Geocaching and industry in Dundee
Dundee is the fourth largest city in Scotland. The industries and jobs that Dundee is home to have changed many times over the years.
In this article you can learn:
- what geocaching is
- about different industries in Dundee
- how the Industrial Revolution affected Dundee
This article is suitable for learning about People, Place and Environment in primary school.
Video - Geocaching and industry in Dundee
Watch as Isla and Connor explore Dundee through geocaching. They learn all about different industries and how the Industrial Revolution affected Dundee.
CONNOR: Hello Dundee!
Geocaching is the perfect way to explore it.
Using GPS, clues and a map, we can find hidden log books inside containers, sign them and put them back for the next person to find.
GPS coordinates tell you exactly where a place is.
They're based on a place's latitude, which is how far north or south it is from the equator, and its longitude, how far east or west it is from the prime meridian that runs through Greenwich in London.
ISLA: Sounds like fun, but we should always be careful that we're exploring safely and responsibly.
Go on, then. What's the first clue?
CONNOR: By the water, not far from the sea, that’s where you will discover me.
ISLA: Look!
Discovery Point on the River Tay.
That's where you will discover me.'
It's right here. Let's go!
ISLA: Wow, this ship, The Discovery, was the first Antarctic research ship.
The Waterfront is where Dundee's history began.
For centuries, it was a port and a base for fishing.
By the eighteenth century fishing and whaling provided work for lots of people.
ISLA: People used to catch whales?
CONNOR: Yes, strange to us now, but in the past whaling was a big primary industry.
A primary industry involves getting raw materials.
Whaling, fishing, farming and quarrying for stone are all primary industries.
ISLA: Building ships like The Discovery also became an important industry in Dundee.
CONNOR: Ship building is a secondary industry.
It uses a primary material, wood, to make ships.
So in Dundee, a primary and secondary industry supported each other.
Whaling and fishing needed ships and ship building was paid for by whaling and fishing.
ISLA: What's the next clue, Connor?
CONNOR: This old mill reveals the history of Dundee’s past textile industry.
ISLA: The GPS says Verdant Works, an old textile mill, is just under a mile North West.
Found it!
Dundee is known for jute, jam and journalism and this is the jute part.
Jute is a textile made from plants grown in India.
Jute plants were softened with whale oil before they could be turned into material.
There was plenty of whale oil here and the city grew to become the biggest jute making city in the world.
These old textile mills were Dundee's biggest employer.
This is another kind of secondary industry, processing the raw materials, jute and the whale oil, into textiles.
CONNOR: Lots of people moved here from the rural countryside to work.
This period was known as the Industrial Revolution.
ISLA: Maybe the next clue will tell us something about Dundee's modern day industries.
CONNOR: A game-changing university, helped to support a new industry.
CONNOR: Hmm.
The GPS coordinates lead us towards Abertay University.
Let's go!
ISLA: So what type of industry is this university?
CONNOR: Universities are tertiary industries.
Tertiary industries provide a service.
It could be hairdressing, hospitals, or schools and universities teaching people.
ISLA: Ah, right.
So what did the clue mean about this being a game-changing university?
CONNOR: Loads of video games are made in Dundee and Abertay became the world's first university where you could study how to design and develop computer and video games.
So, the city began with whaling, because of the whalers, jute could be turned into textile here.
Whaling is a primary industry.
Textile manufacturing is a secondary industry.
ISLA: And today, the new train station and attractions like the V&A Museum behind us, are tertiary industries that serve tourists by providing travel and entertainment.
And there are quaternary industries, which means industries that work with or provide, informationlike video game development, computing or research.
Dundee has an incredible story.
I wonder how it will develop next.
What is geocaching?
 Image source, YAY Media AS / Alamy Stock Photo
Image source, YAY Media AS / Alamy Stock PhotoGeocaching is a type of treasure hunt.
It uses GPS coordinates, clues and maps to help you find hidden log books. You can sign these and put them back for other explorers to find.
 Image source, YAY Media AS / Alamy Stock Photo
Image source, YAY Media AS / Alamy Stock PhotoWhat is GPS?
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It uses satellites to tell you where you are or where you want to get to.
GPS satellites send out signals of where they are above the Earth.
Phones and other devices track these signals. If your device receives signals from four or more satellites, it can work out where you are based on where the satellites are and how long it takes for the different signals to reach you.
What are the clues in geocaching?
Following clues is an important part of geocaching. Clues give you a little bit of information that will help guide you to your destination.
For example, Isla and Connor's first clue was "By the water, not far from the sea, that's where you will discover me".
From this they worked out that their destination was the RSS Discovery, a ship built in Dundee which you can visit at Discovery Point, next to the River Tay.
What is a map?
Isla and Connor had to follow a map while exploring Dundee.
A map is a two-dimensional image of an area. GPS can show you where you and and where you want to go to but a map can help by showing roads, buildings, rivers and other features that you might need to travel along or round.
Industry in Dundee
Dundee has been home to many different industries.
Like all industries, these can be divided into types or sectors of industry.
Primary industry
Primary industries find or grow raw materials.
For example, the forestry industry grows trees and cuts them down for wood, farming grows crops or raises animals, mining digs out coal, metals or other material from the ground.
In the past whaling and fishing were both important primary industries in Dundee.
Secondary industry
Secondary industries make products from the items provided by the primary industries.
As Dundee grew, producing woollen cloth from wool and linen from flax were early examples of secondary industries. During the Victorian era, producing jute cloth became Dundee's biggest industry.
Other important secondary industries in Dundee included shipbuilding and making marmalade and jam.
Learn about work in a jute factory in Victorian Dundee here: Working in Victorian Scotland
Tertiary industry
Tertiary industries provide services. For example, hairdressing, railways, schools, cinemas, shops and hospitals are all tertiary industries.
Dundee grew as a trading port, so shipping goods in and out of the harbour, and buying and selling these goods were important tertiary industries.
Journalism and producing newspapers and comics have also been important tertiary industries in the city. The V&A Museum is a more recent example of one of Dundee's many tertiary industries.
Quaternary industry
Quaternary industries do research or work with, or provide information.
For example, computing, ICT (information and communication technologies), web design, and scientific research are all quaternary industries.
One of Dundee's biggest quaternary industries is video game development.
Industrial Revolution in Dundee
The Industrial Revolution is the name for a time of great change in industry, technology and science. It began around 1760 and led to many of the biggest changes of the Victorian era.
Before the Industrial Revolution, many people in Scotland lived in rural areas. Many worked on crofts or farms. Some people produced goods at home, for example making woollen or linen cloth by weaving.
Click through the slideshow below to see how the industrial revolution changed Dundee and Scotland.
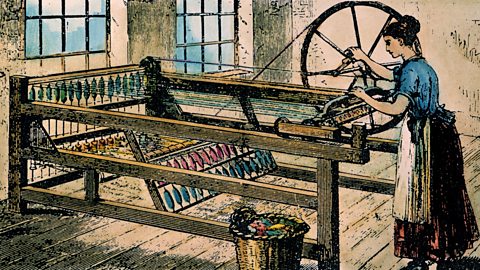
Image caption, Technology
Before the Industrial Revolution craftspeople made things in their own homes or in small workshops. Weavers would use handlooms to make cloth. New machines were invented that could work much faster and on a bigger scale than human hands. The spinning jenny and power loom allowed the textile industries to grow. In Dundee, water-powered spinners were introduced and mills began producing larger amounts of linen cloth than people working at home as weavers could. (The Granger Collection / Alamy Stock Photo)
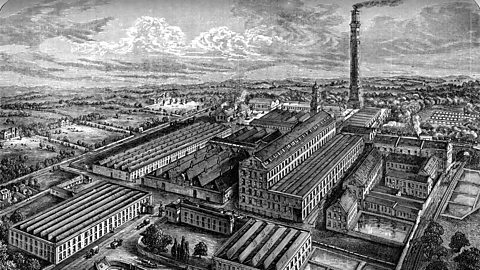
Image caption, Energy
Instead of being worked by hand, new machinery like the power loom could use other energy sources. Coal, oil and gas became important energy sources for people's homes and for industry. The invention of the steam engine powered by coal from Scottish mines allowed mills to develop into much larger factories with many machines. Dundee's Camperdown Works became the world's biggest jute works. It covered 30 acres of land (about the size of 17 football pitches) and had more than 5,000 workers. (The Print Collector / Alamy Stock Photo)

