Join EVA ('Earth's Virtual Assistant') to investigate the climate, animals and plants that characterise two of the planet's major biomes: rainforests and deserts.
The video
KS2 Geography: Biomes. Rainforests and Deserts.
EVA: Get set for an exciting journey.
I am your guide, ‘Earth’s Virtual Assistant.’ But you can call me E.V.A.
Your mission is to explore the world’s biomes. Biomes are areas of the planet with similar climates, landscapes, animals and plants.
[A MAP OF THE EARTH REVEALS SIX BIOMES]
There are six major biomes found on Earth. Rainforests. Deserts. Savannahs. Tundras. Woodlands. And Grasslands.
Let’s investigate…the rainforest biome!
[A GLOBE SHOWS THE POSITION OF THE EQUATOR]
A biome’s climate is mainly controlled by its latitude on Earth - how far north or south it is. A rainforest is hot and wet all year round. This is because they are found close to the equator - an imaginary line that runs around the middle of the Earth, which receives more direct sunlight than other places.
[THE GLOBE ZOOMS IN TO SOUTH EAST ASIA]
It’s time to start this mission so let’s journey to Southeast Asia.
[IMAGES OF RAINFORESTS]
Each biome has special features. The hot and wet climate found in the rainforest biome provides the perfect conditions for a wide variety of animals and plants to thrive. This is why rainforests are rich in biodiversity.
[ON-SCREEN GRAPHICS - BIODIVERSITY]
Biodiversity is the variety of plant and animal life in a place.
The forest floor is dark, as the trees above block out most of the sunlight.
The under canopy is the layer above the forest floor. This area is shady and cooler. These leaves with pointy tips are known as drip tips. This allows water to run off the leaves quickly without damaging them.
The canopy is the continuous layer of tree tops that is more sheltered. These spider monkeys have long, strong limbs and tails to help them climb through this layer of the rainforest.
The emergent layer consists of the tallest trees in the rainforest and they can grow up to 60 metres.
Protecting rainforests is important because they produce oxygen, and they also trap large amounts of carbon too, which helps to limit the rise of global temperatures.
Rainforests are threatened by humans cutting down large areas of trees, to use the wood or make space for activities like farming or mining.
[DEBRIEF - RAINFORESTS]
1: The rainforest biome has a hot and wet climate. 2: It has a huge variety of plants and animals. 3: This biome plays an essential part in maintaining world biodiversity and climate.
[MAP OF THE EARTH REVEALS THE NEXT BIOME]
Our mission continues now and it’s time to explore another biome. The next biome is desert.
[A GLOBE SHOWS THE LOCATION OF THE EQUATOR AND TROPICS]
Most desert biomes are found near two imaginary lines either side of the equator called the Tropic of Cancer to the north, and the Tropic of Capricorn to the south.
But not all deserts are hot, dry and sandy. Some of the world’s largest deserts are cold deserts located near one of the Earth’s poles, or at high altitude.
The thing that characterises all deserts - whether hot or cold - is a lack of rainfall.
[THE GLOBE ZOOMS IN TO AFRICA]
Let’s take a closer look at a hot desert biome.
Deserts cover approximately 33% of the Earth’s land area. Some may go years without a single drop of rain. A desert climate can see temperatures hit as high as 50 degrees Celsius during the day. Then drop rapidly at night. Sometimes to below freezing.
Only specially adapted plants and animals can survive here. These cacti store water in their stems so they can survive for a long time without rain.
[ON-SCREEN GRAPHICS - NOCTURNAL]
Some animals have adapted to avoid the heat of the day and are nocturnal, meaning they are active in the cooler nights.
This animal - found in north African deserts - is the fennec fox, which has adapted to help it survive the extreme temperatures. Their large, bat-like ears release body heat and help keep them cool.
A big challenge for Earth is that more land is turning into desert. This is called desertification, and one of its main causes is climate change.
In most fertile areas alongside existing deserts conditions are not only getting warmer but drier too. The lack of rain and too much wind leaves soil exposed and its quality is reduced - turning it into desert.
[DEBRIEF - DESERTS]
