Key points
Fractions are equivalent if they are of equal value. equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. can have different numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used. Eg, for 1⁄3, the numerator is 1 and denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts. Eg, for 1⁄3, the denominator is 3.
Equivalent fractions can be found by:
- using a bar modelOne or more rectangular bars drawn to represent information. or a fraction wallA set of bar models representing different fractions. A fraction wall is used to compare fractions.
- multiplying both the numerator and denominator of a fraction by the same number
- dividing both the numerator and denominator of a fraction by a common factorA whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers. Eg, 2, 5 and 10 are common factors of 30 and 20
Learning about common factors may be useful when finding equivalent fractions.
How to find equivalent fractions
A fraction wallA set of bar models representing different fractions. A fraction wall is used to compare fractions. is made up of several bars, all of equal length. Each complete bar represents one whole. It can have several bars so more fractions can be compared.
To find equivalent fractions on a fraction wall:
Locate the fraction on the fraction wall.
Draw a vertical line to the right of the fraction.
Any equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. will be aligned to this line.
Example: using a fraction wall
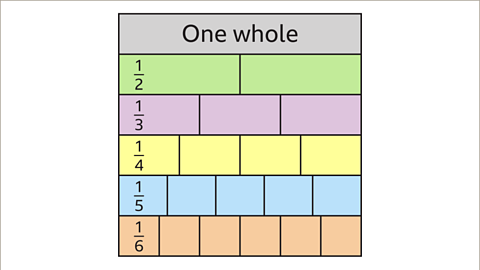
Image caption, A fraction wall can be used to compare fractions and find equivalent fractions.
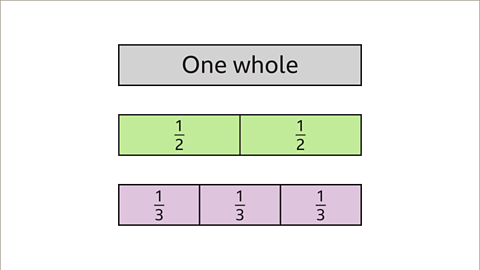
Image caption, One whole is the same as two halves. It is also the same as three thirds.
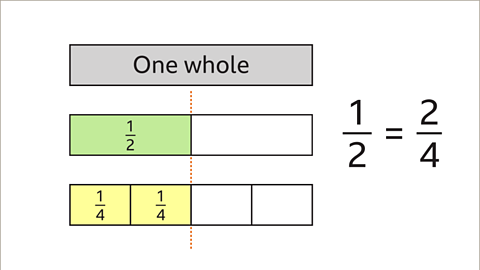
Image caption, 1⁄2 is equivalent to 2⁄4. Both fractions have the same value.
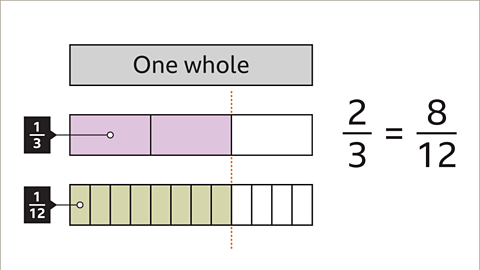
Image caption, 2⁄3 is equivalent to 8⁄12. Both fractions have the same value.
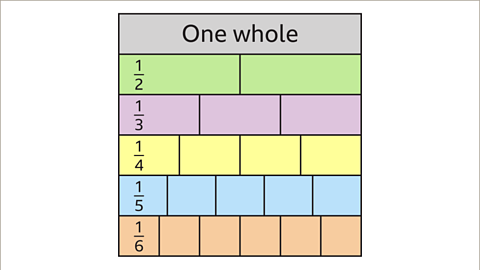
Image caption, Create a fraction wall by starting with one whole. Then create several bars split into 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 equal parts. This can be extended to include more rows when necessary.
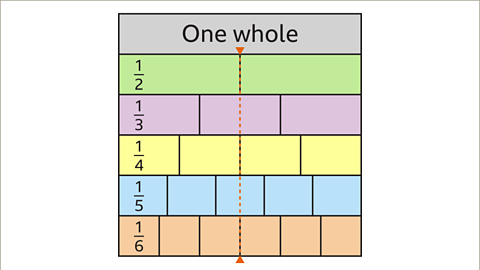
Image caption, What fractions are equivalent to 1⁄2?
