Key points
- Current is electron flow, measured in amps (A) or milliamps (mA). Use an ammeter in series.
- Voltage is the pushing force, measured in volts (V) or millivolts (mV). Use a voltmeter in parallel.
- Resistance restricts current, measured in ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), or megaohms (MΩ). Use an ohmmeter/multimeter.
- Ohm's law is V=ꞮR (Voltage = Current × Resistance).
- Multimeters measure V, Ɪ, R. Connect for voltage (parallel), current (series), resistance (circuit off). Start high, work down.
Understanding units

Current (flow of electrons)
Amp (A) = big current (like in a kettle)
Milliamp (mA) = tiny current (like in LED)
1000mA = 1A
Measurement Tool: Ammeter, connected in series with the circuit.Voltage (pushing force)
Volt (V) = normal battery voltage (like 9V battery)
Millivolt (mV) = tiny voltage
1000mV = 1V
Measurement Tool: Voltmeter, connected in parallel with the component.Resistance (restricts flow)
Ohm (Ω) = small resistance
Kilohm (kΩ) = thousand ohms
Megaohm (MΩ) = million ohms
Measurement Tool: Ohmmeter or multimeter.
A multimeter is a versatile tool that can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. It combines several measurement functions into one device, making it essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical systems.
What is Ohm’s law?
Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (Ɪ), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit.
The law states that:
Voltage = Current × Resistance
or
V=ꞮR
How to use Ohm's law
If you know any two of these quantities, you can calculate the third.
The formula can be rearranged as follows:
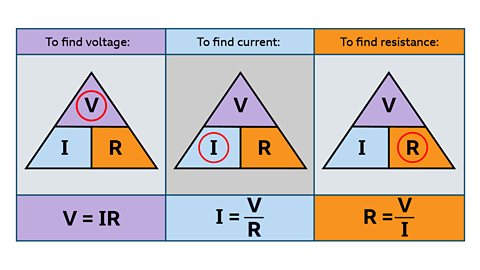
To find voltage:
Voltage = ?
Resistance = 4Ω
Current = 3A
V=ꞮR
Answer:
V = 3A x 4Ω
V = 12V
To find current:
Current = ?
Voltage = 9V
Resistance = 180Ω
Ɪ=V/R
Answer:
Ɪ = 9V / 180Ω
Ɪ = 0.05A or 50mA
To find resistance:
Resistance = ?
Voltage = 6V
Current = 4mA
R=V/Ɪ
Answer:
R = 6V / 0.004A
R = 1500Ω or 1.5KΩ
Test yourself
More on Electronic control systems
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 8

- count3 of 8
