What is energy?
Action! Welcome to science world!
OK, so today we are turning up the heat and putting on the pressure. That's because everything requires energy. Yep, take cooking for example.
If you put this cookie dough in an oven for ten minutes at 200 degrees, or 180 degrees in a fancier oven, look how they cook! But how does it happen? What?! That's why today we're going to ask, 'what is energy?'
Welcome to energy world. Energy is essential for every one of us. Humans have advanced, because we've learned how to change energy from one form into another. Without being able to do that, life would very different.
There are many different forms of energy: kinetic energy, heat energy, light energy, chemical energy, elastic potential energy (or strain energy), gravitational potential energy, electrical energy, magnetic energy and nuclear energy.
Chemical energy is the most widely used type of energy on Earth. It's vital for our existence and it's stored in food. Yum.
As the bonds between the atoms and food break, a chemical reaction takes place and energy is released. We use this energy to keep warm and to move.
A very important law in physics is the law of conservation of energy. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but only changed from one form to another. You can't make energy, you can't get rid of energy but you can change it. The same amount of energy is present at the end as at the start. Oh, hold that thought.
So, you can't create energy you can only change it. So the thermal energy from this oven has transferred to the cookie dough to bake these cookies. The chemical energy from these cookies becomes energy that I can use.
See you next time in science world!
I have definitely burnt these…
Energy is essential for everyone of us. Humans have advanced because we have learnt how to change energy from one form into another. Without being able to do that life would be very different. In fact, there wouldn’t be life at all. So, what is energy and how do we use it?
There are many different forms or types of energy. These include:
- kinetic energy
- heat energy
- light energy
- chemical energy
- elastic potential energy or strain energy
- gravitational potential energy
- electrical energy
- magnetic energy
- nuclear energy

Types of energy
Let’s look at some of these in a little more detail
- Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object
All moving things have kinetic energy, even very large things like planets, and very small ones like atoms. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on:
- the mass of the object
- the speed of the object
An object at rest (not moving) has zero kinetic energy

Heat, elastic and gravitational potential energy

Heat energy
- Heat energy flows from hot objects to cold objects.
A cup of tea “feels warm” because it is giving off heat energy. It is the hot object, you are the cold object. Sometimes heat energy is called thermal energy.


Elastic potential energy
- Elastic potential energy is stored in stretched or squashed materials.
Some objects can change shape when they are pushed or pulled. Rubber balls, springs and elastic bands are like this. When an object is stretched or squashed, it stores elastic potential energy. The energy is released when it returns to its original shape and size.

Gravitational potential energy
- Gravitational potential energy is the type of energy an object stores due to its height above the ground.
When an object is lifted above the ground, or moved higher up, it gains gravitational potential energy. The amount of gravitational potential energy an object stores depends on:
- the mass of the object
- the height above the Earth’s surface
- the gravitational field strength

Chemical, sound and light energy
Chemical energy
- Chemical energy is the energy stored in the bonds that connect atoms and molecules together.
Chemical energy is the most widely used type of energy on Earth and is vital for our existence.
Chemical energy is stored in the food we eat. As the bonds between the atoms in food break, a chemical reaction takes place and energy is released. We use this energy to keep us warm, to move, to climb stairs, to grow, when we sleep and many other things.
Chemical energy is also stored in fuels such as coal, oil, natural gas, wood and peat.