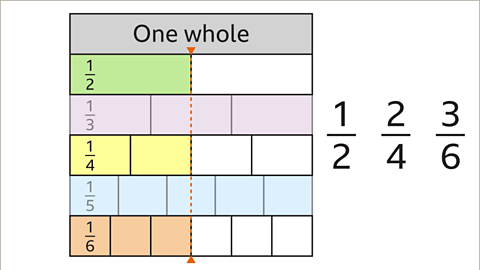
Image caption, Draw a line to the right of 1⁄2 on the fraction wall. 1⁄2 is equivalent to 2⁄4 and 3⁄6
1 of 7
How to create equivalent fractions
To create equivalent fractions using multiplication and division:
Multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. An infinite number of equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. can be created this way.
Divide both the numerator and denominator by a common factorA whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers. Eg, 2, 5 and 10 are common factors of 30 and 20. There may be more than one possible common factor.
To decide if two fractions are equivalent:
simplify (a fraction)To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, also known as its lowest terms. each fraction by dividing the numerator and denominator by their highest common factor (HCF) The largest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. Eg, 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20. Highest common factor is written as HCF. .
Compare the simplified fractions.
If they are the same, the original fractions are equivalent.
Example: using multiplication and division
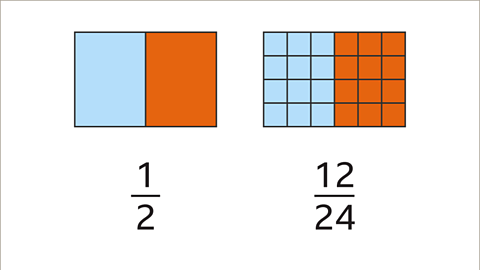
Image caption, 1⁄2 is equivalent to 12⁄24
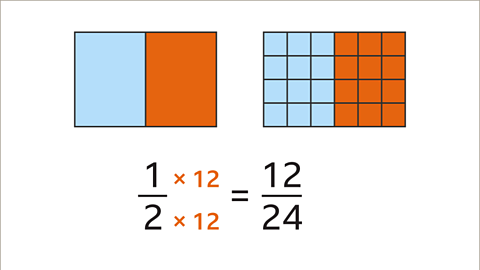
Image caption, 1⁄2 is equivalent to 12⁄24. The numerator and the denominator have both been multiplied by 12
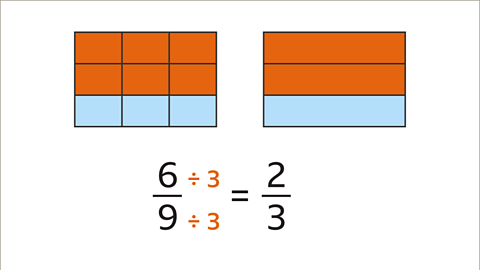
Image caption, 3 is a common factor of 6 and 9. Divide both the numerator and denominator by 3. This gives 2⁄3. 6⁄9 is equivalent to 2⁄3
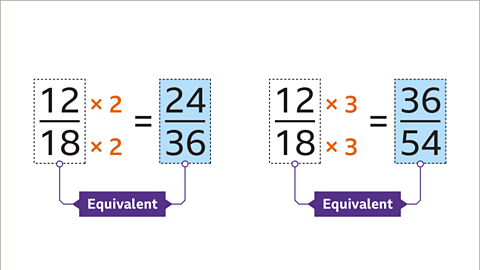
Image caption, 12⁄18 is equivalent to 24⁄36. It is also equivalent to 36⁄54. An infinite number of equivalent fractions can be created this way.
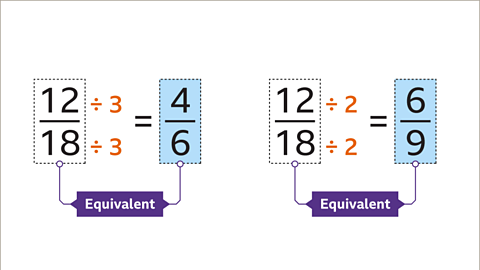
Image caption, 12⁄18 is equivalent to 4⁄6. It is also equivalent to 6⁄9. Equivalent fractions can only be created this way by dividing by a common factor.

Image caption, Are 14⁄20 and 35⁄50 equivalent fractions?
