What is logical reasoning?

Another word for logicalFollowing rules that make sense. is sensible.
We can say an idea, or answer is logical if it follows rules that make sense.
Another word for reasoningThinking sensibly about a problem or situation. is thinking, coming up with ideas and answers to problems.
We can say that logical reasoningUsing agreed rules to think about information and solve problems. is just sensible thinking.
It's about knowing the rules and working out what will happen if you follow them.

What are the rules?
Let's look at an example. Suppose your friend says that they want to wear a spacesuit to school tomorrow. Your friend says no-one will notice.
The school rules say that a school uniform should be worn.
Everyone else in school will be wearing the proper uniform and your friend will look very different from everyone else in their shiny spacesuit.
What do YOU think will happen?
Will they be asked to change into their uniform?
It's sensible to think that they will be noticed by the teachers and will be asked to change into their uniform.
That's sensible thinking based on the rules. In other words, that's logical reasoning.

How can logical reasoning help in the real world?
Let's look at a real-world situation.
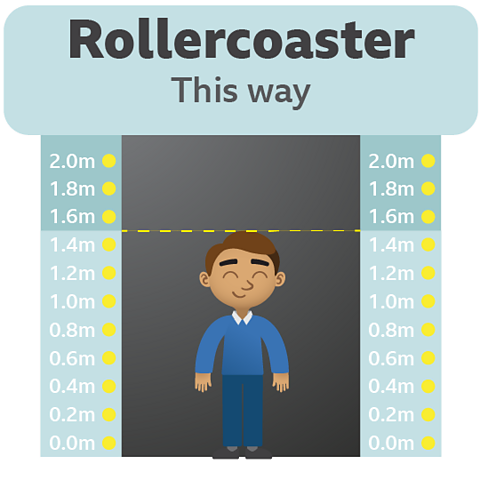
This rollercoaster is only safe for people whose height is 1.5m or more.
The entry gate is controlled by a computer systemA series of connected devices controlled by a computer..
The rollercoaster system has a set of logical rules in place to ensure the safety of riders.

