Key points
When dividing decimals by powers of 10The second power of 10 for example is 100. Powers of 10 are 10, 100, 1000 and so on. , it is useful to have a good knowledge of place valueThe value of a digit that relates to its position or place in a number. Eg, in 1482 the digits represent 1 thousand, 4 hundreds, 8 tens and 2 units..
The short division method of multiplication can be used to divide a decimal by a whole number.
equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. can be used to divide decimals.
It may be useful to review place value.
How to divide decimals by 10, 100 and 1000
When dividing decimals by powers of 10The second power of 10 for example is 100. Powers of 10 are 10, 100, 1000 and so on. , a good understanding of place valueThe value of a digit that relates to its position or place in a number. Eg, in 1482 the digits represent 1 thousand, 4 hundreds, 8 tens and 2 units. is needed.
The order of place value of digits in a number from right to left is: units, tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands, hundred thousands, etc.
Units are often referred to as ones.
To divide decimals by powers of ten using place value labels:
Write the digits of the decimal using place value labels.
Start with the first non-zero digit.
To divide by 10 move each digit one place to the right.
To divide by 100 move each digit two places to the right.
To divide by 1000 move each digit three places to the right.
If the answer is less than one, write a zero to show zero units. Fill any empty columns after the decimal point with zeros. This ensures each digit has the correct value.
The process can also be completed without place value labels.
Examples
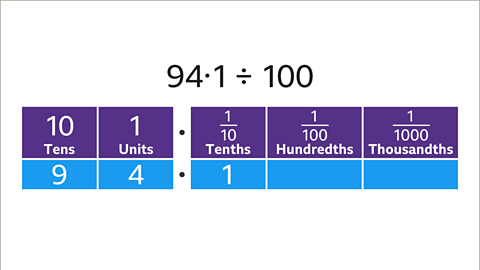
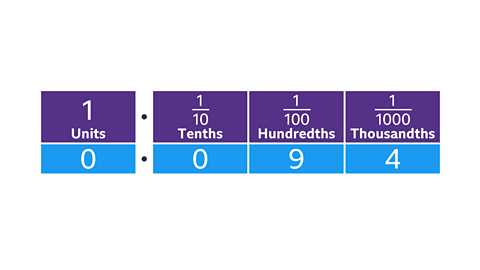
Image caption, Place value labels can be used to process division by powers of ten.

Image caption, Divide 94∙1 by 100
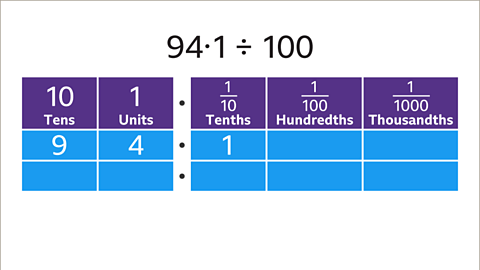
Image caption, Write 94∙1 using place value labels, placing each digit in the correct column. 94∙1 is 9 tens, 4 units and 1 tenth.
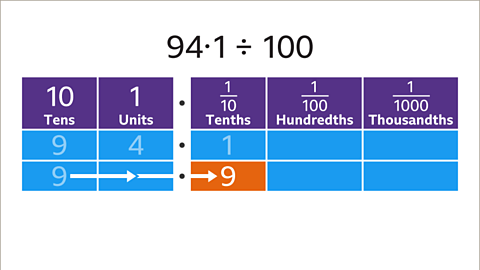
Image caption, To divide by 100, move each digit two places to the right. Start with the first non-zero digit (9). 9 tens move two places to the right to become 9 tenths (0∙9).