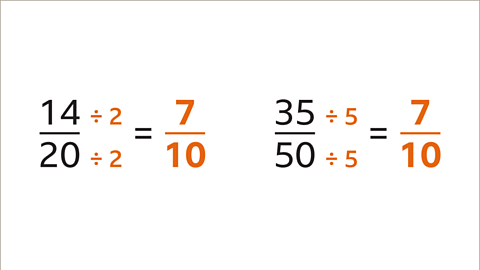
Image caption, The highest common factor of 14 and 20 is 2. 14⁄20 simplifies to 7⁄10. The highest common factor of 35 and 50 is 5. 35⁄50 simplifies to 7⁄10
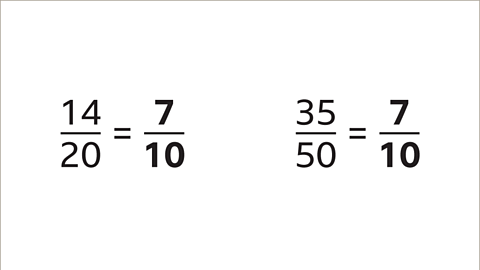
Image caption, Both 14⁄20 and 35⁄50 simplify to 7⁄10. The fractions have the same value - they are equivalent.
1 of 8
Game - Equivalent fractions
Put your equivalent fractions skills into practice with these puzzles from our Divided Islands maths game.
Play the full Divided Islands game.
How to work out a missing value in an equivalent fraction
To work out the value of a missing numerator:
Find the multiplierThe number by which another is multiplied. Eg, in the calculation 4 x 5, the multiplier is 5 or divisorThe number by which another is divided. Eg, in the calculation 30 ÷ 6 , the divisor is 6 by dividing the larger denominator by the smaller denominator.
To find the numerator for the larger denominator, multiply by the number you found.
To find the numerator for the smaller denominator, divide by the number you found.
To work out the value of a missing denominator:
Find the multiplier or divisor by dividing the larger numerator by the smaller numerator.
To find the denominator for the larger numerator, multiply by the number you found.
To find the denominator for the smaller numerator, divide by the number you found.
Examples: missing values
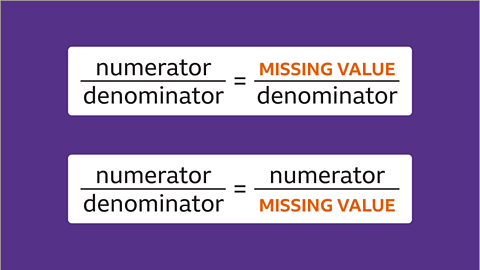
Image caption, These are equivalent fractions with one value missing.
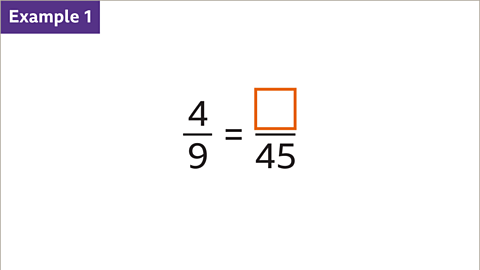
Image caption, The two fractions are equivalent. Find the missing numerator.
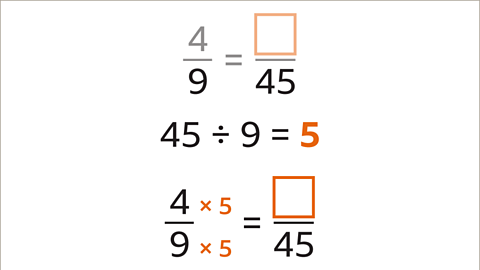
Image caption, Divide the larger denominator by the smaller denominator. 45 divided by 9 is 5. 5 is the multiplier. The numerator and denominator should both be multiplied by 5
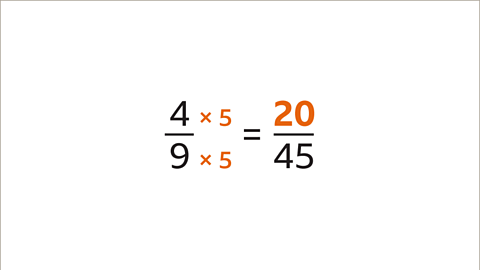
Image caption, 9 multiplied by 5 is 45. 4 multiplied by 5 is 20. The missing numerator is 20. 4⁄9 and 20⁄45 are equivalent.
