Key points
- Electronic circuits are represented by circuit diagrams, which use symbols to depict components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors.
- Input components, such as push-to-make switches, thermistors, and variable resistors, provide signals to the circuit.
- Output components, including LEDs, bulbs, buzzers, and motors, respond to signals from the circuit.
- Power supplies, like single-cell and multi-cell batteries, as well as AC power supplies, provide the necessary power for the circuit.
- Other key components include resistors, potentiometers, diodes, transistors, and thyristors, each serving specific functions within the circuit.
- Measuring devices, such as voltmeters and ammeters, are used to diagnose and troubleshoot electrical circuits by measuring voltage and current.
Electronic devices are built from many different parts. Understanding how these components work together is key to understanding electronics. Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent each component, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs), allowing engineers and technicians to understand how electronic circuits are designed and built.
Examples of input components and their symbols
Push to make switch (PTM)
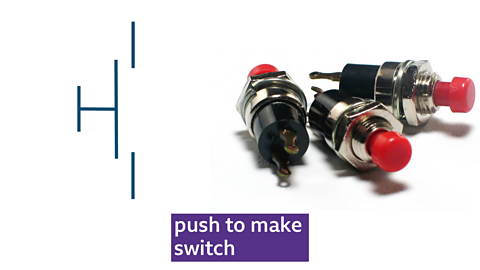
Symbol and photo of a push to make (PTM) switch
- momentary switch
- closes the circuit only while the button is pressed
- commonly used in doorbells and keyboards
- returns to the open position when released
Single pole, single throw switch (SPST)
Rocker switch

Single pole, single throw switch (SPST) photo and diagram
- latching switch
- single pole single throw (SPST) switch
- rocker mechanism to open or close a circuit
- commonly used in power strips and appliances
Toggle switch

Photo and symbol for Single pole, single throw toggle switch (SPST)
- latching switch
- single pole single throw (SPST) switch
- connects or disconnects a single circuit
- used in simple on/off applications like light switches
Single pole, double throw switch (SPDT)
Toggle switch
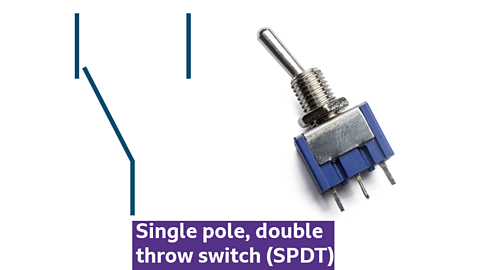
Photo and symbol for single pole, double throw (SPDT) toggle switch
- single pole double throw (SPDT) switch
- connects one input to one of two outputs
- allows switching between two circuits, unlike SPST version which only connects/disconnects one circuit
Slide switch

