Join EVA ('Earth's Virtual Assistant') to investigate the climate, plants and animals that characterise two of the planet's major biomes: woodlands and grasslands.
The video
KS2 Geography: Biomes. Woodlands and Grasslands.
EVA: Get set for an exciting journey.
I am your guide, ‘Earth’s Virtual Assistant.’ But you can call me E.V.A.
Your mission is to explore the world’s biomes. Biomes are areas of the planet with similar climates, landscapes, animals and plants.
[A MAP OF THE EARTH REVEALS SIX BIOMES]
There are six major biomes found on Earth. Rainforests. Deserts. Savannahs. Tundras. Woodlands. And Grasslands.
Let’s investigate…the woodlands biome.
Temperate woodlands are one type of woodland biome. They are habitats where the main plants are trees.
[A GLOBE SHOWS THE POSITION OF THE EQUATOR]
A biome’s climate is mainly controlled by its latitude on Earth - how far north or south it is. The temperate woodland biome is found in higher latitudes between the Tropics and the poles, in the temperate climate zone. This means that temperatures are less extreme and rainfall is more evenly spread across the year.
[THE GLOBE ZOOMS INTO THE UK]
It’s time to start this mission so let’s journey to the United Kingdom.
Temperate woodlands have four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter.
Leaves change colour in autumn and fall from the trees, growing back in the spring. This adaptation allows plants to survive cold winters.
These woodlands experience lots of rain throughout the year. Most of the trees are broadleaf trees such as oak, birch and chestnut.
[ON-SCREEN GRAPHICS - DECIDUOUS]
These are examples of deciduous trees, which are trees that drop their leaves every year.
[ON-SCREEN GRAPHICS - CONIFEROUS]
Temperate woodlands can also be home to some coniferous trees, which have evergreen, waxy needles that remain on the trees all year long, helping to reduce water loss.
Similar to a rainforest, there are different layers to the woodland biome, with trees of different heights. There are plenty of flowering plants within the forest in the spring, before the trees come into full leaf.
Temperate woodlands are rich in biodiversity. Amphibians, like frogs, lay their eggs in small ponds in the spring. Animals like red squirrels store nuts to eat during the winter, when there could be less food available.
Deforestation is one threat to temperate woodlands, when trees are cleared for different reasons including farming and to build houses for growing populations.
[DEBRIEF - WOODLANDS]
1: Temperate woodlands are habitats where the main plants found are trees. 2: This biome goes through distinct seasons. 3: Woodlands are home to lots of different species.
[MAP OF THE EARTH REVEALS THE NEXT BIOME]
The mission continues now and it’s time to explore another biome. This is the grassland biome.
Temperate grasslands are one type of grassland biome. They are vast and open areas of land, which are generally located between deserts and woodlands.
Due to their latitudes on Earth, the climate in temperate grasslands is less extreme than other biomes.
[MAP ZOOMS IN TO EASTERN EUROPE]
Let’s journey to Eastern Europe. A quarter of the planet’s surface is covered by temperate grasslands. This one is the largest. It’s called the Eurasian Steppe. It stretches from Hungary in Europe to China in Asia.
Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers with some rain. And, as their name suggests, grasses are the main plants found here.
The saiga antelope is famous for its bulging nose, which is an adaptation to help it survive in the grasslands. Its swollen nostrils cool their blood during hot, dry summers, and act as a heater in the winter to warm the cold air before it enters the saiga’s lungs.
Grasslands also exist across large parts of America. Temperate grasslands have good soil for farming. Most of the grasslands in the United States have been turned into fields for growing crops like wheat, oats and corn.
Wildfires that occur naturally, ignited by heat from the sun or a lightning strike, can be very destructive. But they can also play an important role in the biodiversity of the grasslands.
[ON-SCREEN GRAPHICS - BIODIVERSITY]
Scientists believe that occasional wildfires help to rid the land of old grasses and allow for new grasses to grow, helping to sustain life.
Threats to the grassland biome include unsustainable farming - such as overgrazing - and climate change, which could eventually turn some grasslands into deserts.
[DEBRIEF - GRASSLANDS]
1:Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers. 2: Occasional, naturally occurring wildfires can help make way for new vegetation. 3: Some farming methods can be harmful, ridding the soil of much needed nutrients.
Congratulations! We’ve come to the end of our fabulous journey exploring two of the world’s major biomes. Mission complete!
Woodlands and Grasslands
Download/print a transcript of this episode (pdf).
Pupils join EVA ('Earth's Virtual Assistant') to discover the climate, plants and animals that characterise two of Earth's major biomes: woodlands and grasslands.
They will discover that woodlands have four distinct seasons; that the woodland biome is characterised by trees, which can be both deciduous (shedding leaves in the winter) and coniferous (evergreen); that the climate of woodlands is temperate, and that consequently this biome is rich in biodiversity.
The video then explores the grasslands biome. Pupils will discover that grasslands are characterised by flat plains; that animals - such as the saiga antelope - have adapted to survive the extremes of temperature the grassland biome can experience; that the Earth's warming due to climate change is threatening this biome with desertification.
Teacher Notes
Download/print the full Teacher Notes with worksheets for this episode (pdf).
Teacher Notes prepared in partnership with the Geographical Association.
Key geographical vocabulary
Biome - large scale ecosystems.
Climate - the state of the atmosphere over many years or over a large area (ie the ‘average’ of the weather).
Temperate - areas with a mild climate, not too hot and not too cold, not too dry and not too wet.
Biodiversity - the variety of plant and animal life in a particular ecosystem.
Ecosystem - a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their environment.
Adaptation - the process by which plants and animals change over time to survive in their environment.
Suggested activities
- Make a flip-book to show how seasons affect trees in the temperate woodland biome, changing from spring > summer > autumn > winter.
- Demonstrate how trees absorb water through their roots and transport to their leaves. Use a cut celery stalk with leavesor white carnations. Place a cutting in a clear jar filled halfway with water. Add food colouring, leave overnight and observe the colour changes to the flower/leaves.
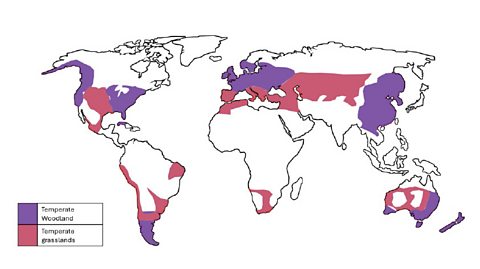
- Maps from memory: divide students into groups of 4 and give them each a number. Taking it in turns, show one pupil from each group (eg number 1s) a copy of the zonal map of the two biomes - keep it secret from others. Pupils have 30 seconds to remember what they can from the map then return to their group and describe where to colour in. Keep repeating until they’ve all had a turn, then see how good the maps are.
- Provide pupils with a blank map of the world. Label the equator and tropics, also 60°N and S. Shade their map to temperate woodlands and grasslands location. Then use an atlas and ask them to find the name of a place that is within that biome. This could turn into a game.
Points for discussion
- Where is the temperate woodlands biome located?
- What does 'temperate' mean?
- Did pupils know they lived in the temperate woodland biome? Were they surprised? Does it feel right?
- What is your local woodland like? What plants and animals are there locally?
- Where are the temperate grasslands located?
- How are grasslands used by people and animals?
- What threats does the grasslands face?
- How might climate change affect the grasslands?
Curriculum notes
This video is suitable for teaching KS2 in England and Northern Ireland, 2nd Level in Scotland and Progression Step 3 in Wales.
Resources
Teacher Notes
Download/print the Teacher Notes for this episode (pdf).

Transcript
Download/print the transcript of this episode (pdf).

Map showing the temperate woodland and temperate grassland biomes. image
Click to display the image full size.
Other videos in this series
Biomes: Rainforests and Deserts. video
Join the mission to investigate the climate, plants and animals of two of Earth's major biomes: rainforests and deserts.

Biomes: Savannahs and Tundras. video
Join the mission to investigate the climate, plants and animals of two of Earth's major biomes: savannahs and tundras.

See also... Settlements. collection
Join EVA on another mission: to discover different types of settlement - including villages, towns and cities - and to investigate the factors determining land use.

