Key points in systems, control and feedback
- the systems approach breaks down electronic systems into input, process, and output stages for analysis
- input uses sensors (LDR, thermistor, microphone, thermostat) to detect changes
- the process stage uses microcontrollers, amplifiers, and timers (including microprocessors) to manipulate signals
- output uses actuators (motor, buzzer, LED) to produce actions
- feedback is vital: sensors constantly monitor and inform the process for accuracy, stability, efficiency, and adaptability (e.g., thermostat controlling temperature)
What is the systems approach method
Inputs, outputs and processes in systems used by designers
[Narrator] You might find reading a bit easier with some light.
UPBEAT MUSIC
ALARM WAILS
Oh, wrong one!
UPBEAT MUSIC
Interesting but I don't think that's what you had in mind. I have a feeling none of these are right.
UPBEAT MUSIC
Definitely not.
ELECTRONIC MUSIC
We could be here for a while.
This is Zoe. Zoe knows that systems are made of inputs, processes and outputs and how they work.
So, an input device is something that takes a real-world signal like light, sound or movement and turns it into an electronic signal like current or voltage.
For example, at a train station when you put your contactless payment card onto the reader at a ticket barrier that's an electronic input.
Or when a train attempts to pass a signal that it shouldn't a train stop on the ground makes contact with something on the train called a trip arm, that's connected to the braking system. That's a mechanical input.
Processes receive the signal from the input stage of the system and change it in some way. They add functionality and intelligence to the system.
So when you've touched your contactless payment card, a micro-controller determines whether your ticket is valid and sends a signal to open the barrier. The micro-controller is an example of an electronic process.
Or when the trip arm has been activated it removes air from the braking system, effectively sending a signal to the train's brakes. That's a mechanical process.
Output devices take a signal, usually provided by the process, and turn it back into a real-world result. For example, bulbs produce light and speakers produce sound.
In the case of a ticket barrier the output device is the motor, producing movement of the barrier itself and an LED producing green light to tell you to walk through.
A mechanical output would be like when the brakes receive the air signal, telling the brakes to apply force to the wheels bringing the train to a stop.
[Narrator] So it's essentially your inputs, processes, and outputs are precisely organised so the system works.
Yes, you need to understand how all the parts of the system work together and keep them organised to get the result you want.
[Narrator] Hmm, that looks like hard work.
- The Systems Approach is a method used to understand and design electronic systems by breaking them down into three main stages: input, process, and output.
- This approach helps in identifying how different components work together to achieve a specific function, making it easier to analyse and troubleshoot electronic control systems.
Input components: sensors and switches

Image caption, Light dependent resistor (LDR): detects light levels

Image caption, Thermistor: measures temperature
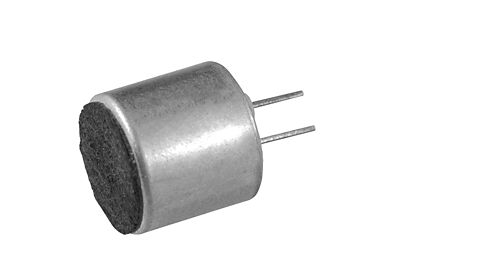
Image caption, Microphone: picks up sound
1 of 3
Process components: microcontrollers, amplifiers, and timers

Image caption, Microcontroller: processes signals from sensors and makes decisions

Image caption, Amplifier: boosts weak signals
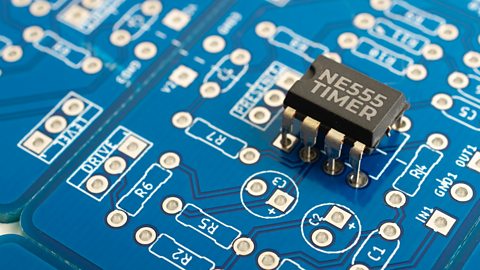
Image caption, 555 timers: delays actions for a set period
1 of 3
Output components: actuators and indicators
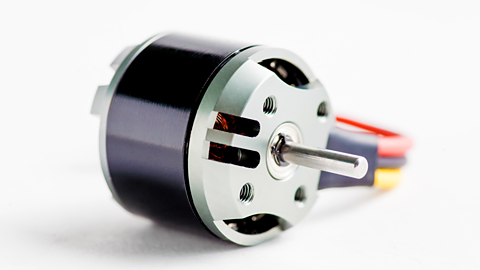
Image caption, Motor: provides rotary movement

Image caption, Buzzer: produces sound
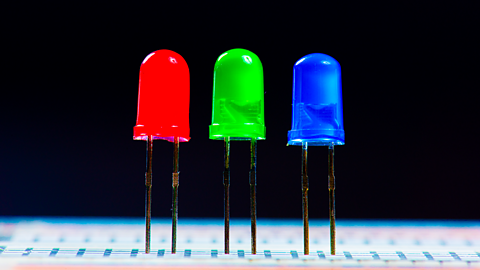
Image caption, LED: emits light
1 of 3
Example: automatic street lighting system

- Input: an LDR detects when it gets dark.
- Process: a microcontroller processes the signal from the LDR.
- Output: the system turns on the street light LEDs.
How feedback works
Feedback is essential in electronic control systems ensuring that the system can adjust and correct itself to maintain desired performance.
Here’s how it fits into the Input-Process-Output model:
Input components: sensors that detect changes in the environment or system.
Example: a thermostat measuring room temperature.
Process components: controllers or microprocessors that process the input data.
Example: a microcontroller comparing the current temperature to the desired set temperature.
Output components: actuators that perform actions based on the microcontrollers programming.
Example: a heater turning on or off to adjust the room temperature.
Feedback: thermostat continuously monitors the temperature and sends this information back to the microcontroller to ensure the room stays at the desired temperature.
Why is feedback important?
- Accuracy: feedback helps maintain precise control over the system, ensuring the output matches what is needed
- Stability: it allows the system to correct any changes from the required performance, maintaining stability
- Efficiency: feedback systems can optimize performance, reducing energy consumption and wear on components
- Adaptability: they can adjust to changes in the environment or system conditions, ensuring consistent performance
Test yourself
More on Electronic and microelectronic control systems
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 13
- count3 of 13

- count5 of 13