Photo and symbol for single pole, double throw switch (SPDT) slide switch
- single pole double throw (SPDT) switch
- slide mechanism to select between two outputs
- used in small electronic devices for mode selection
Microswitch
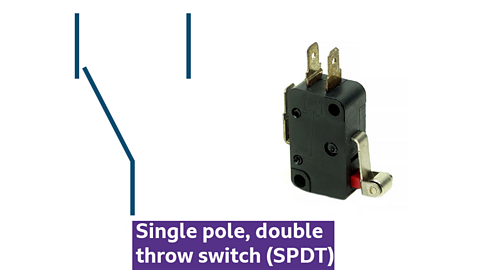
Photo and symbol for single pole, double throw switch (SPDT) - microswitch
- single pole double throw (SPDT) switch
- activated by very little physical force
- used in safety interlocks and limit switches
Reed switch
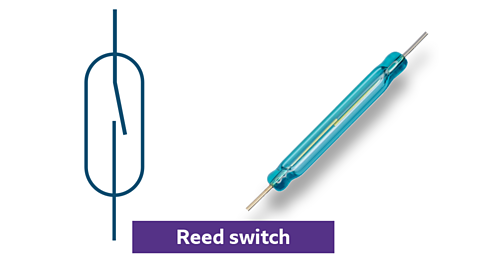
Photo and symbol for a reed switch
- activated by a magnetic field
- closes or opens a circuit when a magnet is near
- commonly used in security systems and proximity sensors
Membrane switches
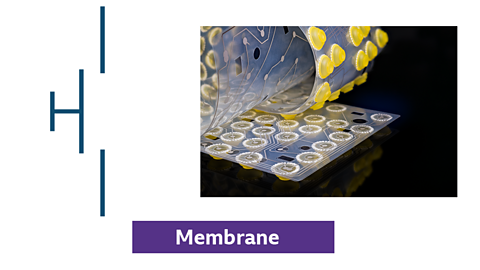
Photo and symbol for a membrane switch
- thin, flexible switch with printed circuits
- activated by pressing a designated area
- similar to a push-to-make (PTM) switch, closing the circuit when pressed
- commonly used in keypads and control panels for a low-profile, sealed interface
Thermistors
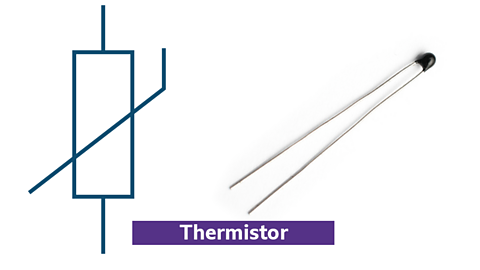
Symbol and photo for a thermistor
- sensitive to temperature changes
- resistance varies with heat levels
- used to create heat or cold sensors
- can be used as an input
Variable resistors
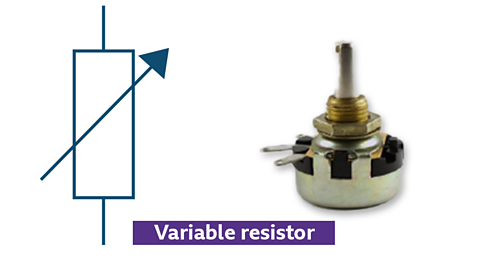
Symbol and photo of a variable resistor
- two-terminal device for adjusting current
- used to dim lights or control motor speeds
- changes resistance directly in a circuit
- different from a potentiometer, which adjusts voltage
- can be used as an input
Examples of output components and their symbols
Light-emitting diode (LED)
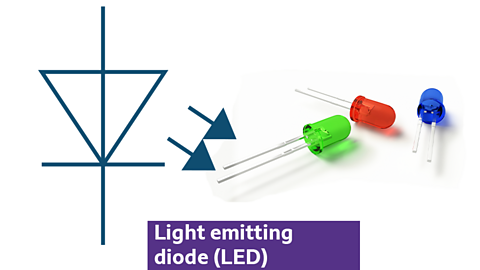
Symbol and photo of LEDs
- emits light when current passes through
- polarised component with positive and negative terminals
- needs a current limiting resistor placed in series to the LED for protection
- available in various types and colours
- used as an output
Bulb

Symbol and photo of bulbs
- light source or indicator
- contains a filament that glows when current passes through
- comes in various sizes and shapes
- used as an output
Buzzer
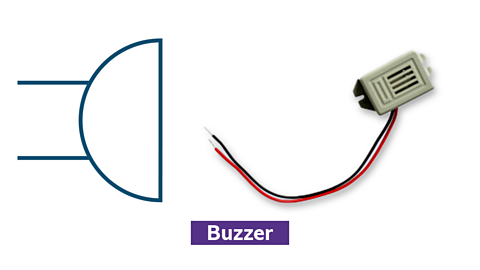
Symbol and photo of a buzzer
- produces sound or warning signals
- polarised component requiring correct connection
- available in different sizes, shapes, and voltages
- used as an output
Motor
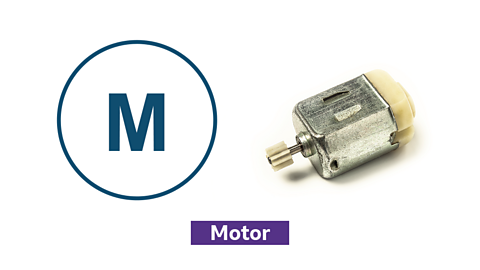
Symbol and photo of a motor
- provides rotary motion
- can move clockwise and anticlockwise
- used to drive mechanisms like conveyor belts and window openers
- used as an output
Examples of power supplies
Single cell battery