Commentator: Ladies and gentlemen, knives and forks, a very warm welcome to this year’s energy race. All food releases energy – some quickly, some slowly. Let’s put this grub to the test! Joining me in the commentary box today is Masher. How are you doing Masher?
Masher: I’m excellent thank you, pal. This is an exciting race.
Commentator: Yes, indeed. Everything in a human body uses up energy: from running to breathing to sleeping. To be healthy, they need to put into their body the same amount of energy that they use up.
Masher: Fast releasing energy foods give humans a quick boost. Slow releasing energy foods are even better, as they provide humans with energy for longer.
Commentator: The best way to tell who is a fast releasing food and who is a slow releasing food is to make everyone race. Let’s see who has the energy to keep going!
Masher: In lane 1, we have Pineapple - a huge unit ripe for the challenge.
In lane 2, Egg is ready to barrel down the track.
Commentator: In lane 3, Sweet Potato looms large.
In lane 4, at a massive 240 calories, it’s Chocolate Bar.
And lastly in lane 5, hoping he doesn’t slip on his own skin, it’s Banana!
Masher: Let’s race down the kitchen table! Are you ready, food?
(ALL CHEER)
Commentator: On your marks…
Masher: Get set…
Commentator: GO!
Masher: And they’re off, Chocolate Bar is already zooming ahead! But will he be able to keep it up?
Chocolate Bar: Wheeeeeee! Look at me go!
Commentator: Remember, it’s not about speed, it’s about how long you can keep going. I’m worried Chocolate Bar is going to use up all his energy.
Masher: Pineapple is not too far behind Chocolate Bar. Maybe she can pace herself better.
Commentator: Going at their own gentle paces are Egg, Banana and Sweet Potato.
Chocolate Bar: Feeling… quite… tired…
Masher: Oh! And would you look at that! Chocolate Bar has dropped out - looks like he’s used up all his energy.
Commentator: Oh, and Pineapple is out too! Just couldn’t keep it up.
Masher: They are high in sugar which gives a big burst of energy, but doesn’t keep people going for a long time.
Chocolate Bar: So we’re just as good as each other?
Pineapple: We both have lots of sugar energy, but I’m healthier – I’ve got lots of vitamins too.
Commentator: Sweet Potato is plodding along in her own merry way. She’s a complex carbohydrate who takes longer to digest. So she releases energy very slowly.
(SWEET POTATO WHISTLES)
Masher: And just like that, Banana has used up all his energy and he’s out of the race.
(BANANA PANTING)
Commentator: Egg and Sweet Potato are battling it out for the top spot. That’s the powerful protein in eggs, pushing him through.
Masher: He’s struggling, he’s struggling, and Sweet Potato hasn’t even broken a sweat.
Commentator: And with that, Egg is out of the race and Sweet Potato is the winner!
Sweet Potato: Yeah!
Masher: Congratulations, Sweet Potato. You release energy the slowest helping power people through the day.
Pineapple: But wait a minute, me and Chocolate Bar were the fastest.
Masher: At first, yes. When food is eaten it is broken down which releases the energy inside it and powers the human. Some foods release their calories slowly and some do it quickly.
Chocolate Bar: And that is why I lost?
Commentator: Exactly.
Banana: So… humans should only eat sweet potatoes?
Commentator & Masher: Oh Banana!
Commentator: Humans should eat a mix of different foods. Starchy carbohydrates are a great way for humans to get energy to keep them going longer, but you are all valuable and give humans lots of energy. In fact, you all get medals.
(ALL CHEER)
Learn about food energy from a sports nutritionist
Food energy is the energy that we get from eating food. And different types of foods give us different levels of energy.
My name is Mayur Ranchordas, and I'm a sports nutritionist. We help professional athletes and elite athletes eat better to perform better and recover better.
So when we talk about food, not all foods are the same. Some foods are what we call carbohydrates,like rice, pasta, potato, cereal, and they give us energy.
Then you've got protein, meat and fish, they help in repairing muscle.
Then you have fats, and fats are very energy-dense, so things like butter, avocados, and they give us a lot of energy.
And depending on what you're doing, what training you're doing, what sport you compete in, the demand changes.
If I was a marathon runner, I would be covering 80–100 miles a week and that means I have a much greater reliance on fats and carbohydrates.
As a sprinter, you might use carbohydrate only because you need to access that energy very quickly.
The most surprising food that you would not think gives you energy is actually milk.
So milk contains protein, it contains carbohydrate, it also contains electrolytes like sodium, potassiumthat are great for hydration. Milk is a bit of a superfood really.
If you're interested in sport and if you're interested in food and you're interested in how they both interact with each other, then sports nutrition is definitely the job for you.
Sound energy
- Sound energy is the energy stored in a sound wave.
Sound waves travel through solids, liquids and gases and are produced when an object vibrates like a plucked guitar string.