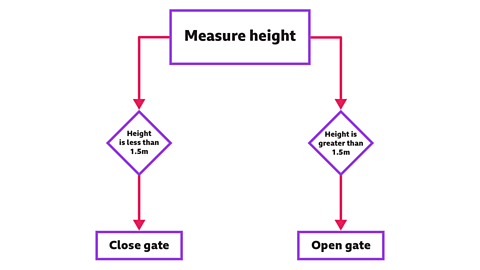
How do we use logical reasoning in a computer program?
The computerA device that processes information by following a set of rules called a program. controlling the entry gate is programmed to open if your height is greater than 1.5m and close if your height is less than 1.5m.
This flowchartA diagram showing the steps in a process or sequence of events. shows the way the program has been written.
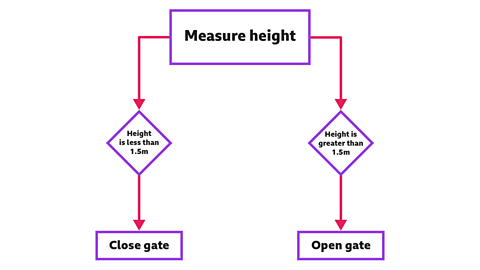
The rules in the programA sequence of instructions written in a coding language that a computer can understand. will ensure that only people who are tall enough will get through the gates and ride the rollercoaster.
Predicting what will happen
We can use logical reasoning to help us predict what will happen when these people try to go through the gate.
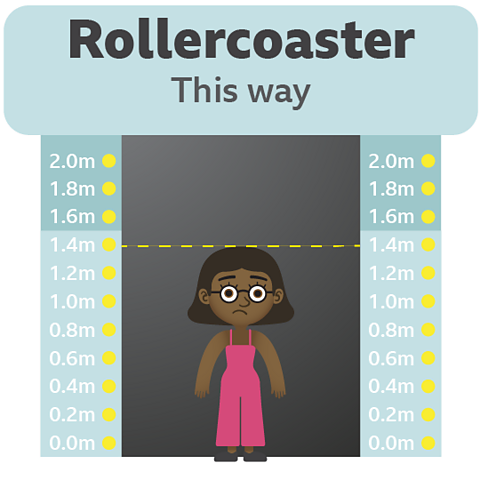
Molly is 1.4m tall.
Will Molly get through?
The rule says if the height is less than 1.5m the gate will close.
We know Molly's height is less than 1.5m, so that's easy, the gate will close.
Molly is not tall enough to ride the rollercoaster.
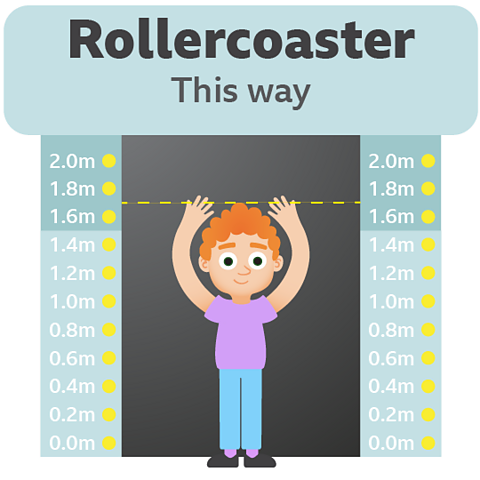
Ben is 1.7m tall
Will Ben be allowed through?
Ben is 1.7m tall, so logically the entry gate will open for him as he's taller than 1.5m.
Remember, the rule says the gate will open if the height is greater than 1.5m.
Using logical reasoning to solve problems
We can use logical reasoning to solve problems and debug programs in a computer-controlled device or system.
We can look carefully at the rules, decide if they are logical and make changes if we think that will solve the problems.
Let's see what happens when Leon tries to ride the rollercoaster.
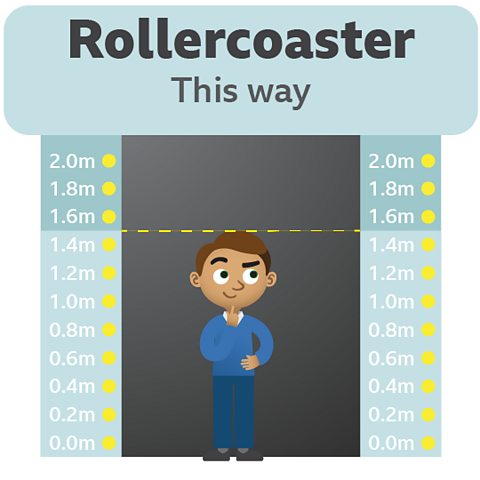
Remember the safety rule for riders is that they have to be 1.5m taller or more.
Leon is exactly 1.5m tall so he's tall enough to safely go on the ride.
The program rule says: If height is less than 1.5m gate will close.
Leon is not less than 1.5m so the gate should open.
But there is a problem. The other rule says the gate will only open if the height is greater than 1.5m.
Leon is not greater than 1.5m, so the gate won't open.

