What changes can be made?
Changes that can be made to substances can be split into two main groups:

Reversing means to go back. Reversible changes are where a change to something can be undone again. The change is only temporary and the substance can be put back to how it was before.

Irreversible changes are the opposite of reversible changes.
This means that when something is changed it cannot be undone and you cannot return the substance to the way that it was before.
It is a permanent change – there is no going back!
Reversible change

A reversible change is a change that can be undone or reversed such as:
- dissolving
- melting
- freezing
- evaporation
- mixing
If you can get back the substances that you started the reaction with, then that's a reversible reaction. For example, water can be frozen and turned into ice, and if you heat the ice then it melts and turns back into water.
A reversible change might change how a material looks or feels.


Image caption, Dissolving
Dissolving is when a substance has been mixed into a liquid and becomes part of the liquid. It looks like the substance has disappeared, but it is still there. If you put salt or sugar into water then it will dissolve and make salty or sugary water.

Image caption, Evaporating
Evaporation occurs when a liquid is heated up and turns into a gas. You can use evaporation to reverse dissolving. You can also see it when you are having a hot shower and the water turns to steam, making the bathroom all steamed up. It also happens naturally when water evaporates in the water cycle.

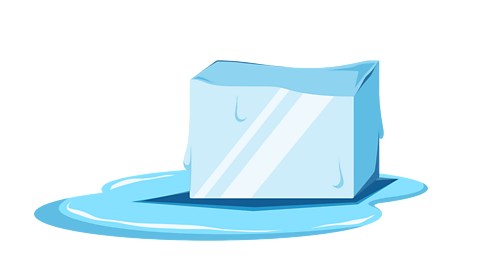
Image caption, Melting
Melting happens when a solid is heated and changes state to become a liquid. You can see this with ice on a hot day. The solid water melts and becomes a liquid. You can reverse this change by freezing the water again, to make it a solid again. This cycle can be repeated over and over again.

Image caption, Freezing
Freezing is when a liquid is cooled to turn it into a solid. You can only do this if the temperature reaches below the liquid’s freezing point. For water this is 0°C. You can freeze ice cream by placing it in containers in a freezer. This change can be reversed by making the frozen object warm again. If you leave your ice cream out of the freezer too long it will melt and turn into liquid cream again.

Image caption, Mixing
Mixing is when you put two or more substances together. Sometimes mixing is a reversible change but mixing can also be an irreversible change. It all depends on whether you can separate out the substances that have been mixed.
1 of 5
Did you know?
Some substances can go through more than one reversible change and still return to how they were before.
Water can be frozen to make ice, melted to make water again, evaporated to make steam and condensed back to water again, and it will still be the original substance.

Irreversible change

An irreversible change means that once something has been changed, it cannot be returned to its former state. This is usually because a chemical reaction has happened and a new product has been made.
There are lots of examples of this.


Image caption, Burning
Burning is an example of an irreversible change. When you burn wood smoke is released and the wood turns to ash. You cannot change the ash and smoke back to wood again.

Image caption, Rusting
Rusting is an irreversible change that happens when metal becomes wet. The oxygen in the water reacts with the metal creating brown patches of rust that can be seen on metal fences, cars and padlocks which are left outside. Once a metal has rusted, you cannot change the metal and water back to how they were before.

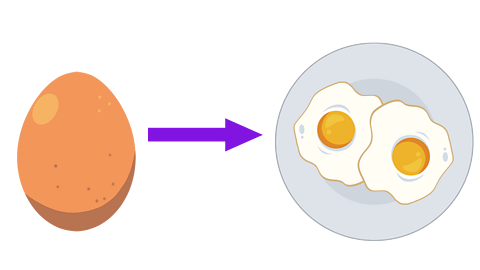
Image caption, Heating
Heating can cause an irreversible change. For example you heat a raw egg to cook it. The cooked egg cannot be changed back to a raw egg again.