Light energy
- Light energy is a form of energy which our eyes can detect.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation and can travel through a vacuum as well as through solids, liquids and gases. Light energy travels to us through space from the Sun. Green plants need light energy for photosynthesis to occur.

Electrical, magnetic and nuclear energy
Electrical energy
- Electrical energy is a form of energy resulting from moving electric charges.
Some objects carry electrical charges. These charged objects can exert forces on each other. Electrical energy can be seen in nature in a bolt of lightning which is a flow of charge through the air.

Magnetic energy
- Magnetic energy is also a form of energy associated with moving charges
Some objects can be magnetised and exert forces on other magnetised objects, or on magnetic materials.

Nuclear energy
- Nuclear energy is stored in the nuclei of an atom
Nuclear energy can be released by splitting heavy atoms or by fusing together two light atoms. Nuclear energy can be used to create electricity, but it must first be released from the atom. All the sun’s energy begins as nuclear energy.

Measuring energy
The unit of energy is named after the famous scientist, James Prescott Joule, who was born on 24th December 1818, and died on 11th October 1889.
He was brought up in Salford, Lancashire, England, and was the son of a wealthy brewer. He became interested in science after being tutored by another famous scientist, John Dalton, at Manchester University in 1835. Dalton was one of the leading chemists of the day and a pioneer of atomic theory.
Joule set up a laboratory in the cellar of the family home. He began a series of experiments on the nature of energy and published the findings that became known as Joule's first law in 1840.
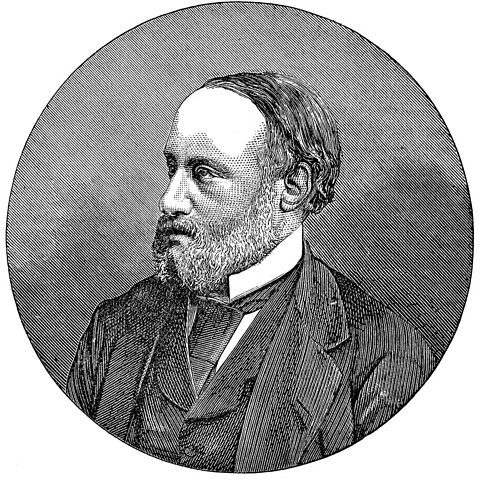

He was able to show that the various forms of energy—mechanical, electrical, and heat—are basically the same and can be changed from one into another.
Eventually his ideas became the cornerstone of one of the most fundamental scientific laws ever discovered, the First Law of Thermodynamics.
In recognition of his significant contributions to science, the unit of energy was named the Joule and given the symbol J.
It takes about 1 J of energy to lift an apple 1 m vertically from the ground.
Conservation of energy
A very important law in physics is the Law of Conservation of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that:
- Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but only changed from one form to another
You cannot make energy. You cannot get totally rid of energy. All you can do is change it. The same amount of energy is present at the end of anything that happens as was there at the start.
Many devices that we use are energy changers. They transfer or convert energy in one form to a more useful form.
For example:
- an electric lamp transfers or converts electrical energy into light energy.
Energy changes can be shown in an energy flow diagram
- a car engine converts chemical energy in petrol into the kinetic energy of the moving car.
Note that energy transfer diagrams only show the useful, or main energy changes.
However, car engines are also noisy and hot and so some of the chemical energy in petrol is converted to heat energy and sound energy. The electric lamps also give out a lot of heat energy. This is usually called waste energy or non-useful energy.
When energy is changed it changes from one form into useful energy and wasted energy.
The wasted energy is usually heat energy. When things move, the force of friction slows them down. Kinetic energy is changed to wasted heat energy and the moving object slows down. The heat energy spreads out into the surroundings. Waste sound energy is also often produced too.
Remember: energy can be wasted but it is never lost!
Some other energy changers
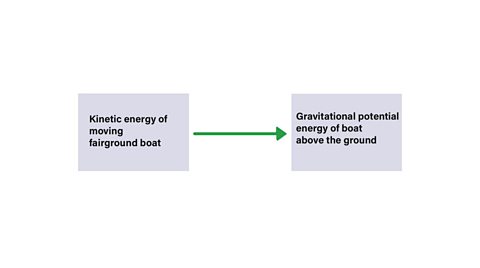
- A fairground ride converts kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy and then back to kinetic energy again as it swings up and down.
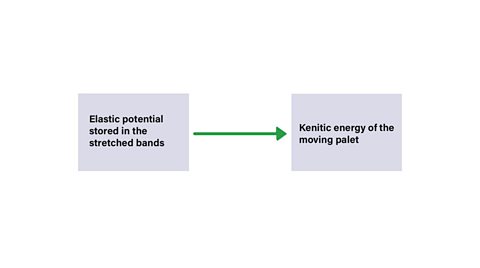
- When the catapult is released, the elastic potential energy stored in the stretched bands is converted to the kinetic energy of the moving pellet.

