What are equivalent fractions?
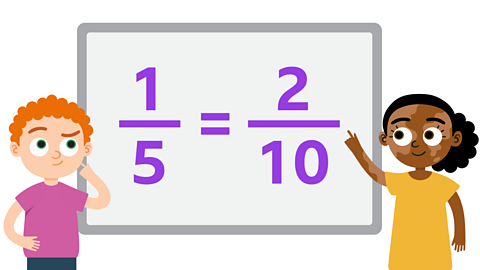
When two fractions have the same value, but have different denominators and numerators, they are called equivalent fractions.
Equivalent means they are equal. They have the same value.
When two different fractions are equivalent, the numerator and the denominator can be:
multiplied by the same number
divided by a common factor to simplify them
Activity: What are equivalent fractions?
Complete this interactive activity to understand equivalent fractions. Then put your knowledge to the test.
Finding equivalent fractions
This fraction chart shows \(\frac {1} {2}\). If you look down the chart you can see which fractions are equal to \(\frac {1} {2}\).
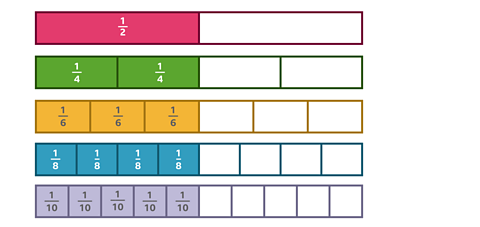
You can see that:
\(\frac {1} {2}\) = \(\frac {2} {4}\)
\(\frac {1} {2}\) = \(\frac {3} {6}\)
\(\frac {1} {2}\) = \(\frac {4} {8}\)
\(\frac {1} {2}\) = \(\frac {5} {10}\)
All these fractions take up the same space on the chart and represent the same value.
They are all equivalent fractions.
Using multiplication to find equivalent fractions
You can use multiplication to find equivalent fractions, by multiplying both the denominator and the numerator by a number.
Here, \(\frac {1} {2}\) has been multiplied by 2. The equivalent fraction is \(\frac {2} {4}\).
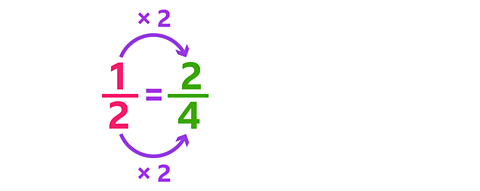
You can multiply by any number to find an equivalent fraction.
Remember to multiply both the denominator and the numerator by the same number.
Using division to find equivalent fractions
You can also find an equivalent fraction by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by a number.
Here, the fraction \(\frac {4} {8}\) has been divided by 2. The equivalent fraction is \(\frac {2} {4}\).
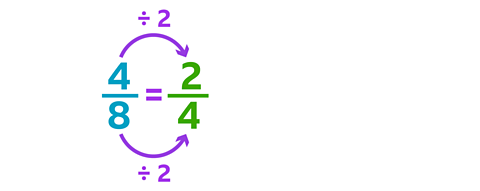
You can divide by any number that evenly divides both the numerator and the denominator to find an equivalent fraction.
Just make sure to divide both parts of the fraction by the same number.
Example 1
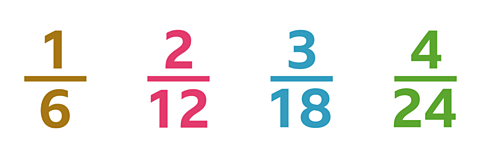
Complete this sentence to describe the proportional relationship between this set of equivalent fractions:
The value of the denominator is always ______ times the value the numerator.
Remember, the number of times the numerator has been multiplied to make the denominator in each equivalent fraction is always the same.
✓ In this set of equivalent fractions, the denominator is always 6 times the numerator.
Every equivalent fraction in this set will follow the same rule.
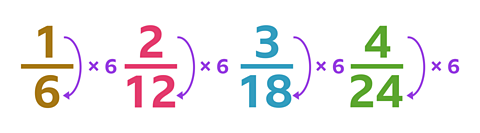
Example 2
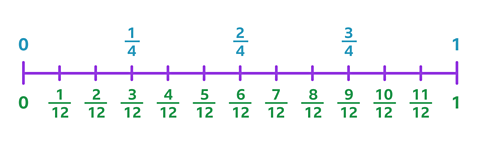
How many pairs of equivalent fractions are on this number line?
What are the equivalent fractions?
To find equivalent fractions on the number line, look for fractions that share a position with another fraction on the line.
✓ There are 3 pairs of equivalent fractions:
\(\frac {1} {4}\) = \(\frac {3} {12}\)
\(\frac {2} {4}\) = \(\frac {6} {12}\)
\(\frac {3} {4}\) = \(\frac {9} {12}\)
Example 3
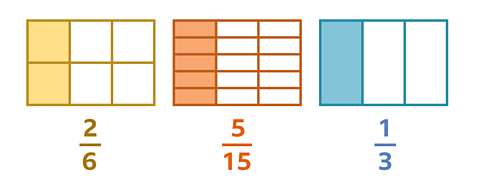
Which 3 equivalent fractions are shown by these area models?
✓ The area models show the equivalent fractions \(\frac {2} {6}\), \(\frac {5} {15}\) and \(\frac {1} {3}\).
The shaded area remains the same, but each model has been divided into a different number of parts.
Area models can be a useful way to spot equivalent fractions.
More on Fractions
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 17
- count7 of 17
- count8 of 17

- count9 of 17