second (m/s). So on Earth the gravitational field strength is 9.8 N/kg and the acceleration of a freely falling object is 9.8 m/s.
Calculating weight
Weight can be calculated using the equation:
weight = mass × gravitational field strength
\(W = m~g\)
This is when:
- weight (W) is measured in newtons (N)
- mass (m) is measured in kilograms (kg)
- gravitational field strength (g) is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
Example
An apple has a mass of 100 g. Calculate its weight on Earth (g = 9.8 N/kg).
\(100~g = \frac{100}{1000} = 0.1~kg\)
\(W = m~g\)
\(W = 0.1~kg \times 9.8~N/kg\)
\(W = 0.98~N\)
Question
Calculate the weight of a 30 kg dog (g = 9.8 N/kg).
\(W = m~g\)
\(W = 30~kg \times 9.8~N/kg\)
\(W = 294~N\)
Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz on weight and gravity.
More on Motion, forces and energy
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 11
- count5 of 11

- count6 of 11

- count7 of 11