- A boat engine converts chemical energy in fuel into the kinetic energy of the moving boat.
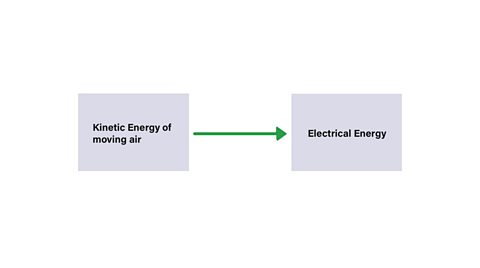
- A wind turbine converts the kinetic energy of moving air (wind) into electrical energy.

Energy resources
Energy resources are the different ways of supplying a particular form of energy
For example:
- Chemical energy is a form of energy.
- Food, oil, coal, gas, petrol, turf and wood are some of the resources which supply chemical energy.
- Kinetic energy is a form of energy.
- Waves, tides, wind and falling water are some of the resources which supply kinetic energy.
Energy resources are needed to generate electricity They are often split into renewable and non-renewable resources.
- Renewable resources are replaced by nature in less than a human lifetime. They will never run out.
- Non-renewable resources cannot be replaced by nature in a human lifetime. They are used faster than they can be replaced by nature and will run out.
Non-renewable resources
Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are non-renewable energy resources, and they include:
- crude oil
- coal
- natural gas
They were formed over millions of years, from the remains of dead plants and animals:
- coal was formed from dead trees, ferns and other plant material
- crude oil and natural gas were formed from dead marine organisms such as plankton
Coal, oil and gas are all being used up much more quickly than they are being replaced. They will run out. It takes about 150 million years for oil to form from plankton, so the oil we use for petrol and diesel in cars and to heat homes is definitely not replaced within a human lifetime!
Electricity from fossil fuels
Fossil fuels store chemical energy.
By the end of 2019, 39% of the electricity generated in the UK came from power stations fuelled by fossil fuels. In Northern Ireland in 2020, approximately 51% of electricity came from non-renewable sources.
Northern Ireland has three fossil fuel power station:
- Ballylumford, near Larne – natural gas
- Kilroot, near Carrickfergus – coal and oil
- Coolkeeragh, at Maydown, Londonderry – natural gas
Recently it has been reported that Kilroot is to be replaced by a new, modern gas-fired power station.
This diagram shows an energy transfer diagram for the generation of electricity from a fossil fuel such as coal.
Coal or gas is burned to produce steam. The steam is forced through a turbine, which is a bit like a fan, and causes it to rotate. The rotating turbine turns a generator to produce electricity.
Advantages of using fossil fuels to generate electricity
- relatively cheap
- relatively easy to obtain because we have been using them for so long
- reliable
Disadvantages of using fossil fuels
- they are non-renewable and will run out
- all fossil fuels release carbon dioxide when they burn, which adds to the greenhouse effect and increases global warming - coal produces most carbon dioxide and natural gas produces the least.
- coal and oil release sulphur dioxide gas when they burn, which causes breathing problems for humans and animals and contributes to acid rain.
- burning fossil fuels causes pollution as unburnt particles are released into the environment which can cause breathing difficulties and lung damage.
Nuclear fuels
Nuclear fuels release energy through nuclear reactions, rather than through chemical reactions. The main nuclear fuels are uranium and plutonium. Apart from the fuel used, a nuclear power station is similar to a fossil fuel power station in that, the energy released is used to boil water. The expanding steam spins turbines, which then drive generators to produce electricity.
Advantages of using nuclear fuel to generate electricity
- They do not produce carbon dioxide and so they do not contribute to global warming
- They do not produce sulfur dioxide and so they do not contribute to acid rain
- They do not produce polluting gasses which contribute to smog
- Requires lower quantity of fuel compared with fossil fuel power stations which reduces mining and transportation effects on environment
- They are reliable
Disadvantages of using nuclear fuel to generate electricity
- Like fossil fuels, nuclear fuels are non-renewable energy resources. They will run out one day if we keep on using them
- If there is an accident, large amounts of radioactive material could be released into the environment
- Nuclear waste remains dangerously radioactive and harmful to health for thousands of years. It must be stored safely which has environmental implications
- Costs of building and safely decommissioning a nuclear power station are very high

