What do you know?
What are biomes?
Biomes are large-scale ecosystems. The surface of the Earth can be divided according to biomes.
Key points
- Biomes are large-scale ecosystemThe living organisms in a particular area (such as plants and animals), together with the non-living components of the environment (such as rocks and soil).. Examples of biomes include tropical rainforests, hot deserts, deciduous forests, boreal (taiga) forests and tundra.
- The location of global biomes is determined by several factors, including latitude, altitude, continentalityThe difference between climates that are located within landmasses and those that are located close to large bodies of water. and ocean currents.
What are biomes?
The surface of the Earth can be divided according to biomes.
Tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are found between the Tropics of Tropic of CancerAn imaginary line that runs parallel to the Equator at 23.5° north. and Tropic of CapricornAn imaginary line that runs parallel to the Equator at 23.5° south., 23.5° north and south of the equatorAn imaginary line that runs around the Earth. The equator marks the dividing line between the Northern and Southern hemispheres.. These dense forests grow in hot, wet conditions and a wide range of animals, such as monkeys, jaguars and parrots, live here.Boreal (taiga) forests
Cold environments, where precipitationAny moisture that falls from the clouds, such as snow, rain, hail and sleet. often falls as snow. Evergreen coniferous trees, often with needles and cones, grow here. Moose, bears, lynx and wolves live in these forests.Hot desert
Dry areas with sparseWhen something is in short supply, for example sparse vegetation means that very few plants are growing. vegetation, commonly found along the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. succulentPlants found in dry arid climates that are able to store water in leaves, stems or roots. plants, such as cacti, and many types of reptiles and insects are found here.Tundra
Cold, dry climates found almost entirely in the far north of the planet. Permafrost prevents trees from growing, but low-lying plants such as mosses thrive. Reindeer and Arctic foxes live here.Deciduous forests
Temperate climates, which means that they are not too hot or too cold. Trees such as oak and elm that lose their leaves during cooler months grow here. Animals such as owls, red deer and badgers live in these forests.

