Modelling
Modelling and prototyping to help with the design process
Modelling can be time-consuming and expensive, but a physical model allows a person to see and handle a product unlike viewing it on a screen through computer aided design (CAD)The process of creating a 2D or 3D design using computer software.. computer aided manufacture (CAM)The manufacture of a part or product from a computer aided design (CAD) using computer-controlled machinery, such as a 3D printer. models made on a 3D printer using a CAD drawing are very accurate but also expensive, time-consuming and limited to 3D-printable materials. Product designers can use easy-to-form and easily accessible materials, eg balsaA lightweight hardwood used for modelling., jelutongA low-density wood used for modelling. and cardboard, to create cheap models quickly and cheaply.
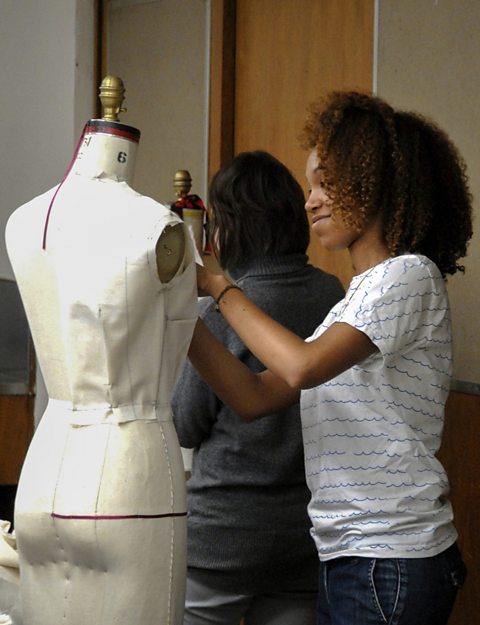


Quick textile designs can be modelled out of newspaper and more detailed models can be made from cotton or calicoA plain-woven textile made from unbleached cotton.. Fabric models are called toileAn early model of a textiles product. and can be made on a mannequinA body-shaped model. to test the dimensionsSizes and measurements. and drape of a garmentAn item of clothing..
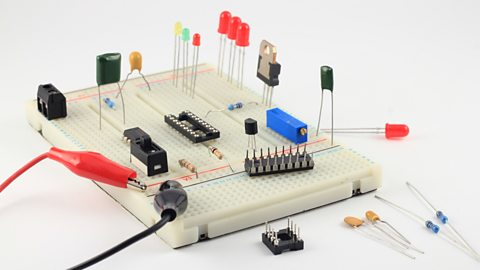
breadboardA non-solder way to model electrical circuits. are used in the early development of electronic products. They are boards containing a series of holes that electrical components Something you solder into a circuit, eg a resistor or a diode. can be pushed into to allow current flow without making a permanent join. Components can then be easily swapped to improve or fix a circuitA closed loop through which current moves - from a power source, through a series of components, and back into the power source..
| Advantages of physical modelling | Disadvantages of physical modelling |
| Allows a designer to physically handle a design and view from all sides | Can be time-consuming and complicated |
| Changes can be made quickly and easily | 3D printed models can be expensive and have limited materials available |
| Materials such as cardboard can be found cheaply and easily | Models can’t generally be used for testing as they don’t use the same materials that the product will be made of |
| Models can be scaled up or down in size | |
| Models can be used to show to a client and get feedback on before production |
| Advantages of physical modelling | Allows a designer to physically handle a design and view from all sides |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of physical modelling | Can be time-consuming and complicated |
| Advantages of physical modelling | Changes can be made quickly and easily |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of physical modelling | 3D printed models can be expensive and have limited materials available |
| Advantages of physical modelling | Materials such as cardboard can be found cheaply and easily |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of physical modelling | Models can’t generally be used for testing as they don’t use the same materials that the product will be made of |
| Advantages of physical modelling | Models can be scaled up or down in size |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of physical modelling |
| Advantages of physical modelling | Models can be used to show to a client and get feedback on before production |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of physical modelling |