Image caption, The remaining digits are also moved two places to the right. 4 units move two places to the right to become 4 hundredths (0∙04) and 1 tenth moves two places to the right to become 1 thousandth (0∙001).
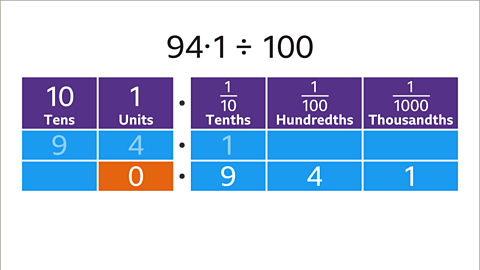
Image caption, The answer is less than a whole. Write a zero to show zero units. 94∙1 ÷ 100 = 0∙941
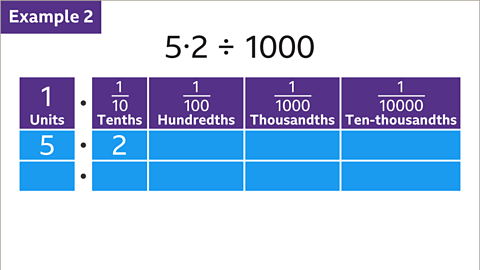
Image caption, Divide 5∙2 by 1000
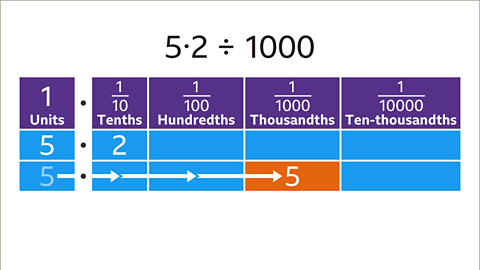
Image caption, Write the digits of the decimal using place value labels. The first non-zero digit is 5 units. To divide by 1000, each digit is moved three places to the right. 5 units move three places to the right to become 5 thousandths (0∙005).
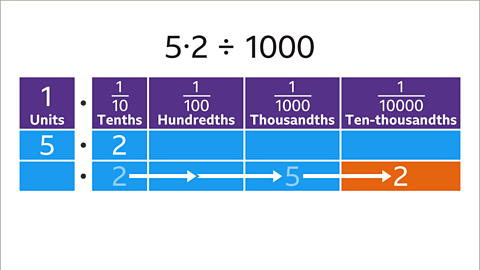
Image caption, The remaining digit is also moved three places to the right. 2 tenths move three places to the right to become 2 ten-thousandths (0∙0002).
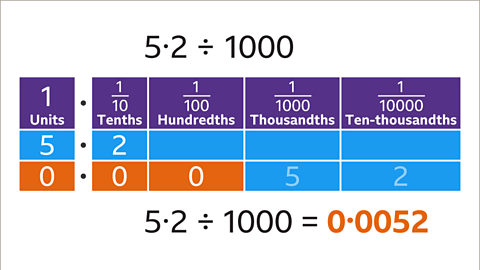
Image caption, The answer is less than one, so write a zero to show zero units. Fill gaps created after the decimal point with zeros to ensure the number has the correct value. 5∙2 ÷ 1000 = 0∙0052
1 of 10
Question
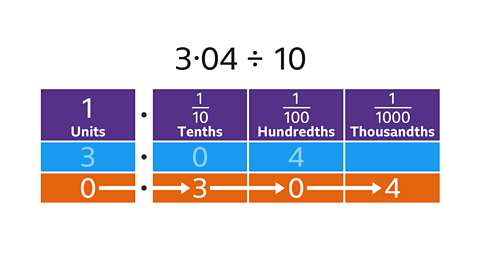
Divide 3∙04 by 10
To divide by 10, each digit moves one place to the right.
3 units become 3 tenths, zero tenths becomes zero hundredths and 4 hundredths become 4 thousandths.
3∙04 ÷ 10 = 0∙304
How to divide a decimal by a whole number
Short division is used to divide a decimal by a single-digit whole number:
Set out the division. Write the question in bus stop form.
The divisorThe number by which another is divided. Eg, in the calculation 30 ÷ 6 , the divisor is 6 goes outside the bus stop.
The dividendIn division, the number that is divided. Eg, in the calculation 30 ÷ 6, 30 is the dividend. goes inside the bus stop.
The quotientThe result of a division. Eg, in the calculation 30 ÷ 6 = 5, the quotient is 5 will be written on the top of the bus stop.
Write the decimal point in the quotient answer space directly above the decimal point of the dividend.
Starting with the first digit, divide each digit of the dividend by the divisor. Write the answers above the line.
If there is a remainderThe amount remaining after division. Eg, 30 divided by 7 is 4 remainder 2 when dividing a digit, carry the remainder to the next digit.
It may be helpful to review short division first.
Examples