Image caption, Mixing
Mixing substances can cause an irreversible change. For example, when vinegar and bicarbonate of soda are mixed, the mixture changes and lots of bubble of carbon dioxide are made. These bubbles and the liquid mixture left behind cannot be turned back into vinegar and bicarbonate of soda.
1 of 4
Did you know?
Irreversible changes happen all around us all the time, and without them our lives would be very different.
Lots of food that we make is a result of irreversible changes; the cakes we bake and eat, the bread we toast, and the eggs we scramble.
Other examples of irreversible changes are cement, which is used to construct buildings, and petrol which is burned as fuel in cars.

Watch: Chemical reactions
Discover what a scientific reaction is with this clip.
Narrator: Breakfast time…eggscellent! Hehe.
clears throat Sorry. Hmm anyway…
Some changes we make to materials are irreversible. So once the change has happened we cant go back again.
If you crack an egg in a frying pan and heat it up, that is an irreversible reaction as you're never getting that raw egg back now.
Mixing water, sand and cement that's an irreversible change. Erm…
I'm guessing nobody explained that to you.
Well, when you put the three together, you get concrete.
It sets very hard and can't revert back to being soft again.
Burning can also cause an irreversible reaction, obviously under strict adult supervision.
Cheers dad.
If you burn paper you get smoke and ash and you can't write or draw on that.
Hey what are you burning there?
Aww brilliant. It's the safety instructions from the cement mixture.
I think we are going to have to cut you out.
Err I don't think that's going to cut concrete I'm afraid. How's your egg?
Whoops!
Fascinating facts
You can make your own volcano using irreversible change. Mixing vinegar and bicarbonate of soda creates a chemical reaction that produces lots of carbon dioxide bubbles, as well as water and a salt. Be sure you ask an adult to help you to make it safely.
Water can be a solid, a liquid or a gas. Water can go through all three states as part of the water cycle.
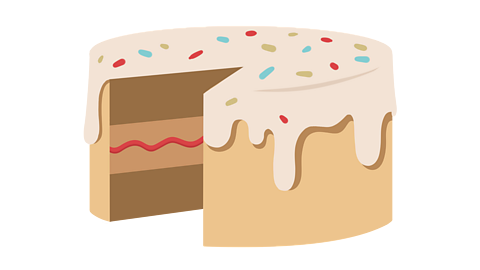
We can see irreversible changes when we cook. When you bake a cake it's impossible to turn it back into its original form of flour, eggs, butter and sugar.
When wood is burned, it turns to ash which is an irreversible change and can't be returned to its original form.
Dissolving is a reversible change.
On average, an evaporated drop of water spends around 10 days in the air before condensing and falling as rainfall.
Evaporation accounts for about 90% of the moisture in the Earth's atmosphere.
Ice melts and becomes water at 0°C, and water boils and becomes steam at 100°C.

Important words

Chemical reaction – The way in which two or more chemicals react to create a different chemical.
Dissolve – When a solid substance has mixed with a liquid to make a transparent (see-through) liquid.
Evaporation – When a liquid turns into a gas slowly, at temperatures below the normal boiling point.
Freezing – The process that sees a liquid change state from a liquid to solid as it cools.
Irreversible change – A change that cannot be undone or reversed.
Melting – When something changes state from a solid to a liquid due to heat.
Mixture – Something that is created when two or more substances are combined together.
Product – A substance formed out of a chemical reaction.
Reversible change – A change that can be undone or reversed.
Substance – Any solid, liquid or gas with its own properties.

Activities
Activity 1 – Identify the irreversible changes
Activity 2 – Take the quiz
Activity 3 – Investigating changes
Investigate some changes (with a grown up to help) and classify them as reversible or irreversible.
You could try:
- stirring some sand into water
- toasting bread
- burning a candle
- adding some vinegar to bicarbonate of soda
- melting an ice cube

Activity 4 – Activity sheet
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Properties and change of materials
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 5

- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5