1: Desert biome climates are extremely dry, with little rainfall due to their latitudes on earth. 2: They can be extremely hot and very cold. 3: Many plants and animals have special adaptations to survive.
Congratulations! We’ve come to the end of our fabulous journey exploring two of the world’s major biomes. Mission complete!
Rainforests and Deserts
Download/print a transcript of this episode (pdf).
Pupils join EVA ('Earth's Virtual Assistant') to discover the climate, plants and animals that characterise two of Earth's major biomes: rainforests and deserts.
They will discover the layers that make up the rainforest from the floor, to canopy and emergent layer; they will see that rainforests are rich in biodiversity and how animals - like spider monkeys - have adapted to live in this biome.
The video then explores the contrasting desert biome. Pupils will discover that deserts can be both hot and cold; that it is lack of rainfall that characterises the desert biome; that animals need special adaptations to survive the extreme temperatures of the desert biome.
Teacher Notes
Download/print the full Teacher Notes with worksheets for this episode (pdf).
Teacher Notes prepared in partnership with the Geographical Association.
Key geographical vocabulary
Biome - large scale ecosystems.
Climate - the state of the atmosphere over many years or over a large area (ie the ‘average’ of the weather).
Tropics - the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn are imaginary lines at 23.5° north and south of the equator.
Biodiversity - the variety of plant and animal life in a particular ecosystem.
Ecosystem - a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their environment.
Adaptation - the process by which plants and animals change over time to survive in their environment.
Suggested activities
- Complete a table to note down the key features of rainforests and deserts: location, climate, plants, animals, threats.
- Have a world physical map on the board. Ask pupils to come up and point out where they would most expect to see rainforests or deserts.
- Demonstrate the five layers of the rainforest with five pupils crouching/ kneeling/ standing/ stretching up at different heights.
- Draw and label a desert scene and a rainforest scene (print example images and names as prompts as needed), including animals and plants specific to each biome.
- Provide pupils with a blank map of the world - see page 5 below. Label the equator and tropics. Pause the video where it shows a biome’s location and ask pupils to shade their map to show rainforest and desert locations. Then use an atlas and ask pupils to find the name of a place that is within that biome. This could turn into a game.
- Choose one biome and design an animal that would suit living here. Sketch it out and label it to show how it would suit the climate. Talk together about why it would suit this biome but not the other.
Points for discussion
- What controls where a biome is found?
- Why does the rainforest biome have so much plant life?
- Did it surprise you that deserts can also be cold?
- Can you name one animal or plant that might be found in a desert or rainforest?
- How do plants and animals adapt to the rainforest biome?
- How do plants and animals adapt to the desert biome?
- How do these places compare to our own local UK environment? Is anything similar?
- What are the layers of the rainforest? Is this like a woodland you’ve been to near home?
- What threats do these biomes face?
- How do humans influence biomes, for better or worse?
Curriculum notes
This video is suitable for teaching KS2 in England and Northern Ireland, 2nd Level in Scotland and Progression Step 3 in Wales.
Resources
Teacher Notes
Download/print the Teacher Notes for this episode (pdf).

Transcript
Download/print a transcript of this episode (pdf).

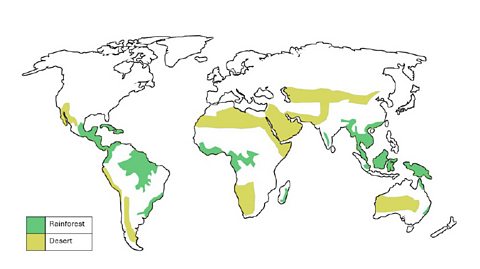
Map showing the rainforest and desert biomes. image
Click to display the image full size.
Other videos in this series
Biomes: Savannahs and Tundras. video
Join the mission to investigate the climate, plants and animals of two of Earth's major biomes: savannahs and tundras.

Biomes: Woodlands and Grasslands. video
Join the mission to investigate the climate, plants and animals of two of Earth's major biomes: woodlands and grasslands.

See also... Settlements. collection
Join EVA on another mission: to discover different types of settlement - including villages, towns and cities - and to investigate the factors determining land use.