Image caption, The bus stop method can be used to divide a decimal by a whole number.
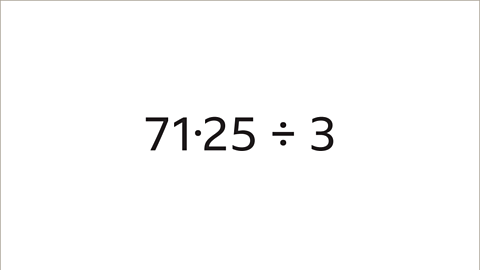
Image caption, Divide 71∙25 by 3
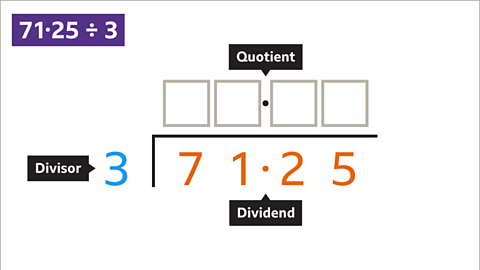
Image caption, Set out the division. Write the question in bus stop form. The 3 is the divisor and goes outside the bus stop. The 71∙25 is the dividend and goes inside the bus stop. The quotient will be written on the top of the bus stop. Add the decimal point in the quotient answer space directly above the decimal point of the dividend.
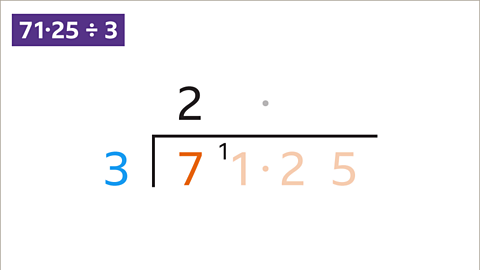
Image caption, 7 ÷ 3 is the first calculation. 7 ÷ 3 = 2 remainder 1. Write 2 above the 7 and carry the remainder 1 to the next digit to give 11
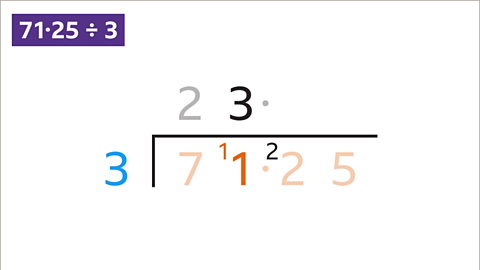
Image caption, 11 ÷ 3 = 3 remainder 2. Write the 3 above the 1 and carry the remainder 2 to the next digit to give 22
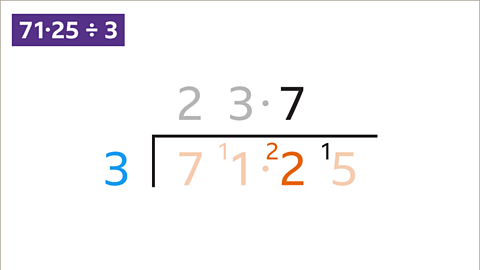
Image caption, 22 ÷ 3 = 7 remainder 1. Write the 7 above the 2 and carry the remainder 1 to the next digit to give 15
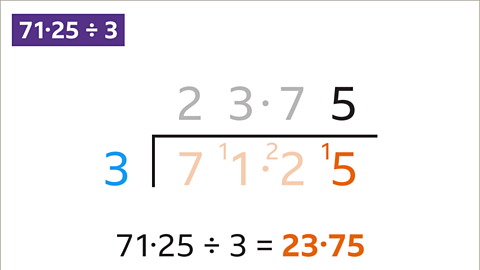
Image caption, 15 ÷ 3 is 5. Write the 5 above the 5. There is no remainder, so the calculation is complete. Write out the answer clearly. 71∙25 ÷ 3 = 23∙75. 71∙25 ÷ 3 = 23∙75
1 of 7
Question
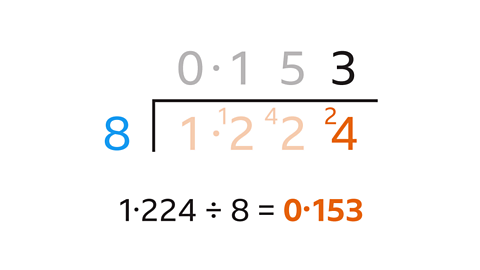
Divide 1∙224 by 8
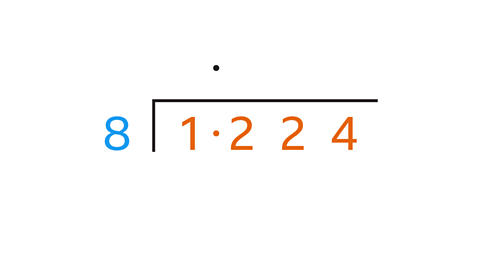
Use short division to work out 1∙224 ÷ 8
Start with 1 ÷ 81 ÷ 8 = 0 remainder 1. Write 0 above 1 and carry the remainder 1 to the next digit to give 12