How different species have adapted to live in the Arctic tundra
Lapland is a place many of us dream of visiting.
There’s plenty to do here – husky rides, visit the grottos, and if you’re lucky, see the spectacular northern lights.
But how has the environment shaped the landscape and this biome?
Lapland is in the region of Northern Scandinavia, part of the Arctic tundra. In Finnish, the word tundra means treeless plain.
The Arctic tundra encircles the North Pole, extending from the frozen Arctic in the North, to the coniferous forest, also known as the taiga, in the south.
Countries across the world such as Canada, Iceland, Norway, Russia, and parts of the USA have tundra biomes.
The climate in the tundra biomes is extremely cold – I mean seriously cold! You wouldn’t want to forget your winter woollies.
The average winter temperatures can be below -30 °C. A domestic freezer is usually -18 °C. Even in the short summers, the average temperature is usually only between 3 °C and 12 °C.
There is very little rainfall, with yearly precipitation being around 150 - 250 mm, which is about a third of London’s annual rainfall.
The freezing conditions mean that one of the main features of the environment is permafrost, which – as the name suggests – means permanently frozen ground. Although, the surface layer – being only a few centimetres – may melt during the summer months, leaving muddy pools of water.
Some plants and vegetation do grow here.
The Bearberry plant has had to evolve to survive the harsh and freezing conditions and the long dark winters. So, its root system is shallow to cope with the thin and frozen soil, and plants grow closely together to provide warmth and shelter from the strong winds.
This is the Arctic Fox. They are extremely well adapted to the freezing conditions. Their thick coat provides insulation, and hair on the pads of their feet stops them slipping on the ice. They can curl their thick bushy tails around their nose and face to keep warm. In winter, their white fur acts as camouflage to help hide them from their prey. They survive by eating a varied diet including dead seals and birds’ eggs.
This handsome-looking mammal is a Musk-Ox, common in North America. Its adaptations include two layers of fur (one short and one long) to trap in the heat and protect it from the weather. They have large and hard hooves so that they can break ice to find water to drink. In the winter, they huddle together in groups to retain heat.
Tundra environments aren’t hugely inhabited by humans, but there are groups of people who call this ecosystem home.
The Sami people inhabit the far north of Scandinavia, where they rear reindeer, sheep, and are experts at fishing. About 10% of the Sami, mostly those involved with reindeer, move their animals across the tundra coniferous forest biomes in response to the seasons.
So, whilst at first this may seem like a bleak, inhospitable landscape, if you know where to look, it is teeming with wildlife, with amazing adaptations to help them not only survive, but thrive, in one of the world's most extreme environments.
Question
Which biome do reindeer live in?
Reindeer live in the tundra in the cold Arctic regions of North America and Eurasia.
Why do global biomes vary?
The characteristics of global biomes are determined by several factors.
latitudeImaginary lines that run east to west around the Earth, parallel to the Equator or 0° latitude. They can be measured in degrees (°).
Biomes closer to the equatorAn imaginary line that runs around the Earth. The equator marks the dividing line between the Northern and Southern hemispheres. are hotter as the sun’s radiation is more concentrated here due to the curvature of the Earth. Biomes closer to the poles are therefore colder. The global atmospheric circulationThe pattern in which air moves across the planet. Global atmospheric circulation is split into six cells; two Hadley cells, two Ferrel cells and two Polar cells. of air evens out this difference in temperature. The movement of air in part of this air circulation, known as the Hadley Cell, is responsible for the moist air that rises at the equator and the dry air that falls over the Earth’s deserts.
altitudeThe height of the land, measured in relation to sea level.
Higher land is cooler and wetter. There is a decrease in air temperature of around 0.6 to 0.7 °C for every 100 m gained in height. Cold mountain or alpine biomes are found at high altitude, even along the equator.
continentalityThe difference between climates that are located within landmasses and those that are located close to large bodies of water.
The sea retains heat during colder months, but remains cool during warmer months. Places closer to the sea have milder and often wetter biomes than those inland. This can be seen with the more moderate temperatures experienced along the coastline of south-western Europe.
Ocean currents
Warm ocean currents bring milder temperatures and higher precipitationAny moisture that falls from the clouds, such as snow, rain, hail and sleet.. Cold ocean currents bring cooler temperatures and lower precipitation. A cold ocean current flowing along the south-west coast of Africa created the Namib desert.
Question
Which biome is found at high altitudes?
The climate at high altitudes is usually cooler and wetter. Mountain or alpine biomes are found at high altitudes.
What is climate?
The global atmospheric circulation system determines many climates.
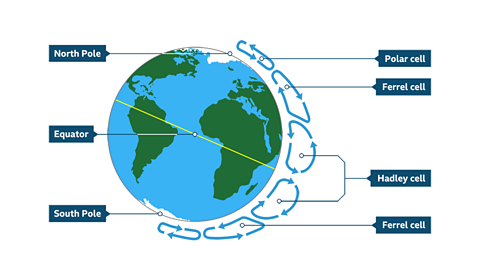
Image caption, Global atmospheric circulation
The movement of air across the planet occurs in a specific pattern. The whole system is driven by the Equator, which is the hottest part of the Earth. Air moves in six large cells: three in the Northern Hemisphere and three in the Southern Hemisphere. The cells have names: the Hadley cells, the Ferrel cells and the Polar cells.
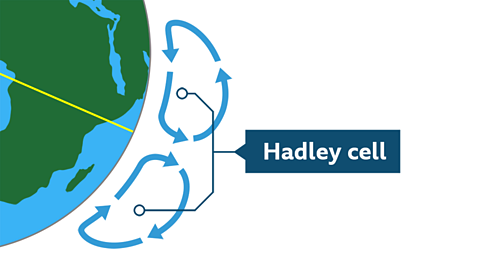
Image caption, Global atmospheric circulation
Air rises at the Equator. Rising air leads to rainfall. The rising air eventually reaches the edge of the atmosphere. It cannot go any further and so it travels to the north and south. This movement forms part of the Hadley cell.
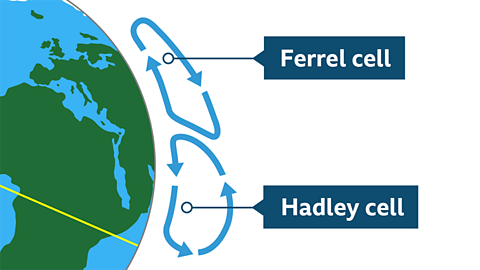
Image caption, Global atmospheric circulation
The air becomes colder and falls back towards the Earth at around 30° north and south of the Equator. This is the point where the Hadley cell and Ferrel cells meet. Falling air is usually dry.
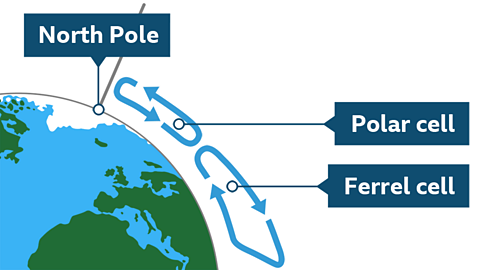
Image caption, Global atmospheric circulation
Air rises again at around 60° north and south and falls again around 90° north and south. This is where the Polar cell lies. Rainy parts of the world are found wherever air rises and dry parts of the world are found wherever air falls.
1 of 4
Factors that determine the climate of a country and the five main climate zones of the world
Climate describes an average of weather conditions in an area over a period of time, usually around thirty years.
There are many different factors that determine the climate of a place, like…
Distance from the Equator: the curve of the Earth means that places furthest from the Equator - like the North and South Poles – are less exposed to the sun’s heat, while those closer to the Equator receive more direct, intense heat.
Elevation: how high or low an area is, as temperature decreases the higher you go.
Distance from the sea: areas by the coast tend to be cooler in summer and warmer in winter because they are cooled and warmed by ocean currents and water holds its temperature for longer.
Vegetation: the release of water vapour as part of photosynthesis impacts on cloud formation so areas like rainforests are very wet.
The world has five main climate zones.
Polar climates are cold and dry with long, dark winters and short summers. Temperatures rise above freezing for only a few months each year.
Temperate climates, like ours in the United Kingdom, have four clear seasons with warm summers, if we're lucky, and cool winters.
Arid climates are found in desert areas like the Sahara, and are hot and dry all year round. They usually receive less than 250mm of rainfall each year.
Tropical climates are found in places like the Amazon rainforest and have hot temperatures all year round with two seasons, one wet and one dry.
And a Mediterranean climate has hot, dry summers and mild winters.
The climate is something that affects us all, from our economy, to the food we eat, to our leisure activities.
Question
What type of climate is found where air rises?
Rising air usually leads to rainfall and so wet climates are found where air rises. Air rises along the equator and at 60° north and south of the equator.
Test your knowledge
Play Planet Planners on Roblox! gamePlay Planet Planners on Roblox!
Explore global locations, solve real-life challenges and make the big decisions that shape the future.

More on Global biomes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5

- count4 of 5

- count5 of 5