Renewable resources
In 2020, 49.2% of total electricity used in Northern Ireland was generated from renewable sources in Northern Ireland. Almost 85%of this renewable electricity was generated from wind.
Wind energy
The wind is produced as a result of convection currents, driven by heat energy from the Sun. Moving air, or wind, has kinetic energy and this is a renewable energy resource. As long as the Sun exists, the wind will too.
Wind turbines
Wind turbines use the wind to drive turbines directly. They have huge blades mounted on a tall tower. The blades are connected to a 'nacelle', or housing, which contains gears linked to a generator. As the wind blows, it transfers some of its kinetic energy to the blades, which turn and drive the generator to produce electricity.
By March 2020 there were over 20 wind farms and more than 800 individual wind turbines across Northern Ireland – 15 years ago there were virtually none.
Advantages of generating electricity from wind
- Wind is a renewable energy resource
- There are no fuel costs
- There are no harmful or polluting gases produced
- Wind is one of the lowest-priced energy sources available today
- Small-scale, stand alone, wind power is particularly suitable for remote locations where normal methods of electricity supply are expensive or hard to achieve
Disadvantages of generating electricity from wind
- Wind farms are noisy and may spoil the view for people living near them
- They are not reliable - the electricity generated depends on the strength of the wind - if there is no wind, there is no electricity!
- Wind farms can harm local wildlife - birds and bats have been killed by flying into spinning turbine blades and this can reduce local populations. This can be partially resolved by carefully siting wind plants
- The initial cost of setting up wind turbines is quite high

Hydropower
Like the wind, water can be used to drive turbines directly. There are several ways that water can be used. These include waves, tides, and falling water in hydroelectric power schemes. Hydropower is energy produced by moving water through a turbine.
- Waves
The water in the sea rises and falls because of waves on the surface. Wave machines use the kinetic energy in this movement to drive electricity generators.
- Tides
Huge amounts of water move in and out of river mouths each day because of the tides. A tidal barrage is a barrier built over a river estuary to make use of the kinetic energy in the moving water. The barrage contains electricity generators, which are driven by the water rushing through turbine blades.
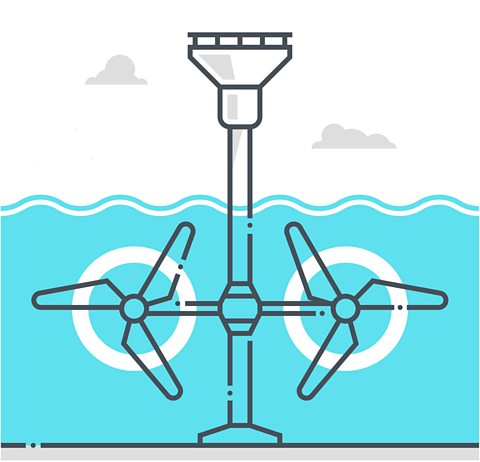
Hydroelectric power
Like tidal barrages, hydroelectric power stations use the kinetic energy in moving water. But the water usually comes from behind a dam built across a river valley. The water high up behind the dam has a lot of gravitational potential energy. This is transferred to kinetic energy as the water rushes down through tubes inside the dam. The moving water drives electrical generators which may be built inside the dam.