Symbol and photo for single cell batteries
- basic power source providing direct current (DC)
- consists of one electrochemical cell
- typically produces around 1.5 volts
- used in small devices like remote controls and clocks
Multi-cell battery
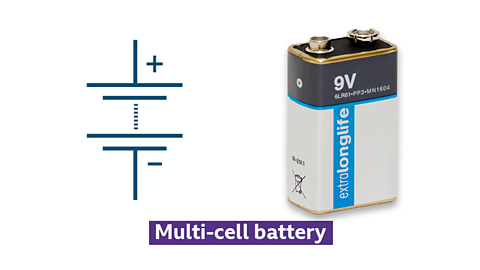
Symbol and photo of a multi-cell battery
- multiple electrochemical cells connected in series or parallel
- provides higher voltage or capacity than a single cell
- commonly used in laptops, power tools, and electric vehicles
- each individual cell typically produces around 1.5 volts
Alternating Current (AC) power supply
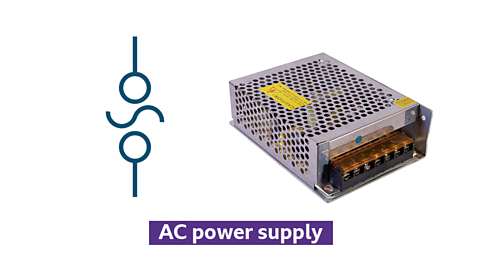
Symbol and photo of an alternating current power supply
- provides alternating current (AC) to electrical devices
- voltage and current change direction periodically
- commonly used in household power outlets
- essential for powering most home appliances and industrial equipment
Earth (wire)
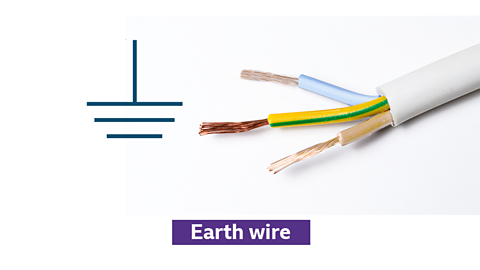
Symbol for earth wire and photo on electrical cable with earth wire highlighted
- provides a safe path for electrical current to the ground
- protects against electric shocks by preventing excess current
- essential in household wiring and electrical safety
- typically connected to metal parts of appliances and electrical systems
- often identified by a green and yellow sleeve
Examples of other electronic components
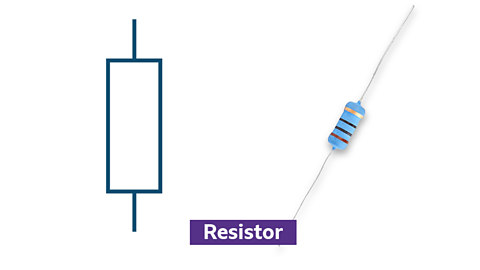
Symbol and photo of a resistor
- limit the flow of electrical current in a circuit
- have a fixed resistance value
- used to protect components and control voltage levels
- available in various resistance values and power ratings
Potentiometer
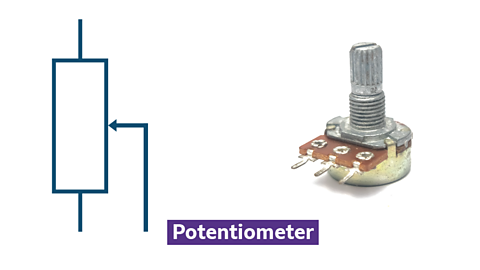
Symbol and photo of a potentiometer
- three-terminal device for adjusting voltage
- used in volume controls and other adjustable settings
- acts as a Voltage dividerUsed to turn a large voltage into a smaller one.