The program has a bugAn error or mistake in a computer program that affects the outcome. and the gate system doesn't know whether to open or close.
Can you find the bug in the program using logical reasoning?
Changing a program using logical reasoning
We need to use our logical thinking skills to work out how to change the program rules so that people who are exactly 1.5m tall can ride.
We need to include them in the rule.
We can change the rule to say:If the height is greater or equal to 1.5m then open the gate.
This is what the new flowchart would look like:
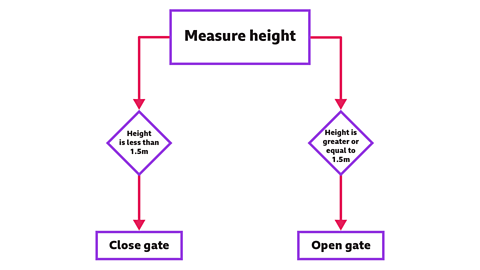
Do you think Leon will be able to ride the rollercoaster now?
The flowchart has changed.
Leon can ride the rollercoaster thanks to our excellent logical reasoning skills.
Why not have a go at measuring your family and friends - can you work out if they are tall enough to ride the rollercoaster?
Use the same rule for the rollercoaster:
If the height is greater or equal to 1.5m then open the gate.
Watch: Logical reasoning
You can find out more about logical reasoning in this video from BBC Bitesize for Teachers.
NARRATION: What is logical reasoning? Another word for logical is sensible. We can say an idea or an answer is logical if it follows sensible rules - rules that make sense. Another world for reasoning is thinking, coming up with ideas and answers to problems. So we could say that logical reasoning is just sensible thinking. It’s about knowing the rules and working out what will happen if you follow them.
Let’s look at an example. Suppose your friend says that they want to wear a spacesuit to school tomorrow. I know, stay with me. Your friend says no one will notice. Now, you know that the school rules say that you have to wear a school uniform, or you will be sent home to change. You also know that everyone else in school will be wearing the proper uniform and your friend will look very different from everyone else in their shiny spacesuit. It’s sensible to think that they will be noticed by the teachers and sent home to change. That’s sensible thinking, based on the rules. That’s logical reasoning.
Let’s look at another real-world problem. We all love a theme park don’t we? Well, I do. This rollercoaster has a set of rules in place… The computer controlling the entry gate is programmed to open if your height is greater than 1.5m. Close if your height is less than 1.5m. Let’s predict what will happen when these people try to go through the gate using our new friend logical reasoning.
Here’s Molly, she’s 1.4m tall. Will she get through? The rule says if the height is less than 1.5m the gate will close. We know Molly’s height is less than 1.5m, so that’s easy, the gate will close, right? Let’s watch…
Lucky for me, I’m 1.7m. So, logically the entry gate will open for me as I’m taller than 1.5m and the rule says the gate will open if the height is greater than 1.5m. Here goes… OK, stop now, stop now! That wasn’t me screaming by the way… anyway!
OK, now it’s Leon’s turn. He’s exactly 1.5m tall, he’s tall enough to safely go on the ride. What do you think the gate will do? Let’s look at the rules and use logical reasoning to predict what will happen. A flow chart will help. The program rule says: If height less than 1.5m gate will close. Leon is not less than 1.5m so the gate should open… But hang on, the other rule says the gate will open only if the height is greater than 1.5m. Leon is not greater than 1.5m, so the gate won’t open… I’m confused! The system has encountered a problem. Poor Leon, how can we get him through the gate?
We need to use our logical thinking skills to change the program rules so that people who are exactly 1.5m tall can ride. So our second rule is now: If the height is greater or equal to 1.5m then open the gate. The flow chart has changed. Let’s see if that works for Leon… Yay, Leon can ride the rollercoaster thanks to our excellent logical reasoning skills.
We should use logical reasoning when we create computer programs to make them have sensible rules and instructions built-in. These rules and instructions make them good at the jobs we want them to do. A large scale example of those types of computer control systems are in the skies above our heads. No, it’s not a bird, it’s a plane.
An autopilot program on an aeroplane needs to have thousands of rules built in to calculate the speed of the plane, the effect of wind on the wings, navigating through the sky to avoid other planes and to also reach the correct destination. But the most important rule, keeping the plane 30,000ft in the air! Luckily, computers are very good at following the rules in their programs and they can do it quickly and accurately, often better than a human can.
We can also use logical reasoning to solve problems, debug, what we notice in a computer-controlled device or system. We can look carefully at the rules, decide if they are logical, and make changes if we think that will solve the problems. In short, logical thinking is awesome!
Activities
Dance Mat Typing game! gameDance Mat Typing game!
Build and test your computing skills with different levels of touch type challenges.

More on Computer science
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 12

- count5 of 12
- count6 of 12

- count7 of 12