Image caption, Work
Factories were powered by coal and steam but people were still needed to keep the machines working. People moved from the countryside, or from other countries like Ireland, to Scottish cities looking for work. Pay was often low, shifts were long and conditions were often dirty, noisy and dangerous. Dundee's mills gave more jobs to women and children because they could be paid less. Eventually laws were introduced to improve conditions for factory workers. This photograph shows a worker checking a spinning frame at a Dundee jute mill in 1938. (SuperStock / Alamy Stock Photo)

Image caption, Transport
Roads were improved, especially with the introduction of macadamised road surfaces that were stronger and smoother. The invention of the steam train and railway made travel and transport much quicker, more reliable and better able to carry heavy loads. Improvements in shipbuilding and design made transporting goods around the world quicker and more reliable. Ships built in Dundee brought jute plants from India to the city and finished jute products like sailcloth, ropes and sacks all around the world. This photography shows the RSS Discovery being built in Dundee in 1901. (The Print Collector / Alamy Stock Photo)
1 of 4
Learn more about the Industrial Revolution in Scotland during the Victorian era: The Industrial Revolution
Key words about geocaching and industry
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - A set of numbers that tell you the position of someone or something.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - Global Positioning System. A system that uses satellites to work out where somewhere is on the surface of the Earth.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - How far north or south somewhere is from the Equator.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - How far east or west somewhere is from the Prime Meridian, a line than runs north and south through Greenwich in London.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - An industry that extracts or grows raw materials, for example mining or farming.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - An industry that turns raw materials into new products, for example turning wood into furniture or wheat into bread.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - An industry that provides a service, for example a hairdresser or a supermarket selling food.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - An industry that works with information and technology, for example medical research or computer game design.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - Cloth made from the flax plant.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - A strong, rough fabric that is made using fibres from the jute plant.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - A period during the 18th and 19th Century when the UK and other countries developed new technology and transport, and cities grew around new factories and industries.
Quiz
Challenge

Explore your local industries
Can you find examples of primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary industries in your local area?
Make a list of products or services you use during a day. Can you group these into the types of industry that provide them?
More to learn
Learn more about landscapes and industry in Dundee with these BBC Bitesize articles for primary learners.
River Tay - lower course. revision-guideRiver Tay - lower course
Travel down the lower course or the River Tay to Dundee and the North Sea.

Work in Victorian Dundee. revision-guideWork in Victorian Dundee
Find out about working life in Dundee's Victorian jute mills.

More on Landscapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 25

- count4 of 25

- count6 of 25