Advantages of generating electricity using waves, tides and hydroelectricity
- Waves, tides and hydroelectricity are forms of renewable energy resources.
- There are no fuel costs
- No harmful polluting gases are produced.
- Tidal barrages and hydroelectric power stations are very reliable and can be easily switched on. Hydroelectricity is particularly useful when there is a surge in demand for electricity.
- Hydroelectricity is low cost compared to coal and natural gas.
Disadvantages of generating electricity using waves, tides and hydroelectricity
- It has been difficult to set up wave machines to produce large amounts of electricity.
- Tidal barrages destroy the habitats of estuary species, including wading birds and fish.
- Tidal power is relatively new and so is quite expensive.
- Dams flood farmland and push people from their homes. Large scale hydroelectricity projects can be particularly devastating for local environments. The Three Gorges Dam in China reportedly displaced more than 1.2 million people, flooding 13 cities, 140 towns, and 1,350 villages.
- Biomass
Biomass is organic matter – anything that is alive or was a short time ago - that can be used as an energy source. Examples of biomass include wood, crops, seaweed and animal waste. Biomass gets its energy from the Sun and is a renewable energy source.
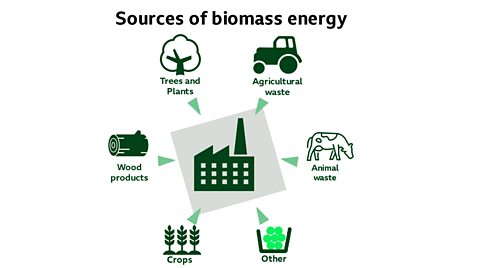
Most electricity generated from biomass is produced by directly burning it. The biomass fuel is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam flows over a series of turbine blades, causing them to rotate. The rotation of the turbine drives a generator, producing electricity.
Animal dung or human sewage can also be collected in oxygen-free tanks called digesters. Here, the material is decomposed by bacteria that produce methane to form a renewable natural gas, which can then be purified and burnt to generate electricity.
Advantages of generating electricity from biomass
- Biomass is a renewable energy resource - humans and animals will always create waste and plants will always grow
- Using waste to create energy means that less of it goes into the landfill which is good for the environment
- Burning biomass doesn’t release sulfur dioxide and it releases less nitrogen than burning coal
- It’s a relatively cheap way to generate electricity
Disadvantages of generating electricity from biomass
- Crops grown in order to be burnt for energy take up a lot of land. That land could be used for other things like growing crops for food
- The burning process releases CO₂ which is a greenhouse gas
- It also releases carbon monoxide, which adds to air pollution
- When trees are cut down specifically to create energy there is a negative impact on the environment
The Lisahally Biomass plant in Londonderry, uses recycled wood to generate electricity. The power plant was the first of its kind in Ireland. Over its lifetime the project is expected to save over two million tonnes of wood from landfill sites.