12 ÷ 8 = 1 remainder 4. Write 1 above the 2 and carry the remainder 4 to the next digit to give 42
42 ÷ 8 = 5 remainder 2. Write 5 above the 2 and carry the remainder 2 to the next digit to give 24
24 ÷ 8 = 3. Write 3 above the 4
There is no remainder, so the calculation is complete.
1∙224 ÷ 8 = 0∙153
How to divide two decimals using equivalent fractions
To divide two decimals using equivalent fractions and short division:
Write the division as a fraction. The numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used. Eg, for 1⁄3, the numerator is 1 is the dividend and the denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts. Eg, for 1⁄3, the denominator is 3 is the divisor.
Make the divisor a whole number by rewriting the fraction as an equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. with a whole number denominator:
Multiply the denominator by the appropriate power of ten.
Multiply the numerator by the same power of ten.
Set out the division in bus stop form. The divisor (numerator) is outside the bus stop and the dividend (the denominator) is inside the bus stop. Write the decimal point in the quotient answer space directly above the decimal point of the dividend (if there is one).
Process the division.
It may be helpful to review short division first.
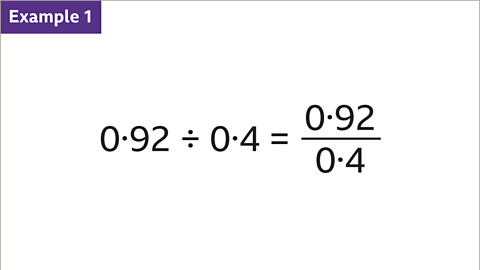
Image caption, Divide 0∙92 by 0∙4. Write the division as a fraction, with the numerator (0∙92) as the dividend and the denominator (0∙4) as the divisor.