- different from a variable resistor, which adjusts current
Diodes
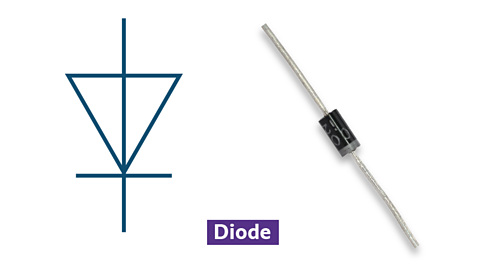
Symbol and photo of a diode
- allow current to flow in only one direction
- used for converting AC to DC
- protect circuits from reverse voltage
Transistors (NPN)
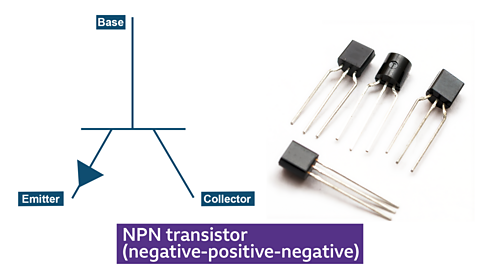
Symbol and photo of NPN transistor
- acts as a switch or amplifier in circuits
- allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter when a small current is applied to the base
- used in amplification and switching applications
- essential in digital and analogue circuits
Thyristor
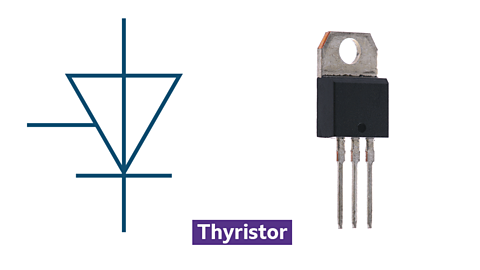
Symbol and photo for a thyristor
- acts as a latching switch, staying on until reset
- triggered by a small current at the gate leg
- commonly used in alarms and other control systems
- allows current to flow continuously once activated
Light dependent resistor (LDR)
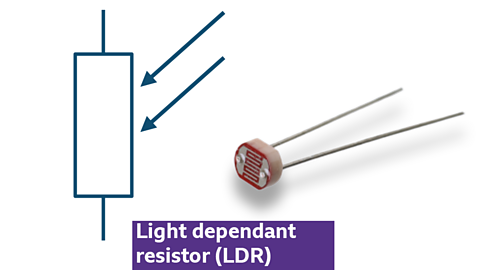
Symbol and photo of a light dependant resistor (LDR)
- Changes resistance based on light intensity
- Low light causes high resistance, and resistance drops as light intensity increases
- Used in light-sensitive circuits like automatic street lights and light meters
- Sensitivity varies with the wavelength of light
Voltmeter (multimeter)

Symbol and photo of a voltmeter
- measures the voltage difference between two points in a circuit
- connected in parallel with the component being measured
- essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical circuits
- displays readings in volts (V)
Ammeter (multimeter)
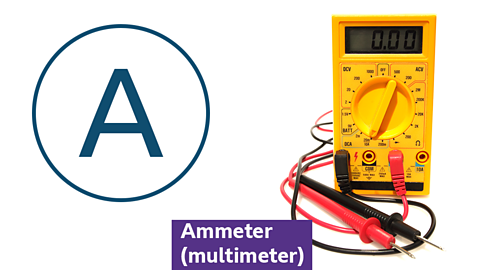
Symbol and photo for an ammeter
- measures the current flowing through a circuit
- connected in series with the component being measured
- essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical circuits
- displays readings in amperes (A)
Test yourself
More on Electronic control systems
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 8

- count6 of 8
- count8 of 8