Geothermal energy
Hot water and steam from deep underground can be used to drive turbines. This is called geothermal energy.
Volcanic areas
Several types of rock contain radioactive substances such as uranium. These release energy, which warms up the rocks. In volcanic areas, the hot rocks heat water and this may rise to the surface naturally as hot water and steam. Here the steam can be used to drive turbines and electricity generators.
Hot rocks
In some places, the rocks are hot, but no hot water or steam rises to the surface. In this case, deep wells can be drilled down to the hot rocks and cold water pumped down. The water runs through cracks in the rocks and is heated up. It returns to the surface as hot water and steam. The diagram shows how this works.
Advantages
- Geothermal energy is a renewable energy resource.
- There are no fuel costs and no harmful polluting gases are produced.
- The hot water and steam can be used to heat buildings directly.
Disadvantages
- Most parts of the world do not have suitable areas where geothermal energy can be exploited.
Solar energy
What is solar energy?
My day-to-day entails physical inspection of the solar farms. I'll follow a schedule checklist, looking for early stage faults, checking the safety of the site and the general condition of the grounds on site.
My name's Liam, I'm an electrical engineer and I specialise in the solar industry.
Solar energy is the energy produced by the Sun. When light travels from the Sun to the Earth, you have ultraviolet, visible, and infrared light. When the light travels to the Earth and hits the solar module, there's a reaction within the silicon crystal within that module that creates a current. And then what you do is you give that current a path to then be transformed into energy, and it goes out into the grid and can be used.
The reason that solar farms produce more energy in the summertime than in the wintertime is because the Sun is higher in the sky, the Sun's rays are a lot stronger and you have less overcast cloudy daysthan you do in the wintertime.
Today's weather will have an effect on the power generation due to snow on the modules, and that is going to have a negative effect on the amount of current that will be able to be produced by those modules.
The positives to solar energy are it's renewable, it's free, provided by the Sun, there's no negative effect on the environment and it can be harnessed and used to feed the grid.
This is something we have to do. We have to push for renewable energy because we've got to look after the world we live in. I feel like as well as making a living, I'm making a difference.
The Sun is a renewable energy resource. As long as it exists and continues to shine, it will release energy. The Sun’s energy comes from nuclear energy released when hydrogen nuclei in the Sun join together.
- Solar cells
A solar cell is a device that converts light energy directly into electrical energy. Some pocket calculators use solar cells and you may have seen large panels of solar cells on house roofs.

- Solar heating
Do not confuse solar cells with solar panels, which use energy from the Sun to just heat water, and not to produce electricity. These may also be put onto house roofs so that they can absorb the Sun’s energy.
Advantages of generating electricity using solar cells
- Solar energy is a renewable energy resource
- There are no fuel costs
- No greenhouse gases are produced
- No harmful polluting gases are produced
- Solar cells can provide electricity in remote locations where there is no mains electricity
- Maintenance costs are low
Disadvantages of generating electricity using solar cells
- Solar cells are expensive and inefficient, so the cost of their electricity is high.
- Solar power is unreliable - solar cells do not work at night and not as well when it is cloudy
- They use up a lot of space – some roofs are not big enough for the number of cells required
Solar energy quiz
Test your knowledge of solar energy with this quick quiz.
Summary
Types of energy include:
- kinetic energy, heat energy, light energy, chemical energy, elastic potential energy (or strain energy), gravitational potential energy, electrical energy, magnetic energy, nuclear energy
The unit of energy is named the Joule with the symbol J
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that:
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but only changed from one form to another
- Energy resources are the different ways of supplying a particular form of energy
For example:
Chemical energy is a form of energy
Food, oil, coal, gas, petrol, turf and wood are some of the resources which supply chemical energy
Renewable energy resources are replaced by nature in less than a human lifetime. They will never run out
Non-renewable energy resources cannot be replaced by nature in a human lifetime. They are used faster than they can be replaced by nature and will run out
Non-renewable resources include:
- The fossil fuels; crude oil, coal and natural gas
- Nuclear fuels such as uranium and plutonium
Renewable resources include:
- Wind, waves, tides, hydroelectricity, biomass, solar, geothermal
Every single Joule of energy
in the universe today
was present at the
Big Bang 13.7 billion years ago…
More on Physics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count8 of 8

- count1 of 8
- count2 of 8

- count3 of 8