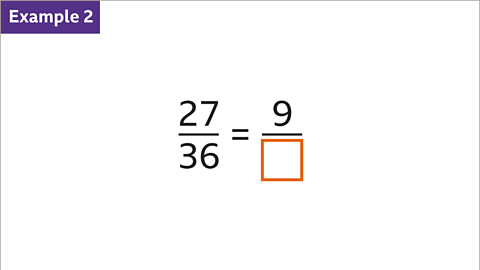
Image caption, The two fractions are equivalent. Find the missing denominator.

Image caption, Divide the larger numerator by the smaller numerator. 27 divided by 9 is 3. 3 is the divisor. The numerator and denominator should both be divided by 3
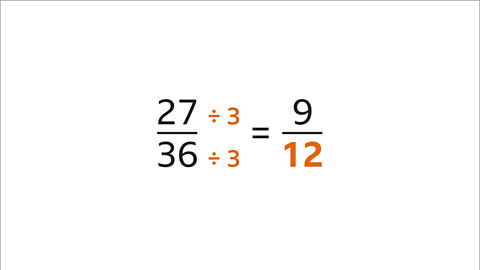
Image caption, 27 divided by 3 is 9. 36 divided by 3 is 12. The missing denominator is 12. 27⁄36 and 9⁄12 are equivalent.
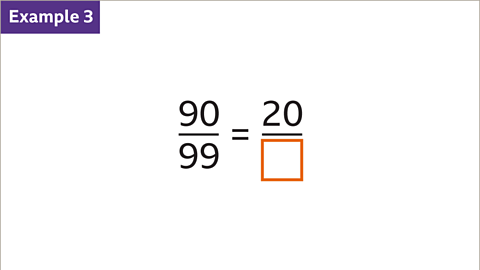
Image caption, The two fractions are equivalent. Find the value of the missing denominator.
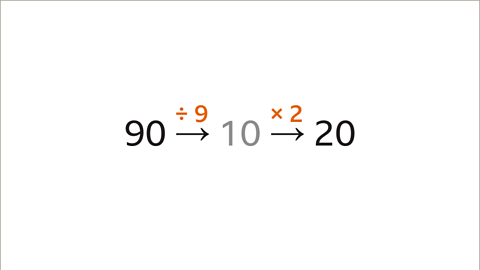
Image caption, 90 divided by 9 is 10 and 10 multiplied by 2 is 20. The numerator and denominator both need to be divided by 9 and then multiplied by 2
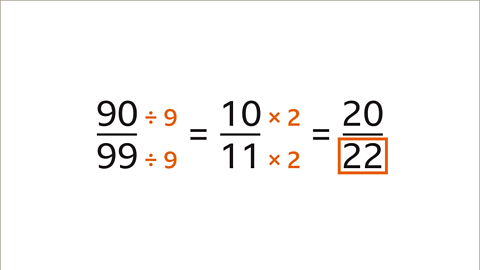
Image caption, 90 divided by 9 is 10, and 99 divided by 9 is 11. 10 multiplied by 2 is 20, and 11 multiplied by 2 is 22. The missing denominator is 22. 90⁄99 and 20⁄22 are equivalent.
1 of 10
Game - Equivalent fractions
Try out these extra equivalent fractions puzzles from our Divided Islands game.
Play the full Divided Islands game.
Practise equivalent fractions
Try this quiz to practise finding and creating equivalent fractions by simplifying them.
Quiz
Real-world maths

Equivalent fractions are used in industries like architecture. Architects prepare scale models and drawings of their designs. They use equivalent fractions in a practical setting.
Equivalent fractions can also be used in cooking or baking to adjust a recipe. For example, a cupcake recipe may make enough for [24] cupcakes. A home baker may want to change that number of cupcakes to [12]. They would need to work out the fraction of each ingredient to make sure it is equivalent to the original recipe.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Fractions
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 14
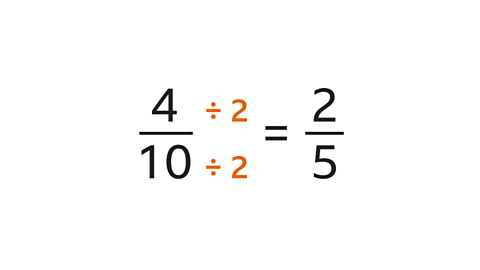
- count4 of 14
- count5 of 14
- count6 of 14