Image caption, Make the divisor (0∙4) a whole number (4) by rewriting the fraction as an equivalent fraction with a whole number denominator.

Image caption, Multiply the denominator (0∙4) by the appropriate power of ten (10). Multiply the numerator (0∙92) by the same power of ten (10). The calculation is now 9∙2 ÷ 4

Image caption, Set out the division. Write the question in bus stop form. The divisor (4) is outside the bus stop and the dividend (9∙2) is inside the bus stop. Write the decimal point in the quotient answer space directly above the decimal point of the dividend.
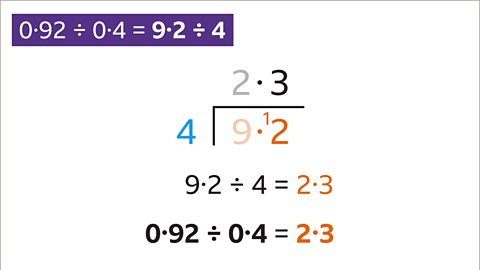
Image caption, 9 ÷ 4 is 2 remainder 1. Write 2 above the 9 and carry the 1 to the next digit to give 12. 12 ÷ 4 is 3. Write the 3 above the 2. There is no remainder, so the calculation is complete. 9∙2 ÷ 4 is equivalent to 0∙92 ÷ 0∙4, so they have the same answer. 0∙92 ÷ 0∙4 = 2∙3
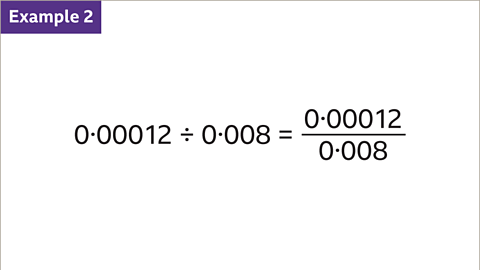
Image caption, Divide 0∙00012 by 0∙008. Write the division as a fraction, with the numerator (0∙00012) as the dividend and the denominator (0∙008) as the divisor.

Image caption, Make the divisor (0∙008) a whole number (8) by rewriting the fraction as an equivalent fraction with a whole number denominator.

Image caption, Multiply the denominator (0∙008) by the appropriate power of ten (1000). Multiply the numerator (0∙00012) by the same power of ten (1000). The calculation is now 0∙12 ÷ 8
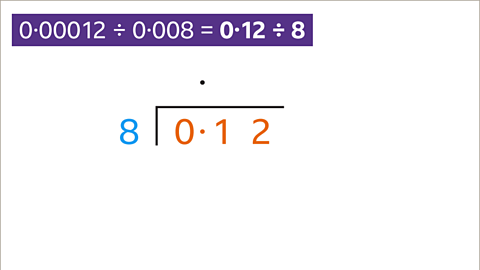
Image caption, Set out the division. Write the question in bus stop form. The divisor (8) is outside the bus stop and the dividend (0∙12) is inside the bus stop. Write the decimal point in the quotient answer space directly above the decimal point of the dividend.

Image caption, Process the division. 0∙12 ÷ 8 = 0∙015. This division equivalent to 0∙00012 ÷ 0∙008, so they have the same answer. 0∙00012 ÷ 0∙008 = 0∙015
1 of 10
Question
Divide 0∙00582 by 0∙03
Rewrite the division as a fraction and write an equivalent fraction with a whole number denominator.
Use short division to work out 0∙582 ÷ 3
Start with 0 ÷ 3. 0 ÷ 3 = 0 remainder 0. Write 0 above 0 and move on to the next digit 5
5 ÷ 3 = 1 remainder 2. Write 1 above 5 and carry the remainder 2 to the next digit to give 28
28 ÷ 3 = 9 remainder 1. Write 9 above the 8 and carry the remainder 1 to the next digit to give 12
12 ÷ 3 = 4 with no remainder. Write the 4 above the 2. The calculation is complete.
0∙582 ÷ 3 = 0∙194 is the same as 0∙00582 ÷ 0∙03 = 0∙194

Practise dividing decimals
Practise dividing decimals in this quiz. You might need a pen and paper to help with your workings out.
Quiz
Real-world maths

In decimal measurements, conversions between measurements can involve division by 10, 100 and 1000.
A joiner given a length in millimetres will convert to centimetres by dividing by 10.
To convert a length in millimetres to metres it will be a division by 1000.
A dressmaker uses 0∙4 metres of ribbon to make a rosette. Ribbon comes in 2∙5 metre lengths on a spool.
To work out how many rosettes can be made from one spool of ribbon, the calculation is 2∙5 divided by 0∙4.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Decimals
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 4
- count2 of 4
- count3 of 4